WISC IV Student CopyBehavior Sampled by Intelligence Tests
advertisement

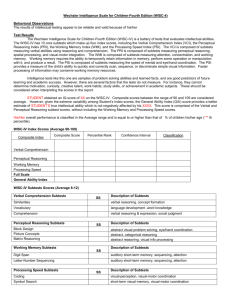
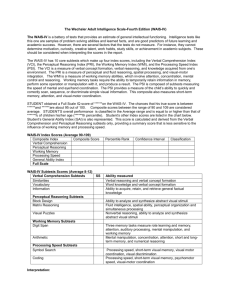
EDS 711 Spring 2015 http://www.thinktonight.com/WISC_IV_subtests_s/331.htm Behavior Sampled by Intelligence Tests. WISC IV The WISC IV has been normed on normal peers and for special education populations: Mental Retardation (MR), Attention-Deficit / Hyperactivity Disorder (AD/HD), Learning Disabilities (LD), both AD/HD and LD, Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI), etc. WISC-IV (which is an update of the WISC-III) indicates significant advances in the understanding of cognitive abilities. Time Required: Administered between 65 and 80 minutes, the WISC-IV contains 10 core subtests and 5 additional subtests. These are summed to four indexes : Verbal Comprehension Index (VCI): Requires verbal conceptualization, stored knowledge access and oral expression. Orally presented questions that assesses common-sense reasoning, reasoning out or retrieving word associations, and the ability to describe the nature or meaning of words. Knowledge acquired from one's environment. Verbal expression required (length of response varies). One of the best predictors of overall intelligence. 1. Similarities 2. Vocabulary 3. Comprehension (Information) 5. L (Word Reasoning) Perceptual Reasoning Index (PRI): Requires visual perception, organization and reasoning with visually presented, nonverbal material to solve the kinds of problems that are NOT school taught. The Block design also requires spatial processing, visual-motor coordination and the ability to apply all skills in a quick, efficient manner. The highest scores reflect both accurate and very quick responses. Picture Concepts score may differ from these other subtest because of the effect of language on the performance. 1. Block Design 2. Picture Concepts 3. Matrix Reasoning 4. L (Picture Completion) 1. Digit Span 2. Letter-Number Sequencing 3. L (Arithmetic) Processing Speed Index (PSI): Requires visual perception and organization, visual scanning, and the efficient production of multiple motor responses. These tasks require executive control of attention and sustained effort for a 2-minute period of time while working with simple visual material as quickly as possible. Performance on Coding is also dependent on paired-associative learning. 1. Coding 2. Symbol Search 3. L (Cancellation) The WISC-IV has a total of 15 subtests, 10 are retained from the WISC-III These are the five new subtests: 1. Word Reasoning 2. Matrix Reasoning 3. Letter-Name Sequencing 4. Symbol Search 5. Cancellation WISC IV Dr. Sanford 1 EDS 711 Spring 2015 One Full Scale IQ (FSIQ), which range from lowest 40 to highest 160 points. Subtests are given for additional examination of processing abilities. The age range for this test is between 6 years and 16 years 11 months. In terms of difference in scores, an individual who has taken the WISC-III, then retested with the WISC-IV may show a 5-point drop in FSIQ. This is due to new aspects of the test, and the novelty of some of the new items and subtests. Object Assembly subtest from the WISC III is gone. On the WISC III there was Picture Arrangement, now on the WISC IV there is Picture Concepts, under Perceptual Reasoning Index. Parents of child with NVLD were concerned about the loosing these two subtests: Object Assembly and the Picture arrangement. Scoring: Current reports show that most students re-tested with the WISC-IV will have approximately a 5 point discrepancy, lower (to the negative) because of this newer version of WISC, its novelty and its increased difficulty. With 4 composite scores (vs. 2 as is the case with the WISC III), there is no standard discrepancy formula, it now all has to be evaluated in terms of the child's ability, test results, current educational functioning, achievement test expectations based on ability, evaluation of the subtests as well as evaluation of the composite sets. Some evaluators have suggested that a 19-point discrepancy in the VCI/PRI composites may warrant further investigation. Standard deviation is 15 points, it is not clear that these score will tell enough about the child's areas of weakness. The Verbal Scale Measures how well children are able to express themselves verbally and how well they are able to understand what is being said to them. Performance Scale measures the nonverbal areas of being able to perceive spatial relationships; such as in putting puzzles together, and being able to transfer visual information rapidly. Another way to organize these subtests: Verbal Comprehension: Vocabulary, similarities, information Perceptual Organization: Picture completion, block design, matrix reasoning Working memory: Arithmetic, digit span, letter-number sequencing Processing speed: Digit-symbol coding, symbol search WISC IV Dr. Sanford 2