Click here to
advertisement

SHIFT-2
CLASS-XII
Physics
Session 2013 – 14
Q1. . An electric dipole is held in a uniform electric field (i) using suitable diagram show that it
does not undergo any translatory motion and (ii) drive an expression for the torque acting on it
and specify its direction.
Q2. State Gauss’s theorem & apply this theorem to obtain an expression for the electric field
intensity at a point due to (i)an infinitely long uniformly charged straight wire (ii) a uniformly
charged infinite sheet (iii) a uniformly charged thin spherical shell at an (a) outside point (b)
inside point.
Q3. (a)Deduce an expression for the capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor with air as the
medium between the plates (b)A dielectric slab of thickness‘t’ is kept in between the plates each
of area A of parallel plate capacitor separated by a distance of‘d’. Drive an expression for the
capacitance of capacitor for t <<d.
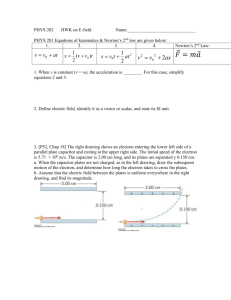
Q4. (i) Explain briefly how a capacitor stores energy on charging. Obtain expression for energy
stored (ii) A parallel plate capacitor of plate separation’s’ is charged to a p.d. ‘V’. A dielectric
slab of thickness d and dielectric constant K is introduced between the plates while the battery
remains connected to the plates.
(a) Find the ratio of energy stored in the capacitor after and before the dielectric in
introduced, give physical explanation for this change in stored energy.
(b) What happens to the charge on the capacitor?
(c)How does the electric field between plates change.
Q5. In a Van de Graaff type generator a spherical metal shell is to be a 15 × 106 V electrode. The
dielectric strength of the gas surrounding the electrode is 5 × 107 Vm–1. What is the minimum
radius of the spherical shell required? (You will learn from this exercise why one cannot build an
electrostatic generator using a very small shell which requires a small charge to acquire a high
potential.) [Ans 30cm]
Q6. A parallel plate capacitor with air as dielectric is connected to a power supply and charged to
a potential difference Vo. After disconnecting from power supply, a sheet of insulating material
is inserted between the plates completely filling the space between them. How will its (i) charge
on the plates (ii) electric field between the plates (iii) potential difference between the plates (iv)
capacitance (v) energy stored in the capacitor.
Q7. (a) Describe the formula for the equivalent EMF and internal resistance for the parallel
combination of two cells with EMF E1 and E2and internal resistances r1 and r2 respectively.
(a)What is the corresponding formula for the series combination?
(b) Two cells of EMF 1V, 2V and internal resistances r2 and r1 respectively are connected in (i)
series, (ii) parallel. What should be the external resistance in the circuit so that the current
through the resistance be the same in the two cases? In which case more heat is nerated in the
cells?
Q8. Deduce the condition for balance in a Wheatstone bridge. Using the principle of
Wheatstone bridge, describe the method to determine the specific resistance of a wire in the
laboratory. Draw the circuit diagram and write the formula used. Write any two
precautions.
Q9. Describe the principle and construction of potentiometer. Explain how a potentiometer can
be used to compare the emfs of two primary cells?
Q 10. Draw Circuit diagram for a meter bridge to determine the unknown resistance of a
resistor. Obtain the balance condition for a meter bridge. Find the shift in the balance
point for a meter bridge when two resistors in its two gaps, are interchanged.
Q 11. Are the paths of e’s straight lines between successive collisions in the (i) absence of
electric field (ii) presence of electric field. Establish a relation between drift velocity and
current. Hence obtain the relation between current density and drift velocity.
Q12. With the help of a neat and labeled diagram, explain the underlying principle and working of a
moving coil galvanometer. What is the function of (i) uniform radial field (ii) Soft iron core?
A: (i) The torque on the coil is same in all positions of coil in the radial magnetic field. This
provides a linear current scale.
(ii) Due to high permeability of soft iron, the magnetic field line crowd through the soft iron.
This increases the magnitude of magnetic field and makes it radial. Hence sensitivity of
galvanometer increases.
Q13. Derive a mathematical expression for the force per unit length experienced by each of the two
long current carrying conductors placed parallel to each other in air. Hence define one ampere of
current. Explain why two parallel straight conductors carrying current in the
opposite direction kept near each other in air repel.
A: Each current carrying conductor produces
magnetic field around it. So each conductor
experiences a force due to the magnetic field of
the other. According to Fleming’s left hand
rule, the direction of the force is perpendicular to
the two wires and is outwards. Hence the two
wires repel each other.
Q14. Draw a neat and labeled diagram of a cyclotron. State the underlying principles and
explain how a positively charged particle gets accelerated in this machine. Show
mathematically that the cyclotron frequency does not depend upon the speed of the particle.
Q15. State the Biot-Savart’s law for the magnetic field due to a current carrying element. Use this
law to obtain a formula for magnetic field at the center of a circular loop of radius R
carrying a steady current I. Sketch the magnetic field lines for a current loop.
