Tectonic Processes Review
advertisement

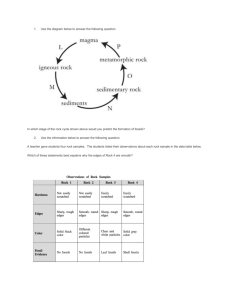
Unit 2: Tectonic Processes Review Geo 12 Ms. Thind Definitions: Mantle/Mesosphere, Centrosphere/Inner and Outer Core, Lithosphere/Continental and Oceanic Crust, Asthenosphere, Mohorocivic discontinuity, Magma Geomorphology, Intrusive Igneous Rock, Extrusive Igneous Rock, Sedimentary Rock, Metamorphic Rock, Strata/Beds of Rock, Plutons/Batholiths, Sills, Dikes, Crystallization, Lithification, Weathering Plate Tectonics, Pangea, Continental Drift, Theory of Isotacy , Divergent Boundary, Convergent Boundary, Transform Boundary , Subduction Faulting, Normal Fault, Reverse or Thrust Fault, Block Mountain or Horst Rift Valley or Graben, Folding, Anticline, Syncline, Compression , Tension Volcanism, Volcano, Cinder Cone, Composite Cone, Shield Cone, Tephra, Pyroclastic Flow, Lahar, Vent , Bombs, Fumerole Earthquake, Body Wave, P Wave, S Wave, Surface Wave, Rayleigh Wave, Love Wave, Epicenter, Richter Scale Diagrams to know and label: Layers of the Earth The Rock Cycle Cross Section of the Earth Plate Boundaries Continent to Continent Collision Oceanic to Continent Collision Oceanic to Oceanic Collision Relief Features Fault Landforms Anticlines and Synclines Types of Volcanoes Volcano Seismic Waves Things to know and understand: 1. What elements make up the earth? Inner Core? Outer Core? Continental Crust? Oceanic Crust? 2. How are igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rock formed? What do they look like? 3. How do we classify minerals? 4. What is the rate of cooling and depth of Igneous Rocks? 5. Examples of Intrusive and Extrusive rock structures. How are they formed? 6. Describe the theory of Pangea? Supporting Evidence? 7. Relief Features: How are deep sea trenches formed, volcanic belts, volcanic island arcs, block mountains, rift valleys, and reverse faults? 8. Describe what happens at plate boundaries: plate formation, plate destruction, and moving past one another. 9. What are the effects of plate movement? 10. What is the theory of isotacy? How does this explain the interaction between plates? 11. How are normal, reverse or thrust, block mountains or horsts, rift valleys or grabens produced? 12. Compare and contrast the different types of volcanoes. 13. Give examples of volcanic hazards. Describe. 14. Earthquakes: Where, why, how 15. Effects/impacts of earthquakes What to know from your map: 1. Have a look at common collision, subduction, divergent and transform zones. 2. Have a look at where fold mountains, subduction mountains, subduction trenches, rift zones, island arcs are on your map and why. Eg: If I gave you a diagram showing the pacific plate subducting at the south American plate what feature is likely to be created as a result? A: Volcanic Belt Eg: Map of Hawaii is given and volcanoes are labelled on this map. What type of volcanoes are indicated on this map? A: Shield Eg: If I gave you a diagram of a divergent boundary and then a map of the world. Indicate where this would be happening: A: Along mid oceanic ridges (mid atlantic ridge), rift valley in Africa Eg: If I gave you a map: Where are collizone earthquakes most common at? A: Europe, Asia