arch study guide exam 2
advertisement

1
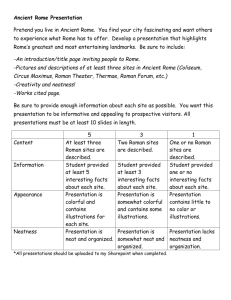
-Rome
- founded on 7 hills
- at time of birth of Christ, Rome had over 1 million inhabitants
-Basilica
-all purpose meeting hall for everything
-often oblong in plan with a high central space lit by clerestory windows
-Greek Temple or stoa turned inside out (peristyle on inside)
-large encloses space
-Forum
-centerpiece of Roman town
-Forum Romana- a group or forums; incredible conglomeration of buildings
-Forum Agustus- open space with temple and 2 curved forums
- part is cut off to make way for the road
-insula
-apartment houses, high-rise apartment block
-existed in more populous Hellenistic cities
-an ancient Roman apartment block
-6 floor walk ups, sometimes as high as 12 stories high
-50,000 in Rome
-domus
-an ancient Roman house
-inward-looking, cool, and quiet house tightly organized around a core space called the atrium
-single family house for wealthy or a full floor apartment
-esp. look @ Pompeii
-economy begins to fail; 20% of people are unemployed
- bread and circuses = more people are on welfare perform public circus
- 2/3 of days in calendar become public holidays
- SPQR- representative democracy; does nothing
-Pompeii
-port town never had more than 20,000 inhabitants therefore it was a small/insignificant town
-earliest surviving examples of standard Roman building types: amphitheater and basilica
-had a main north-south avenue and had paved streets with stepping stones
-atrium open space/courtyard the main inner hall of a Roman house, with an open roof
and a central basin to catch rainwater
-house with peristyle inside and rear courtyard Greek building turned inside out
-tendency of Romans towards axial planning
-essentially had internal plumbing through rain water caught in courtyard and pumped to rest of house
-shops sometimes surround houses (taberna)
-had many mosaics and fresco decorations
-domestic architecture level of luxury
-depicted trompe l’oeil of columns and spatial depictions etc.
-79 AD mount Vesuvius erupted, great archaeology find of Pompeii and Herculaneum
-Empire
-Julius Caesar, Octavious Caesar, Tiberius, Claudius (illiterate), Caligula (insane), Claudius (murdered by Agropina),
Nero
-“absolute power corrupts absolutely”
-caput mundi head of the world, they were gods
-64 AD Rome burned under Nero, took place b/c a party got out of hand
-Domus Aurea = “golden house built for Nero” p. 209
-excavated 100 rooms, they think there were over 200
-great lake with 100 ft. high statue of Nero at the end as the sun god
-Severus & Celer = architects of this palace
-Oculus = hole cut in top of dome to let in light a round window, often in a roof
-octagon room is centered around a dome - clever
-amphitheater adopted from Greeks
2
-a round, semicircular, or oval outdoor arena surrounded by rising tiers of seats
-theater form with scele building = backdrop aggrandized
-Colosseum take Greek theater and enclose it
-on site of domus aurea, fill in lake and build it on top of it
-most well known amphitheater, entertainment
-gladiators and other public activities public palace
-best example of Hellenistic tendencies in Roman Empire
-underground rooms where animals and warriors waited (filled with water for naval battles sometimes)
-series of barrel vaults running round on top of each other continuous, semicircular vault that extends in
a straight line
-non-structural arches decoration for façade (usage as decorative features rather than as structural shows
changing ideas)
- ropes and canvas were put over Coliseum to essentially make it the first dome building
-Rome at richest state now
-arches are now decorative features not solely functional for aqueducts (an artificial channel for water,
sometimes underground, but often elevated on arches)
-Trajan’s Forum p.213
-Trajan = emperor
-forum = a public civic and commercial square in ancient Rome, it was usually surrounded by a colonnade and
included a basilica and temple
-projections at side of Forum, curved architecture, protected by stoa and pocketed into the hillside
-ext raordinary market structure that was a multilevel, intricate commercial facility steeply terraced
-Trajan’s Market
-world’s fi rst shopping mall
-public, commercial space
-circular projection at the side of the Trojan forum
-stre et surrounding it with building on top
-regarded as world’s first shopping mall – atrium in center with commercial stores on either side of it
-kept the population entertained with food and circus etc.