Q16. (i) Using Biot-Savart’s law, derive the expression for the magnetic
field due to a current carrying circular loop of radius R, at a point which is at
a distance x from its center along
the axis of the loop.
(ii) Two small identical circular loops, carrying equal
currents are placed with the geometrical axes
perpendicular to each other as shown in the figure.
Find the magnitude and direction of the net
magnetic field produced at the point O.
Q17. Using Kirchoff’s laws, calculate the potential difference across
the 8 ohm resistor.
[Ans : Current through resistance 8= 0.46A, P. d. = 3.68Volts]
Q18. E2 =1.02V, PQ=1m.When switch S open, null position is obtained at a distance of 51 cm
from P. Calculate (i) potential gradient (ii) emf of the cell E1 (iii) when
switch S is closed, will null point move towards P or Q. Give reason for
your answer.
[Ans: (i) Potential gradient k = 0.02V/cm (ii) emf of the cell E1 = 2V
(iii) When switch S is closed, null point is not affected because no
current drawn from cell E1 at the null point. ]
Q19. In the potentiometer circuit shown, the balance point is at X. State
with reason, where the balance point will be shifted
when (i) R is increased; (ii) S is increased, keeping R
constant. (ii) Cell P is replaced by another cell whose
emf is lower than that of cell Q.
Q20. Two identical plane metallic surfaces A and B are
kept parallel to each other in air separated by a distance of
1 cm as shown in figure.
A is given a positive potential of 10V and the outer surface
of B is earthed. (i) What is the magnitude and direction of
the uniform electric field between Y and Z? (ii) What is the work done in moving a charge of 20
C from X to Y?
Ans : (i) E = 1000 V/m, direction from A to B
(ii) Zero.
Q21. The following data was obtained for the dependence of the
magnitude of electric field, with
distance, from a reference point O, within the charge distribution in
the shaded region.
Field Point
A
B
C
A’
B’
C’
Magnitude
E
E/8
E/27
E/2
E/16
E/54
of electric
field
(i) Identify the charge distribution and justify your answer.
(ii) If the potential due to this charge distribution, has a value V
at the point A, what is its value at the point A’?
Q22. Use Gauss’s law to obtain an expression for the electric
field due to an infinitely long straight uniformly charged wire.
Electric field in the above figure is directed along + X direction
and given by Ex = 5Ax + 2B, where E is in NC-1 and x is in metre, A and B are constants with
dimensions
Talking A=10NC-1m-1 and B = 5NC-1 calculate. (i) the electric flux through the cube. (ii) net
charge enclosed within the cube.
[Ans (i ) 0.05Nm2/C (ii) 44.25X10-14C ]
Q23. Two point charges of charge values Q and q are placed at distance x and x/2 respectively
from a third charge of charge value 4q, all charges being in the same straight line. Calculate the
magnitude and nature of charge Q such that the net force experienced by the charge q is
zero. [Ans Q = q/4 , +ive ]
Q24. How will a dia, para and ferromagnetic material behave when kept in a non-uniform
external magnetic field? Name two main characteristics of a ferromagnetic material which helps us to
decide its suitability for making (i) a permanent magnet and (ii) an electromagnet. Which of these
two characteristic should have a high or low values for each of these two types of magnets?
Q25. A short bar magnet placed with its axis inclined at 300 to the external magnetic field of 800 G
acting horizontally experiences a torque of 0.016 Nm. Calculate - (i) the magnetic moment of
magnet (ii) the work done by an external force in moving it from most stable to most unstable
position. (iii) What is the work done by the force due to the external magnetic field in the process
mentioned in (ii)?
A: (i) m = 0.4 Am2
(ii) Most stable position = 00 and most unstable position = 1800 ,
W = - mB (cos 180 – cos 0) = 2mB = 0.64J
(iii)W = - 0.64J.
Q26Total capacitance of the combination between A
and B in the given figure is 15μF. Calculate the
capacitance of capacitor C.
[ Ans. 60 μF]
Q27. On charging a parallel plate capacitor to a potential V, the spacing between the plates is
halved, and a dielectric medium of r = 10 is introduced between the plates, without
disconnecting the d.c source. Explain using suitable expressions, how the (i) capacitance (ii)
electric field (iii) energy density of the capacitor change.
[Ans(i) C1= 20Co (ii) E 1=2Eo (iii) u1 = 40uo]
Class XII –English Holiday Homework-2013-14
ClassXII (English Core)
Session 2013-14
1. 1.A.K.International School ,Shivaji Nagar, Meerut is looking for a receptionist for the school. Write
an advertisement on behalf of the administrative officer in the classified columns of the local
newspaper giving necessary details. Draft the advertisement in not more than 50 words.
2.
3. 2.Suman/Suresh has cleared the Pre-Medical Entrance Examination. The family is elated at the
achievement and they decide to have a get-together for all friends. Draft an informal invitation
giving necessary details.
4.
5. 3.The Student’s Council of your school has organized an excursion to Goa for students of class XII
during the Autumn Break. As President of the council, write a notice in not more than50 words
informing the students about this excursion.
6.
