Unit 6 Answer Key
advertisement

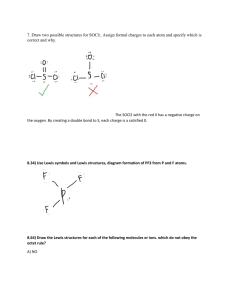
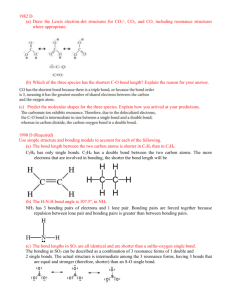
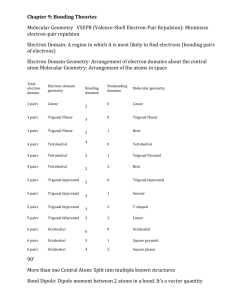
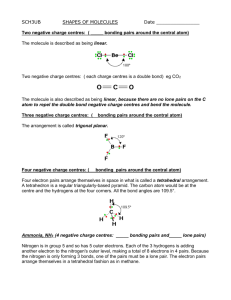
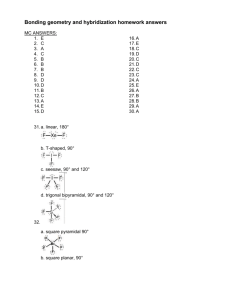
Unit 6 Answer Key PS 9 - #1,6,8,10,13,14,16,17,18,36-42 even,48-56 even,62-68 even,72,76,78,86,92,112 (28) (1) An e- is transferred from the metal (Na) to the non-metal (Cl). The resulting oppositely charged ions are electrostatically attraction. (6) two s electrons are lost (8) decreases across a period, increases down a group (10) <same shape as PE diagram for H2 in notes, only pm and kJ/mol are different> (13) increases across a period, decreases down a group (14) difference in electronegativies is proportional to polarity (16) odd number of electrons (NO), boron (“the moron”) compounds, expanded octets (PF5, SF6) (17) stronger bonds are shorter (18) ave. strength (in kJ/mol) of a type of bond; by adding up the bonds broken (+) and the bonds formed (-) (36) Rb+<Rb, cations always smaller than atom; Se<Se-2, anions always larger than atom (38) N-3<P-3, same charge but P’s outer shell is the 3rd while N’s is the 2nd (40) Cs+<I-<Te-2, isoelectronic so charge determines the radius (42) (48) N-Cl < H-Se < P-Cl (50) negative charge of Se and Cl; N-Cl is nonpolar (52) (54) (56) (62) (64) (66) (68) (72) C-H = 107 pm, C-Cl = 177 pm (76) -54 kJ (78) ionic, ionic, ionic, covalent (86) (92) (112)183 kJ/mol PS 10A - #1,2,3,4,18,24-32 even (10) (1) Geometry determined by (1) need to maximize space between e- pairs (2) unshared (lone) e- pairs require more room than shared e- pairs (3) double and triple bonds act like a single shared e- pair (2) linear, trigonal planar, tetrahedral, trigonal bipyramid, octahedron (3) equatorial position is roomier (4) symmetry of molecule may cause polar bonds (or their resultants) to cancel each other (18) repulsion by NH3 forces BF3 to change from trigonal planar to trigonal pyramid, covalent bond forms (24) bent, trigonal pyramid, trigonal planar, tetrahedral (26) linear, tetrahedral, trigonal pyramid, bent (28) square pyramid, trigonal bipyramid, seesaw, octahedral (30) octahedral, linear, square planar, seesaw (32) trigonal pyramid and T-shaped, seesaw PS 10B - #7,8,9,36,40,42,46,56,58 (9) (7) 109.5° (8) σ is cylindrical around the bond axis; π bond has e- density above and below bond axis (9) sp2 hybridization; one hybrid overlaps to bond the C atoms, others to bond to H’s; single unhybridized p from each C atom overlap to form the second bond in the double (36) (a) bent, sp2 hybrids, central Ge surrounded by 2 bonding pairs and 1 lone pair (b) bent, sp2 hybrids, central N surrounded by 2 bonding pairs and 1 lone pair (c) trigonal pyramid, sp3 hybrids, central P surrounded by 3 bonding pairs and 1 lone pair (d) tetrahedral, sp3 hybrids, bent, central Ge surrounded by 4 bonding pairs and 0 lone pairs (40) sp3d, sp3d2, sp3d, sp3d2 (42) sp3d (46) double bond can’t swivel without breaking the π bonds (56) sp3, sp, sp2 (58) in trans isomer, Cl’s and NH3’s are directly opposite each other and so bond polarities cancel PS 10C - #11,13,14,48,50,64,66 (7) (11) e- density between nuclei is higher in a bonding orbital, lower in an antibonding orbital (13) two 2s orbitals combine to form one bonding σ orbital and one antibonding σ orbital (14) six 2 p orbitals combine to form three bonding σ orbitals and three antibonding σ orbitals (48) (a) B.O = 1.5, stable, paramagnetic (b) 0, unstable, diamagnetic (c) 2.5, (very) stable, paramagnetic (50) B.O. = 2, diamagnetic (64) B.O. = 1 (66) N2 has BO=3, N2+ has BO=2.5 (1 less e- in bonding orbital), N2- has BO=2.5 (1 more e- in antibonding) PS 24 - #1-5 all,7,9,18,28-40 even,50,52,56 (18) (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (7) (9) (18) (28) (30) (32) (34) (36) (38) (40) (50) (52) (56)