-Trajan’s Column
-more than 100 ft. high
-monum ent to Trajan’s importance – tells the story of the Dacians (Romania) who conquered
-in the middle of the forum
-2500 figures spiraling upwards showing the conquering of Albania
-Arch of Titus
-right next to Colosseum
-put up by various emperors and demonstrates how powerful the Roman Empire is
-monument not quite a building; has no function
-Hadrian Emperor
-Pantheon
-Hadrian’s greatest architecture
-originally ceiling = gold, but it was taken down for fuel to be melted down
-cylindrical building with temple front porch
-has a dome 140 ft high. With oculus cut produces a spotlight effect on emperors and gods
-Agrippa built this, FALSE, Hadrian built this inscription, paying honor to building built before
-Campus Martius
-alternating arrangement of god and emperor images
-statues aren’t still there today but niches and spaces are
-putting god and emperors on the same level
-model of structure of universe
3
-Hadrian’s Villa @ Tivoli
-outside of Rome
-house, retreat his escape where he would ponder his faith
-Hadrian = most powerful man at the world in the time yet his lover was killed in Africa
-reflecting pool with statues around it, arch forms for the sake of arch forms
-vaulted space and enclosures around the pools
-crocodile at main pool commemorating death of his lover
-arch masonry work
-villa = a country house, sometimes including its outbuildings and gardens
-villa rustica = villa serving agricultural purposes
-villa urbana = served a recreational purpose and was not a true working farm
-Aurelian Walls
-testament to Roman building skill very fast
-built and named after emperor
-Roman Empire is slipping who knows what is going to happen militarily
-if they build even bigger and better things maybe people won’t notice late roman empire, esp. in public baths
-Baths of Caracalla
-modeled after old Penn Station
-stadium seating with an open garden for exercise, shops, storage facilities for commercial goods, baths in the center
-Caldarium the hot water room in an ancient Roman bath, circular architecture form, hot bath, eastern Christian
churches
-Tepidarium the moderately warm room in ancient Roman baths, warm bath
-Frigidarium the room with a cold water pool in ancient Roman baths, cold bath, longitudinal plan (western
Christian churches)
-thermal window = semicircular and divided into 3 parts (window = wall opening usually admitting light and air)
-Temple of Minerva Medici
-not a temple but a glorified picnic pavilion in a park
-centrally planned
-18th century artists and poets fell in love with it
-1960: Caesar Augustus statue copied in Vegas for Caesar’s palace to have image
of decadence and excess
-Mithras fleshy god from east, part of trinity in mazrian religion, comes from Persia
-god of light and water vs. Jesus Christ (god of poor)
-popular with military troops
-place where he is worshipped is underground
-Early Christian state religion is now Christianity, republic is gone forever now new Empire
-catacomb an underground system of passages used as a cemetery, underground
burial tumbles, usually in pagan graveyards hold entry
-some finest depictions of late Roman life
-fresco of 3 Hebrews in fiery flames, raising of Lazarus from dead
-snake their way under surface roads
-crypts for bodies etc.