7. 4.Your are Shekhar/Savita a student ofA.P.Public School, Noida. Principal of two schools from
Germany visited your school as part of a cultural exchange programme. Students of the school put
up a cultural show in their honour. Write a report about it for your school magazine in about 100125 words.
8.
9. 5.You are Rahul, the Head boy of Creative Public School, Shakti Nagar. Recently your school
hosted the Regional Level CBSE Science Exhibition. Write a report of this event for your school
newsletter in about 125 words.
10.
11. 6.You are Satish/ Sonali, the student prefect in charge of the school library. You have been asked
to place an order for children’s story books (Ages 10-13). Write a letter to M.S.Book Depot
Ramanagar, Bikaner placing an order for the books. Invent other necessary details yourself.
12.
13. 7.You are NItin/Natasha a student of Class XII at K.P.N.Public School, Faridabad. The student is
required to cope with lot of pressure in today’s competitive environment. Write a letter to the
editor of a national daily highlighting the increasing stress faced by students and suggest ways to
combat the same.
14.
15. 8.You are Suresh/Smita. You came across an advertisement for the post of a Nursery teacher in a
national daily. You consider yourself suitable and eligible for the post. Write an application in
response to the advertisement.
16.
17. 9.Computer games and Video games have become popular with children today. As a result
outdoor games seem to have no place in their life any more. You are Satish/Sakshi. You had the
opportunity of playing Hide-and-Seek when you visited your cousins in a small town. You decide
to write an article on your experiences about the joys of playing outdoor games for the school
magazine. (200 Words)
18.
19. 10.You are Amit/Amita a student of class XII at K.K.Public School, New Delhi. You recently visited
a hill station along with your parents. It was an exhilarating, adventurous and joyful experience.
Write an article for the school magazine sharing your experience in about 200 words.
20.
Class- XII Subject- Chemistry
Solid State
1. What is the number of atoms per unit cell in a body-centred cubic structure?
2. What is the total number of atoms per unit cell in a face-centred cubic (fcc) structure?
3. Which point defect in crystals of a solid in which density decreases, increases or
remainsame?
4. A compound of element X and Y has crystalline nature. The ccp lattice is formed by
anions of element Y and cation of element X occupies 2/3 rd of the octahedral voids.
What will be the formula of the compound?
5. Account for the following:
(a) Glass of old building is milky.
(b) Crystalline substances are anisotropic.
6. Explain each of the following with a suitable example:
(i) Paramagnetism
(ii) Antiferromagnetism
(iii) Frenkel defect in crystals
(iv) Ferromagnetism
(v) Ferrimagnetism
(vi) Schottky defect
7. (a) Explain electrical property of substances on the basis of Band Theory.
(b) Describe the two main types of semiconductors.
8. How would you account for the following?
(i) Frenkel defects are not found in alkali metal halides.
(ii) Schottky defects lower the density of related solids.
(iii) Impurity doped silicon is a semiconductor.
9. Iron has a body-centred cubic unit cell with a cell edge of 286.65 pm. The density of
iron is 7.87 g cm−3. Use this information to calculate Avogadro’s number.
(At. Mass of Fe = 56 g mol−1)
Solutions
1. State Henry’s law correlating the pressure of a gas and its solubility in a solvent and
mention two applications for the law.
2. An antifreeze solution is prepared from 222.6 g of ethylene glycol [C 2H4(OH)2] and
200 g of water. Calculate the molality of the solution. If the density of this solution be
1.072 g mL−1, what will be the molarity of the solution?
3. Calculate the temperature at which a solution containing 54 g of glucose, (C 6H12O6),
in 250 g of water will freeze.(Kf for water = 1.86 K mol−1 kg)
4. State Raoult’s law for solutions of volatile liquids. Taking suitable examples explain
the meaning of positive and negative deviations from Raoult’s law. Why are they
caused?
5. Define the term osmotic pressure. Describe how the molecular mass of a substance
can be determined by a method based on measurement of osmotic pressure?
6. Differentiate between molality and molarity of a solution. What is the effect of change
in temperature of a solution on its molality and molarity?
7. 100 mg of a protein is dissolved in just enough water to make 10.0 mL of solution. If
this solution has an osmotic pressure of 13.3 mm Hg at 25°C, what is the molar mass of
the protein?(R = 0.0821 L atm mol−1 K−1 and 760 mm Hg = 1 atm)
8.. A solution prepared by dissolving 1.25 g of oil of winter green (methyl salicylate) in
99.0 g of benzene has a boiling point of 80.31 °C. Determine the molar mass of this
compound. (B.P. of pure benzene = 80.10 °C and Kb for benzene = 2.53 °C kg mol−1)
9. Calculate the freezing point depression expected for 0.0711 m aqueous solution of
Na2SO4. If this solution actually freezes at −0.320°C, what would be the value of Van’t
Hoff factor? (Kf for water is 1.86 °C mol−1)
Electrochemistry
1. Express the relation between conductivity and molar conductivity of a solution.
2. What is primary cell? Give an example.
3. The resistance of a conductivity cell containing 0.001 M KC1 solution at 298 K is
1500Ω. What is the cell constant if the conductivity of 0.001 M KCl solution at 298 K is
0.146×10−3 S cm−1?
