Intro & 5 Themes of Geography
advertisement

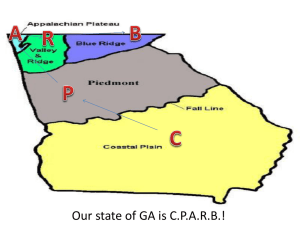
Geography Final Exam Study Guide Intro & 5 Themes of Geography What is geography? Map conventions: o scale o key o compass rose o typeface 5 Themes o Place o Movement What qualifies as geographic movement and what doesn’t? o Region formal functional perceptual o Location absolute latitude (Equator) longitude (Prime Meridian) What is a hemisphere? relative o Human-Environment interaction Physical Geography Climate vs. weather – how are they different? How are they connected? o What factors influence a place’s climate? Renewable vs. nonrenewable resources o fossil fuels natural gas fracking o geothermal energy o solar energy Planetary movement o rotation o revolution o solstice (summer & winter) o equinox (spring & fall) 1 o tilt of axis (influence on experience of seasons) Tectonic plates o convergence o subduction o faulting o spreading o Which result in which surface experience? o Ring of Fire Climates o Continental grasslands – prairies vs. savannas – cover centers of most continents forests – deciduous vs. coniferous o Tropical wet o Tropical wet & dry o Arid/Semiarid o Highlands o Mediterranean o Subarctic/tundra o Which ecosystems are common in each climate zone? Landforms & waterbodies o ocean/sea o gulf/bay o delta o strait o plateau o plain o escarpment o archipelago o isthmus Weathering & erosion – how are they different but connected? Human Geography What is demography? o birthrate o deathrate o population density o population pyramids (know how to analyze them!) 2 Population distribution o How is earth’s population distributed? o What are the factors that draw people to settle in a place? Culture o convergence o diffusion o divergence Urbanization o countries where it is common o positive & negative impacts Government o authoritarian monarchy dictatorship oligarchy o democratic republic confederation federation Economics o Command o Market o Traditional o Mixed o GDP GDP per capita o Subsistence vs. commercial industries o Tariffs o Types of economic activities primary secondary tertiary quaternary Pennsylvania Regions o Allegheny Plateau o Erie Plain o Piedmont o Ridge & Valley o Atlantic Coastal Plain Major cities: 3 Resources o coal types & locations o natural gas Marcellus Shale fracking Physical features o Appalachian Mountains o Susquehanna River o Ohio River o Delaware River o Lake Erie History o founder o Philadelphia & Valley Forge – American Revolution o Gettysburg – Civil War United States Regions o Northeast water = major resource dense population o South flat, fertile land = major resource mild climate bayou; mangrove “Sunbelt” o Midwest fertile land = major resource (“nation’s breadbasket”) Mississippi River as trade/shipping route Great Lakes Great Plains grain exchange o West mostly semiarid climate (except Alaska & Hawaii) gold rush in California; oil in Alaska Rocky Mountains forests aqueducts Early cities built along waterways & railroads, and near natural resources Where do most people in the U.S. live? Nation’s capital? Government? Last states added? Their importance? NAFTA 4 Canada Regions o Atlantic Provinces sea = major resource; “maritime” Gulf of St. Lawrence forestry, farming o Ontario & Quebec major culture centers “heartland” St. Lawrence seaway Canadian Shield Quebec’s separatist movement o Prairie Provinces major cities built along railroads farming o British Columbia marine west coast climate Pacific port = Vancouver o Northern Territories subarctic/tundra climate mineral resources, difficult to access Inuit population Which physical features are shared with the U.S.? How are Canada & the U.S. different in their global roles? Where do most people in Canada live? Why? Latin America History of colonization o Spain o Portugal o French, British, Dutch Fights for democracy o caudillos o Mexican revolution Physical features o rainforests deforestation why is it done? why does it sometimes backfire? 5 biodiversity Amazon River basin o Andes Mtns o Sierra Madres Mtns o Brazilian Highlands/sertao o Caribbean Sea o Gulf of Mexico o Atlantic & Pacific Oceans o Natural disasters: hurricanes, tsunamis, earthquakes, volcanoes Economic activities o farming (esp. on pampas) coffee (Colombia, Venezuela, Brazil) conflict over land distribution o oil (Mexico, Venezuela) Urbanization o positive & negatives o favelas Europe Cooperation o United Nations o European Union euro – why was it developed? Positives & negatives? Conflict o WWI o WWII o Cold War British Isles & Nordic nations o Which countries make up the United Kingdom? o What is the difference between Ireland & Northern Ireland? What kind of energy does Iceland use? Nordic/Viking ancestry Celtic/Norman ancestry climate = marine west coast; some subarctic Physical features Thames River = England Scottish moors (bogs, peat) Kjolen Mtns o aurora borealis o England = major Industrial Revolution center o Major industries of this region? o o o o o 6 Central Western Europe o Benelux countries land reclamation – polders dense population o France major industries? climates? Rhine River separates it from Germany Pyrenees Mtns separate it from Spain English Channel separates it from UK o Germany major industries? involvement in world wars o Switzerland & Austria high standard of living Alps Mtns political neutrality Mediterranean Europe o Spain & Portugal Iberian peninsula Pyrenees Mtns several ancient cultures still represented o Italy & Greece Po River Valley – major industry? Alps Mtns in Italy; Pindus Mtns in Greece Greek & Roman empires centered & still reflected here Eastern Europe o Balkan peninsula o Baltics o Former Yugoslavia o Former Soviet Union When was the USSR active? What was their goal? Berlin wall o Climates? o Ecosystems steppe taiga 7