-Dura Europas Syria
-cut out of secret rooms to worship Judaism, Christianity
-underground room
-Constantine = new Roman emperor
-Milvian Bridge- Constantinople becomes powerful military leader
-Constantine becomes emperor- wins battle for Christ
-Byzas [Constantinople] moves the capital and creates a new
Rome here, splits empire in 2
-Arch of Constantine
-Constantine steals parts of the arch of Trajan and uses them in this arch by the Colosseum
4
-Basilica of Constantine new apse for himself
-adopted the basilica + churches can now come up
out of the ground in new Rome
-S. Sabina
- basilica church (made out of wood, or vaulted stone concrete and some other sophisticated abilities slip
away); the form of an early Christian church that is oblong with a high clerestoried nave ending in an apse flanked by
2 lower aisles and covered with a timber roof
- narthex entry port
- nave center, major space in middle with columns on either side
-columns were often cannibalized other buildings
- side aisle surround nave
- apse projection at end usually with altar = wall recess or extension of a hall
- transept the transverse arms of a cross-shaped church, crossing the main axis
at a right angle, secondary entrance points, makes cross, before apse
- aedicule = 1. A wall recess framed by columns supporting an entablature and
pediment, and intended as a shrine or as a shelter for a statue; 2. A door, window, or
other opening framed by columns or pilasters and crowned with a pediment
- atrium the colonnaded forecourt of a Christian church
-Old St. Peters no longer exists
-church
-was on site of old pagan cemetery where peter denied Christ 3 times
-burial spot of St. Peter as well
-triumval arch triple arch form
-baldachinno aedicule device
-an ornamental canopy over a tomb, altar, or throne; sometimes portable
-brings scale of building down, where altar would be
-canopy that you can see person in scale against
-Tomb of Santa Costanza
-Constantine’s daughter, he built her a circular/centrally planned building form for her burial
-focuses in on her tomb
-ambulatory processional passageway around a shrine or flanking the apse of a Christian church, walking space,
makes available to make circular movement
-Church of the Holy Sepulchre, Jerusalem
-centrally planned rotunda tomb with ambulatory “looks like lollipop”
-basilica form = longitudinal
-St. Simeon Stylites
-Simeon believed he was being corrupted by every day life
-commemorates spot where he sat on top of a column for 40 years
-central building form with column in middle but 4 basilicas arranged like a pinwheel around it
-Central plan = a ground plan that is symmetrical in all directions vs. Longitudinal plan
-The Last of Rome 4th, 5th, 6th centuries instability led to Constantine’s power, cannot rely on people’s allegiance
-Goths, Vandals, Huns, etc.
-Barbarians sweep in and plunder, terrifying/nomadic/ruthless people
-Roman army is essentially done
-Arles France built inside of amphitheater shows instability of Rome
-aqueducts become silt up and no one cares for them so there is no water, no vibrant life either
-building techniques like use of concrete and vaults slipped away, small scale/local plans
-Theodore, “King of Rome” Goth, Barbarian from the North
-declares himself king of Rome, probably last Roman Emperor
-St. Augustine, City of God
-writes why things turned out the way they did, 22 volumes, called city of god
5
-what matters is not on earth it’s the next life, it is the celestial city that’s what’s important
-Byzantine Empire (eastern Christian empire)
-ByzasConstantinople {Istanbul} became the “New Rome”
-Golden Horn geographic shape of land
-Constantine built new city on an acropolis, he felt more comfortable here, featured a forum and all Roman elements,
has a hippodrome too (perhaps too decadent?), all the trappings of a great capital elements used in a new
Christianized way
-terrific location because you can build series of walls and is an impregnable fortress of a city, high up
-wont be invaded for over 1000 years = Constantinople
-beginnings of a “city of god”
-after Constantine dies there is some instability on east and west
-Arians = other brand of Christianity that countered Constantine, did not accept mysterious aspects such as trinity
etc. battles b/w Trinitarians and Arians, those who believed and mystery and those who wanted more
straightforward
-western Christianity centered on Rome is null
-Justinian Byzantine Emperor from 6th century & Theodora = Justinian’s wife, very ambitious, actress,
ruthlessness
-try to recreate as the Roman Empire before it collapsed, attempt failed to be as great in terms of expanse or
significance
-after Justinian died his empire fell apart
-swamped in politics about theology, also there is a lot of corruption