4. Predict the products of electrolysis in the following:
(i) A solution of H2SO4 with platinum electrodes.
(ii) A solution of CuCl2 with Pt electrodes.
(iii) A solution of AgNO3 with silver electrode
5.What type of a cell is the lead storage battery? Write the anode and the cathode
reactions and the overall reaction occurring in a lead storage battery while operating.
6. Formulate the galvanic cell in which the following reaction takes place:
Zn(s) + 2Ag+(aq)
Zn2+ (aq) + 2Ag(s)
State:
(i) Which one of its electrodes is negatively charged.
(ii) The reaction taking place at each of its electrode.
(iii) The carriers of current within this cell.
7. Corrosion is essentially an electrochemical phenomenon. Explain the reactions
occurring during corrosion of iron kept in an open atmosphere.
8. Conductivity of 0.00241 M acetic acid solution is 7.896 × 10 −5 S cm−1. Calculate its
molar conductivity in this solution. If
for acetic acid be 390.5 S cm2 mol−1, what would
be its dissociation constant?
9. Three electrolytic cells A, B and C containing solutions of zinc sulphate, silver nitrate
and copper sulphate respectively, are connected in series. A steady current of 1.5
ampere was passed through them until 1.45 g of silver was deposited at the cathode of
cell B. How long did the current flow? What mass of copper and what mass of zinc were
deposited in the concerned cells?
(Atomic masses of Ag = 108, Zn = 65.4, Cu = 63.5)
10.Define molar conductivity of a substance and describe how for weak and strong
electrolytes, molar conductivity changes with concentration of solute. How is such
change explained?
11. A voltaic cell is set up at 25°C with the following half-cells:
Al | Al3+ (0.001 M) and Ni | Ni2+ (0.50 M)
Calculate the cell voltage.
13. Calculate the equilibrium constant and Δ rG° for the reaction
14. One half cell in a voltaic cell is constructed from a silver wire dipped in silver nitrate
solution of unknown concentration. Its other half-cell consists of a zinc electrode dipping
in 1.0 M solution of Zn (NO3)2. A voltage of 1.48 V is measured for this cell. Use this
information to calculate the concentration of silver nitrate solution used.
15. (a) State Kohlrausch law of independent migration of ions. Write an expression for
the molar conductivity of acetic acid at infinite dilution according to Kohlrausch law.
(b) Calcualte
Given that
for acetic acid.
(HCl) = 426 S cm2 mol−1
(NaCl) = 126 S cm2 mol−1
(CH3COONa) = 91 S cm2 mol−1
Chemical Kinetics
1. For the reaction
the rate law is expressed as
2
rate = k[Cl2][NO] . What is the overall order of this reaction?
2. The decomposition of NH3 on platinum surface,
is a
zero order reaction with k = 2.5 × 10−4 M s−1. What are the rates of production of N2 and
H2?
3. Define the term
(i) rate of a reaction.
(ii) order of reaction
4. A first order decomposition reaction takes 40 minutes for 30% decomposition.
Calculate its t½value.
5. What is meant by the ‘rate constant, k’ of a reaction? If the concentration be
expressed in mol L−1 units and time in seconds, what would be the units for k (i) for a
zero-order reaction and (ii) for a first-order reaction?
6. (a) Derive the general form of the expression for the half-life of a first-order reaction.
(b) The decomposition of NH3 on platinum surface is a zero-order reaction. What are the
rates of production of N2 and H2 if k = 2.5 × 10−4 mol−1 L s−1?
7.(a) List the factors on which the rate of a chemical reaction depends.
(b) The half-life for decay of radioactive 14C is 5730 years. An archaeological artefact
containing wood has only 80% of the 14C activity as found in living trees. Calculate the
age of the artefact.
8. A reaction is of second order with respect to a reactant. How will the rate of reaction
be affected if the concentration of this reactant is
(i) Doubled,
(ii) Reduced to half?
9. A first-order reaction has a rate constant of 0.0051 min −1. If we begin with 0.10 M
concentration of the reactant, what concentration of reactant will remain in the solution
after 3 hours?
10. The rate constant for a reaction of zero order in A is 0.0030 mol L −1 s−1. How long
will it take for the initial concentration of A to fall from 0.10 M to 0.075 M?
11. A reaction is of first order in reactant A and of second order in reactant Β. How is the
rate of this reaction affected when (i) the concentration of B alone is increased to three
times (ii) the concentrations of A as well as B are doubled?
Class-XII Biology Home work
Summer-vacation
Q.No.1-What are pre-fertilization and post fertilization events in sexually
producing organisms.?
Q.No.2-Draw the well labeled diagram of human male reproductive system.
Q.No.3-Draw the well labeled diagram of human female reproductive system.
Q.No.4-Describe process of formation of microgametophyte in angiosperms.
Q.No.5-Describe the process of formation of megagametophyte angiosperms.
Q.No6-Describe embryology of angiospermic plants.
