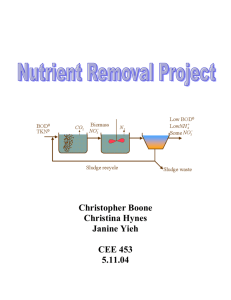
2-1 ch3
advertisement

Ch.3-1: Cycles Mrs. Boyd Earth is a closed system for _____ and an open system for _____. Most of the energy lost from our system is in the form of _____. Components of Ecosystems Limiting factor – the factor that is holding back a population from reaching its biotic potential (max growth) Factor could be matter or energy! Important limiting factors in aquatic systems? Dissolved oxygen, salinity, temperature, light, nutrients, etc. Nutrient cycles Atmospheric – Carbon and Nitrogen Sedimentary – Phosphorus and Sulfur Hydrologic cycle – water cycle helps to transport many nutrients The Water Cycle (hydrologic cycle) Hydrologic cycle Evaporation Condensation Precipitation transpiration Runoff Percolation Infiltration Effects of Human Activities on Water Cycle We alter the water cycle by: Withdrawing large amounts of freshwater. Clearing vegetation and eroding soils. Polluting surface and underground water. Contributing to climate change. What is infiltration? Percolation? Transpiration? Condensation? Carbon cycle Atmosphere (CO2) Photosynthesis/respiration Fossil fuels Limestone (CaCO3) Dissolved in the ocean (making it acidic) Effects of Human Activities on Carbon Cycle We alter the carbon cycle by adding excess CO2 to the atmosphere through: Burning fossil fuels. Clearing vegetation faster than it is replaced. Carbon dioxide is removed from the atmosphere by _____. Carbon dioxide is added to the atmosphere by _____. Nitrogen cycle (very important) Nitrogen in the air (N2) (about 78% of atmosphere) Ammonification: N2 ammonia Nitrification: ammonia nitrite NO2- nitrate NO3Assimilation: nitrite/nitrate plants Overall, N fixation: process of taking N out of the atmosphere into a non-atmospheric form. Denitrification: The Nitrogen Cycle: Bacteria in Action Legumes Effects of Human Activities on the Nitrogen Cycle We alter the nitrogen cycle by: Adding nitrous oxide(N2O) to the atmosphere through farming practices which can warm the atmosphere Contaminating ground water from nitrate ions in inorganic fertilizers. Plants that have nodules in their roots that house N fixing bacteria are called _____. The end product of nitrification is _____. The end product of denitrification is _____. Effects of Human Activities on the Nitrogen Cycle Human activities such as production of fertilizers now fix more nitrogen than all natural sources combined. Dead Zones (Anoxic Zones) When nutrients go into a body of water and cause an algal bloom. Algae do photosynthesis and live near the surface of the water. If too much algae grows on the surface, it blocks light from the other plants at the bottom, so the plants die Eventually, the nutrients run out and then algae start to die All of the dead algae and plants start to decompose Bacteria that do decomposition require oxygen, and they are happy at this point (plenty of dead stuff to break down) But… Eventually the oxygen in the water runs out So the fish die, the plants are dead, and only anaerobic organisms can survive You can see the algal bloom from space! Check for Understanding: 1. The form of nitrogen most usable to plants is _____. 2. Plants with nodules on their roots with bacteria that fix nitrogen are called _____. 3. List 3 ways carbon gets into the atmosphere. 4. Nitrate is converted to nitrogen gas through the process of _____.