-Ravenna (naval outpost on Adriatic)
-Tomb of Galla Placidia [Chrine of St. Lawrence]
-greek cross plan (equal on all sides), no dome but high rising
-particularly humble brick building
-has sort of triumval arch
-exterior = intentionally reserved, interior = dazzling otherworldliness
-simple and straightforward building plan
-architecture is to represent mysteries of Christian church
-lighting reveals building in an incomplete way
-San Vitale (530-548)
-church that Justinian built, took 18 years, his most important piece
-remnants of western Christian building forms (entry port and apse)
-humble brick exterior
-piling up of elements
-spectacular interior- mosaics and marble on inside
-structural system comes to 8 points (make support web shaped in an incove)
-pendentive = spherical triangular piece that is used to translate geometric
shapes in plane, square plan to circular dome
-apse points East to holy land
-S. Apollinaire in Classe
-bell tower is separated not attached to building b/c they settle differentially into soil conditions
-golden mosaics, Latin cross plan – basilical plan
-sculpted bell tower
-San Lorenzo, Milan
-eastern decorative influence
-piled up center plan
-classical architecture in interior
-Greek Cross
-favored centrally planned building eastern Christian church
-dome in middle, squat
-west likes Latin cross plan
-Emperor + Patriarch = God
6
-God is made up of 2 halves: secular ruler (emperor) + religious ruler (patriarch)
-changes architecture (favor centrally planned building form, Greek cross, West prefers Latin cross plan)
-new standard
-responsible for creating city of god on earth
-Constantinople
-Church of Holy Apostles –4th century church from time of Constantine
-Justinian and Theodora rebuilt it and became model for Greek cross churches to be built in Byzantine Empire
-centrally planned
-S.S. Sergins & Bacchus
-also under Justinian
-central building form with octagon and apse, narthex etc.
-not very decorated, but great architectural forms
-Nika Riots armed battles in the streets b/w Arians and Orthodox Christians, 3000 people = killed
-Hagia Sophia
-church that is one of the greatest buildings in the history of the world
-[Church of Holy Wisdom]
-currently Islam came and turned it into mosque
-stunning architectural achievement
-finest example of the rationality of the ancient world
-other worldly, ethereal architecture
-elongated centrally planned form, main dome with half dome on each side, has double narthex, entry porch,
buttresses added later
-tore down first dome and built steeper dome, for aesthetic and pressure reasons
-dome is held in place by giant iron chains inside to counteract sideways thrust
-complex spatial arrangement with other worldly image
-highly decorated and very exotic capitals wit Persian influence
-dome has windows (on drum) , meant to look like it is hovering above you
-Benedictine ritual w/ mass and Eucharist?
-architecture in the form of churches could display the idea of god being more important (what
St. Augustine wanted to portray) – supposed to emulate what St. Augustine thought to be heaven
-Islam [submission]
-found building a particularly powerful statement, it matters/is important
-remains great rival to western Christianity and Judaism
-would present an alternative to eastern orthodox Christianity that’s remarkable in its context, Islam has no mysteries
it is simple and straightforward
-there is one god monotheistic, Allah pay homage to him by living a virtuous life, praying , and no materialism
-Muhammad he was born at Mecca in 570 AD, at 25 he married a woman 15 yrs older and he just studied religion
in Arabian peninsula, influenced by Jewish and Christian traders also native holy men unhappy with paganism
effected him, in 611 at age of 40 he had a call from the angel Gabriel and he became a prophet/last great chance
-Medina 622, Muhammad moved here and tried to spread his ideas (became more worldly and accepted) from the
call
-Mecca place at the center of the world, place of Islamic religion
-630: political religion of Islam is created after wear between believers in Medina vs. Mecca
-Kaaba (Qaaba) means cube, most holy building in Islam, cube shaped, covered by black and gold cloth, sacred
center of Islam
-black stone at the corner, possibly brought by Gabriel as white and has been turned black by impurities of
humans, forms base for building, could be asteroid etc.
-region = a desert place
-when Muhammad comes back in 630 he cleans it and gets ride of pagan idols etc.
-haj once in your lifetime make the trip to Islam, yearly pilgrimage and do the “cleaning”, off limits to nonMuslims
-jihad spiritual crusade, “holy war” spread of religion of Islam (spread of ethical conversion,
nationalistic ideas, etc.)