Q.No.7-Describe the process of implantation of human embryo.
Q.No.8-Explain the structure of DNA.
Q.N09.-Describe various kinds of RNAs.
Q.No.10-Read unit-1 and unit-2 of biology.
ECONOMICS HOLIDAY HOMEWORK
CLASS-XII
1. If ratio of change in quality ( Q) to original quality (Q) is 0.5 and elasticity is (-) 1.25, calculate in
price.
2. In case of commodity ‘B’, the ratio of change in price ( P) to original price (P) is (-) 0.4.if price
elasticity of demand is (-) 0.5, calculate the percentage change in quantity demanded.
3. The percentage change in demand is three times the percentage change in price. If original
demand was 30 units at the price of RS.7 per unit, then calculate the price elasticity of demand,
given price increased by 10%. Indicate whether the demand is elastic or not. Also calculate the
new quantity demanded.
4. The price elasticity of demand of good X is half the price the price elasticity of demand of good
Y. A 25% rise in the price of good Y reduces its demand from 400 units to 300 units. Calculate
percentage rise in demand of good X when its price falls from RS.10 to RS.8 per unit.
5. The demand for good X and Y has equal price elasticity. The demands of X form 100 units to 250
units due to a 20 per cent fall in its price. Calculate the percentage rise in demand of Y, if tits
price falls by 8 percent.
6. The price elasticity of demand for goods X and Y are known to be 1 and 2 respectively. Price of X
rises by 5% while that of good Y falls by 5%. What are the percentage change in the quantities
demanded of X and Y?
7. The price elasticity of demand for good X is known to be twice that of good Y. price of X falls by
%5 while that of good Y rises by 5%. What is the percentage change in the quantities demanded
of X and Y?
8. When price of a good falls from RS.8 per units to RS.7 per units, its demand rises from 12 units
to 16 units. Compare expenditure on the good to determine whether demand is elastic is elastic
or inelastic.
9. When price of a good falls RS.10 per unit to RS.9 per units, its demand rises form 9 units to 10
units. Compare expenditure on the good to find price elasticity of demand.
10. A consumer buys 40 units of a good at the price of RS.3 per unit. When the price rises to RS.4
per units. Calculate the price elasticity of demand by total expenditure method.
11. As the price of a product decreases by 7%, the total expenditure on it goes up by 3.5%. What
can we say about the elasticity of demand for this product?
12. Calculate the elasticity of demand by total expenditure method:
PRICE (RS.)
TOTAL EXPENDITURE (RS.)
5
50
6
50
13. Calculate the elasticity of demand by total expenditure method:
PRICE (RS.)
TOTAL EXPENDITURE (RS.)
4
40
6
50
14. With rise in price from RS.8 to RS.14, total expenditure on the commodity rises by 40% and
becomes RS. 1,120. Calculate price elasticity of demand. Also indicate whether demand is elastic
or inelastic.
15. A dentist was charging RS.300 for a standard cleaning job and it’s used to generate total
revenue equal to RS.30,000 per month. She has, since last month, increased the price of dental
cleaning to RS.350. As a result, fewer customers are now coming for dental cleaning, but the
total revenue is now RS.33,250. From this, what can we conclude about the elasticity of demand
for her dental service?
16. A consumer spends RS. 80 on a commodity when its price is RS.1 per unit and spends Rs.96
when its price is Rs.2 per units. Calculate price elasticity of demand for the commodity by the
percentage method?
17. Calculate price elasticity of demand:
PRICE (RS.)
TOTAL EXPENDITURE (RS.)
5
500
6
420
18. When price of good fall from RS.5 to RS.3 per unit, its demand rises by 40%. Calculate its price
elasticity of demand.
19. When the price of commodity is RS.20 per unit, its quantity demanded is 800 units. When its
price rises by RS.5 per unit, its quantity demanded falls by 20 per cent. Calculate its price
elasticity of demand. Is its demand elastic? Give reasons for your answer.
20. The price of commodity is RS.15 per unit and its quantity demanded is 500 units. Its quantity
demanded rises by 80 units as a result of fall in its price by 20 per cent. Calculate its price
elasticity of demand. Is its demand inelastic? Give reason for your answer.
SUMMER VACATION HOME ASSIGNMENT
ACCOUNTANCY- XII STD
CHAPTER - I
Accounting for partnership firms - Fundamentals\
Q.1
What is the status of partnership from an accounting viewpoint ?
Q.2
List the items that may appear on the debit side and credit side of a partner's
fluctuating capital account.
Q.3
Give two points of difference between Profit and Loss and profit and loss appropriation
A/c.
Q.4 P and Q are partners with capitals of Rs. 6,00,000 and Rs. 4,00,000 respectively. The
profit and Loss Account of the firm showed a net Profit of Rs. 4, 26,800 for the year.
Prepare Profit and Loss account after taking the following into consideration:(i)
Interest on P's Loan of Rs. 2,00,000 to the firm
(ii)
Interest on 'capital to be allowed @ 6% p.a.
(iii)
Interest on Drawings @ 8% p.a. Drawings were ; P Rs 80,000 and Q Rs.
