Winter Bridge Cheat Sheet for Geography definitions Latitude
advertisement

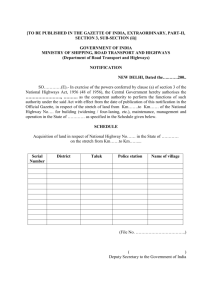
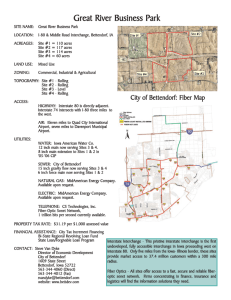
Winter Bridge Cheat Sheet for Geography definitions Latitude - the angular distance north or south from the equator of a point on the earth's surface. Longitude - Angular distance on the earth's surface, measured east or west from the prime meridian at Greenwich, England, to the meridian passing through a position, expressed in degrees (or hours), minutes, and seconds. Grid System - Collective term for the parallels and meridians that form an imaginary grid over the Earth’s surface, making it possible to locate a specific point. Region – a way to break down the earth to make it easier to study. A part of the earth's surface (land or sea) of considerable and usually indefinite extent: a tropical region. State Routes – The California highway system maintained by the state. http://www.cahighways.org/hwy-key.html Length: 61.28 miles; 55.81 miles traversable, 5.47 miles unconstructed Average Daily Traffic: 11,520 to 51,773 vehicles per day Functional Classification: 57.08% principle arterial; 36.83% minor arterial; 5.44% collector; 0.65% rural minor collector/local road. Freeway: 71.97% of the route (44.10 miles) is defined as part of the Freeway and Expressway system. Federal Aid: Under the pre-1992 Federal Aid program, 15.33% was FAI (Interstate) funding, 72.50% was FAP, 5.71% was FAU, 6.02% was FAS; and 0.44% was unfunded. Roadway classification: 74.57% rural, 4.19% sm. urban, 21.24% urban. Interstate Highway System - The Dwight D. Eisenhower National System of Interstate and Defense Highways, commonly called the Interstate Highway System, is a network of limited-access highways (also called freeways or expressways) in the United States that is named for President Dwight D. Eisenhower, who championed its formation. The entire system, as of 2006, has a total length of 46,876 miles (75,440 km),making it both the largest highway system in the world and the largest public works project in history. While Interstate Highways usually receive substantial federal funding (90% federal and 10% state) and comply with federal standards, they are owned, built, and operated by the states or toll authorities. A network of U.S. highways connecting the 48 contiguous states and most of the cities with populations above 50,000, begun in the 1950s and estimated to carry about a fifth of the nation's traffic. Counties - The largest administrative division of most states in the United States. California has 58 counties. Relative location - A location of a place in relation to another place (i.e. south or downhill). Absolute location - A point on the earth's surface expressed by a coordinate system such as latitude and longitude. Relative location means to locate a place relative to other landmarks while absolute location is locating a place using a coordinate system. For example, you could give the relative location of St. Louis, Missouri as being in eastern Missouri along the Mississippi River southeast of St. Charles, but the absolute location of St. Louis is 38°43' North 90°14' West. Weather - The state of the air or atmosphere with respect to heat or cold, wetness or dryness, calm or storm, clearness or cloudiness, or any other meteorological phenomena; meteorological condition of the atmosphere; as, warm weather; cold weather; wet weather; dry weather, etc. Climate - the long-term weather pattern of an area, including temperature, precipitation, and wind. Weather refers to the conditions of a certain moment as opposed to climate, the long-term average of weather conditions.