-entire Arabian peninsula had absorbed Islam by Muhammad’s death Islam spread b/c it provided an alternative
and “truth”
-Dome of the Rock [Mt. Moriah] 690: Islam arrived in Israel and this great mosque was put in place
7
-in Jerusalem that is very close to the church of the holy sepulcher was built with a dome because it
echoed the other dome as well echo/1 better
-newly arrived religion is equally or more powerful
-architectural/faith propaganda demonstrate Islam has arrived
-built over a rock
-spot where prophet Muhammad rose to heaven after death – Islam
-spot where Judaism was where Adam was conceived – Judaism
-golden dome, ambulatory, decorative detail, mosaics, glittering nature of eastern Christianity now
appropriated by Islam, colorful interior, a long way from Muhammad’s initial teachings
-mosque basic building of prayer for Islam, building of worship – the principle Muslim religious building
-all that is needed is space to pray b/c religion is so simple
-need place to cleanse yourself and a place to pray and face Mecca
-giant hypostyle hall with a courtyard
-Mosque @ Samarra was a giant hypostyle hall with courtyard, so you can face Mecca
-minaret tower that calls for prayer, at mosques – a tall slender tower of a mosque from which the faithful are
called to prayer
-mihrab niche in qibla designates direction in which you pray (now highly decorated element) – a wall recess in a
Muslim religious building indicating the direction toward Mecca
-qibla wall that helps you face Mecca to pray, that has in it a niche (mihrab)
-squinch own Islamic version of pendentive (favored form of eastern Christian orthodox, they make cuts and cut of
corners in series and continuous matter
-Mosque of Ahmed I
-in Constantinople, almost an exact replica of Hagia Sophia
-to counter buildings of Christianity
-courtyard/atrium w/ fountain, qibla, mihrab, minarets, centrally planned building form
-colorful patterning and decorative detail is famous in Islamic culture
-Iconoclastic Controversy occurred in Byzantium, 8th century
-theological argument within the Byzantine church
-decided that the production of religious images were prohibited, they became iconoclasts
-western Christianity had no problems with statues, pagans, or idols
-raging controversy within Christian church
-Quran (holy work of Islam) says that statues are the work of devils dragged into conflict, depictions of
people should only be god’s job therefore no illustrations of people at mosques it is now taken by pattern and
script
-Taj Mahal, India -perhaps the most famous Islamic building
-spread to India and ran up against Hinduism
-not a mosque but a tomb for the wife of Iraj
-planned to build black tomb for himself facing his wife’s white tomb
-minarets, centrally planned building form inappropriate for tomb
-Great Friday Mosque, Mali
-In Africa, simple and spectacular
-made out of mud
-640: Islam spread to Egypt eventually to Sicily, Italy, Paris, Vienna
-Islam brings ideas to the west medicine etc.
-Islam in Spain
-Alcazar @ Seville
-has a great garden, perhaps earthly version of Islamic paradise itself
-Red Mosque @ Cordoba
-Islamic arch on outside, followed by many arches in hypostyle hall red and white stripes
-contains hypostyle hall, qibla, and mihrab (which is architecturally celebrated), fancy vaulting
-when Christianity takes back Cordoba the church eclipses it and goes in middle
of mosque mosque and Christian church slammed together
-Alhambra @ Granada built on mountains with walls surrounding it
-the last gasp of Islam
-arched entry spaces decorated with patterns and words of prophets of Islam
8
-confronted by great gardens, water is everywhere
-rhiad = space formed by buildings around it basic planning unit
here (patio framed by architecture)
-arch form and lighting in contrast to exterior
-famous lion fountains with 4 streams that go to the different
corners of the world (evocation of throne of King Solomon)
-patterning of word of prophet
-remarkable squinch stalactite structure with unusual light sources at top
-Moors people of Iberian Peninsula that were Islamic, created striking architecture in West, often used image of
paradise in great garden (because they were from the desert)
-Mudejar influence, continuing trace of Islam that comes out in things like patterning and vaulting (star vaulting)
-just because religious faith was expelled the architectural elements remain