1000,000.
(iv)
Q is to be allowed a commission on sales @ 3%. Sales for the year was Rs.
1000000
(v)
10% of the divisible profits is to be kept in a Reserve Account.
Q.5 A, and C are partners with fixed capitals of Rs. 2,00,000, Rs. 1,50,000 and Rs. 1,00,000
respectively. The balance of current accounts on 1st January, 2004 were A Rs. 10,000
(Cr.); B Rs. 4,000 (Cr.) and C Rs. 3,000 (Dr.). A gave a loan to the firm of Rs. 25,000 on
1st July, 2004. The Partnership deed provided for the following:(i)
Interest on Capital at 6%.
(ii)
Interest on drawings at 9%. Each partner drew Rs. 12,000 on 1st July, 2004.
(iii)
Rs. 25,000 is to be transferred in a Reserve Account.
(iv)
Profit sharing ratio is 5:3: 2 upto Rs. 80,000 and above Rs. 80,000 equally. Net
Profit of the firm before above adjustments was Rs. 1,98,360.
From the above information prepare Profit and Loss Appropriation Account, Capital and
Current Accounts of the partners.
Q.6
Yogesh, Ajay and Atul are partners sharing profits in the ratio 4:3:2. Yogesh withdraws
Rs.3,000 in the beginning of every month. Ajay withdraws Rs. 2,000 in the middle of every
month whereas Atul withdraws Rs. 1,500 at the end of every month. Interest on capitals and
drawings is to be calculated @ 12% p.a. Ajay is also to be allowed a salary of Rs. 1,000 per
month. After deducting salary but before charging any type of interest, the profit for the year
ending 31stpecember, 1997 was Rs.,1,14,780. Prepare Profit & Loss Appropriation Account,
Partners' Capital Accounts and Current Accounts from the additional information given below:
Q.7
Ram and Shyam were Partners. in a firm sharing profits in the ratio of 3 : 5. Their Fixed
Capitals were ': Ram Rs. 5,00,000 and Shyam Rs. 9,00,000. After the accounts of the year had
been closed, it was found that interest on capital at 10% per annum as provided in the
partnership agreement has not been credited to the Capital Accounts of the partners. pass
necessary entry to rectify the error.
Admission of a Partner
Q.1
Dinesh, Yasmine and Faria are partners in a firm, sharing profits and losses in 11:7:2
respectively. The Balance Sheet of the firm as on 31st Dec 2001 was as follows:
Liabilities
Rs. Assets
Sundry Creditors
800 Factory
Public Deposits
Rs.
7,350
1,190 Plant & Machinery
Reserve fund
1,800
900 Furniture
Capital A/c
2,600
Stock
1,450
Dinesh
5,100 Debtors
Rs. 1,500
Yasmine
3,000 Less: bad debts Rs.
300
1,200
provisions
Faria
5,000 Cash in hand
15,900
1,590
15,900
On the same date, Annie is admitted as a partner for on-sixth share in the profits with
Capital of Rs. 4,500 and necessary amount for his share of goodwill on the following
terms:a.
Furniture of Rs. 2,400 were to be taken over by Dinesh, Yasmine and Faria
equally.
b.
A Liability of Rs. 1,670 be created against Bills discounted.
c.
Goodwill of the firm is to be valued at 2.5 years' purchase of average profits of 2
years. The profits are as under:
2000:- Rs. 2,000 and 2001 - Rs. 6,000.
d.
Drawings of Dinesh, Yasmine, and Faria were Rs. 2,750; Rs. 1,750; and Rs. 500
Respectively.
e.
Machinery and Public Deposits are revalued to Rs. 2,000 and Rs. 1,000
respectively.
Prepare Revaluation Account, Partners' Capital Accounts and Balance Sheet of
the new firm.
Q.2
X and Y are partners as they share profits in the proportion of 3:1 their
balance sheet as at 31.03.07 as follows.
BALANCE SHEET
Liabilities
Rs. Assets
Capital Account
Land
X
1,76,000 Furniture
Y
1,45,200 Stock
Creditors
91,300 Debtors
Rs.
1,65,000
24,500
1,32,000
35,200
Bills Receivable
28,600
Cash
27,500
4,12,500
4,12,500
On the same date, Z is admitted into partnership for 1/5th share on the following terms
a.
Goodwill is to be valued at 3½ years purchase of average profits of last for year which
were Rs. 20,000 Rs. 17,000 Rs. 9,000 (Loss) respectively.
٠
Stock is fund to be overvalue by Rs. 2,000 Furniture is reduced and Land to be
appreciated by 10% each, a provision for Bad Debts @ 12% is to be created on Debtors
and a Provision of Discount of Creditors @ 4% is to be created.
٠
A liability to the extent of Rs. 1,500 should be created for a claim against the firm for
damages.
٠
An item of Rs. 1,000 included in Creditors is not likely to be claimed, and hence it should
be written off.
Prepare Revaluation Account, Partners: Capital Accounts and Balance Sheet of the new
firm if Z is to contribute proportionate capital and goodwill. The capital of partners are to be in
profit sharing ratio by opening current Accounts.
Q.3.
Rashmi and Pooja are partners in a firm. They share profits and losses in the
ratio of 2:1. They admit Santosh into partnership firm on the condition that she
will bring Rs. 30,000 for Goodwill and will bring such an amount that her capital
will be 1/3 of the total capital of the new firm. Santosh will be given 1/3 share in
future profits. At the time of admission of Santosh, the Balance Sheet of Rashmi
and Pooja was as under:
Liabilities
Rs. Assets
Capital Account
Cash
Rashmi
1,35,000 Machinery
Pooja
1,25,000 Furniture
Rs.
90,000
1,20,000
10,000
Creditors
30,000 Stock
50,000
Bills Payable
10,000 Debtors
30,000
3,00,000
3,00,000
It was decided to:
a.
revalue stock at Rs. 45,000.
b.
depreciated furniture by 10% and machinery by 5%.
c.
made provision of Rs. 3,000 on sundry debtors for doubtful debts.
Prepare Revaluation Account, Partners: Capital Accounts and Balance Sheet of the
new firm. Give full workings.
Q.4
A, B and C are equal partners in a firm, their Balance Sheet as on 31st
March
2002 was as follows:
Liabilities
Sundry Creditors
Employees Provident Fund
Rs. Assets
Rs.
27,000 Goodwill
1,17,000
6,000 Building
1,25,000
Bills Payable
45,000 Machinery
72,000
General Reserve
18,000 Furniture
24,000
Capitals:
Stock
A
2,17,000 Bad Debts
B
1,66,000 Cash
C
90,000 Advertisement
1,14,000
1,02,000
12,000
Suspense
3,000
A/c
5,69,000
5,69,000
On that date they agree to take D as equal partner on the following terms:
a.
D should bring in Rs. 1,60,000 as his capital and goodwill. His share of goodwill
is valued at Rs. 60,000.
b.
Goodwill appearing in the books must be written off.
c.
Provision for loss on stock and provision for doubtful debts is to be made at 10%
and 5% respectively.
d.
The value of building is to taken Rs. 2,00,000.
e.
The total capital of the new firm has been fixed has been fixed at Rs. 4,00,000
and the partners capital accounts are to be adjusted in the profit sharing ratio.
Any excess is to be transferred to current account and any deficit is to be brought
in cash.
Required : Prepare the Revaluation Account, Partners Capital Accounts, and the
Balance Sheet of the new firm.
BUSINESS STUDIES- XII STD
Chapter -1
NATURE AND SIGNIFICANCE OF MANAGEMENT
ANSWER THE FOLLOWING HOTS QUESTIONS IN ONE
WORD OR ONE SENTENCE. (EACH ONE MARK)
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13
14.
15.
16.
Which force is consisted as the essence of management?
‘Doing the task with minimum cost” name the term associated with management?
‘ In order to be successful , an organization must change its goals according to the needs of
the environment. Whish characteristics of management are highlighted in this statement.
Which function of management is bridges the gap between where we stand today and
where we want to reach/
Name the function of management which establishes organization structure and establishes
authority and responsibility relations?
In which functions of management standards are compared with actual, deviations are find
out and corrective steps are taken?
Anything (-) management is equal to what?
Departmental manages are included at which level of management?
Name the level of management the following parts belongs to.
1.
Purchase managers.
2.
CEO
3.
Superintendent.
‘Survival profit and growth are essential target of any business’ which objectives of
management is referred here?
‘Every organization whether it is business or non-business should use environmental
methods of production, give employment opportunities and provide basic amenities like
schools and crèches to employees’ name the objective of management indicated here?
The activities involved in managing an enterprise are common to all organizations whether
social or political’ which characteristics of management is highlighted by this statement?
What is PODSCORB?
How Management is an intangible force?
“Management is essential for successful running of an enterprise”, How?
Father of Mr. ‘Y’ acts as Vice President in ABC Ltd. Name the level of
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
Management he is working? Explain Any two functions performed by him?
Mr. Anil working as a ‘Sales department Head in XYZ Ltd. Name the level of
Management he is working? Explain Any two functions performed by him?
Explain any 3 functions performed by operational Level?
‘Co-ordination’ is the essence of Management’ Explain.
“Management is critical ingredient of a nation’s growth” Comment.
Why Mgt is considered as Multi dimensional function?
“Mgt is Science as well as act”. Explain this statement.
Chapter -2
PRINCIPLES OF MANAGEMENT
1.
How re principles of management formed?
2.
Why is it said that the principles of management are universal?
3.
Why is it said that principles of management are flexible?
4.
Which principles of management promotes team spirit.?
5.
Who was the first to identity functions of management?
6.
Which principle of management suggests that a subordinate should receive orders from and be
accountable to one superior?
7.
Who gave the concept of scientific management? What was his profession?
8.
Which principle of scientific management suggest the introduction of scientific investigation and
analysis of management practice?
9.
What is the basis of formation of scientific management?
10.
Which principle of management is violated if an employee is asked to receive orders from two
superiors?
11.
“Workers should be encouraged to develop and carry out their plans for improvements”.
Identify the principle of management formulated by Fayol.
12.
It has been observed that the prevailing situation in an organization is due to the violations of
the principle of ‘order’. What might have been your observation?
13.
Which principle of management is violated when a manager grants one month medical leave to
a superior with pay and only one week medical leave to an accountant?
14.
Mohan a manager, expects his colleagues to get work out of subordinates without giving them
any powers. Which principle of management is being overlooked and why?
15.
Which principle of management aims at securing the loyalty and devotion of the employees by
giving them fair and just treatment?
16.
Which principle of management envisages that each group of activities having the same
objective must have one head and one plan? Explain the principle with suitable example.
17.
If an organization does not provide the right place for physical and human recourses in the
organization, which principle is violated? What are its consequences?
18.
The production manager of an automobile company asked the foreman to achieve a target
production of 200 units (Scooters) per day. But he did not give him the authority to requisition
tools and materials from the store department. Can the production managers blame the
foreman if he is not able to achieve the desire target? Explain briefly the principle relating to the
situation.
19.
Name and explain that principle of Fayol which suggest that communication from top to bottom
should follow the official lines of command?
20.
Identify the technique of scientific management which are described by the statement given
below:i.
When specialists supervise each worker.
ii.
Change in the attitude of workers and management towards one another. From
competition to Co-operation.
iii.
When uniformity is introduced in materials. Machine, tools, method of works
and working conditions after, due research.
21.
Hina & Harish are typist in a company having same educational qualification. Hina is getting
Rs.3000 per month and harish Rs. 4000 per month as salary far the same working hour. Which
principle of management is violated in this case? Name and explain the principle?
Chapter -3
Business Environment
Which environment describes characteristics of the society in which the organization exists.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
Which element / dimension of business environment involves improvement and innovations
which provide new ways of producing goods and services and new methods and techniques of
operating a business.
Which environment prohibits the advertisement of alcoholic beverages?
Banking sector reforms have led to easier credit terms and better services. This is an example of
a key component of the “Business Environment “ name this component?
‘Demand for reservation in jobs for minorities refers to an example of key component of general
environment of business. Name this component.
It is the process by which government control over the industry is being loosened. Give the term
to which this statement is trying to indicate.
Which process aims at giving greater role to the private sector role to the public sector?
State the characteristics of business environment.
State the economics reforms since 1991 or new Economics policy.
State the factors of Micro Environment.
State the factors of Macro Environment.
State the difference between general and specific environment with example.
Explain any five positive effects of liberalization and globalization on business and industry.
Explain any five negative effects of liberalization and globalization on business and industry in
India.
Write the impact of changes in government policy on business and industries.
State the component of business Environment.
State the importance of business.
Chapter -4
PLANNING
Qus:1 How does planning provide direction?(Any Three)
Qus:2 The planning function of management is conducted at which level of management ?
Qus:3 One of the functions of management is considered as a base for all other functions. Name that
Function.
Qus:4 : Planning strangulates the initiative of the employees and compels them to work in an inflexible
manner” Discuss.
Qus:5 Which limitation of planning suggest that the employees stop thinking and become the blind
followers of Plan?
Qus:6 A company needs a detailed plan for its new project- construction of shopping mall. What type of
plan Is it ?
Qus:7 In which type of plan the sequence to perform a job is determined?
Qus:8 Which plans suggest action and non action of employees?
Qus:9 “No Smoking : the statement is related to which type of plan?
Qus:10 Mc Donald does not give its franchise to any other company which is running food business. This
is Related to which type of plan?
Qus:11 Name the type of plan which serve as a guide for overall business planning and define the future
state of Affair which the organization strive to realize?
Qus:12 In which step of planning process the planners make prediction and assumptions regarding
future?
Qus:13 How should a manager select the best possible course of action?
Qus:14 Without one function of management the controlling function is not possible. Name the
concerned function.
Qus:15 Planning is an activity which enables a manager to look ahead and anticipate changes. Mention
the Benefit of planning highlighted here.
Qus:16 Planning ensures clarity in thoughts and actions, works is carried on smoothly without
interruptions . Which importance of planning is mentioned here?
Qus:17 It helps the manager to look into future and make a choice amount various alternative courses of
Action enumerate the importance of planning indicate here.
Qus:18 Planning lays down the base for other functions of management which feature of planning is
Highlighted here?
Qus:19 A plan is framed it is implemented and is followed by another plan and so on. Mention the
feature of Planning indicate here?
Qus:20 Which features of Planning is stressed by saying that planning is an intellectual activity of
thinking Rather than doing?
Mathematics Holidays
Homework-- 2013-14
1. Let R be the relation in the set N given by
R = (a, b)| a = b – 2 , b > 6} . Whether the relation is
reflexive or not ?justify your answer.
2. Check whether the relation R is reflexive, symmetric
and transitive.
R = { (x , y): x – 3y = 0} on A ={1, 2, 3……….13, 14}.
3. Let N be the set of all natural numbers & R be the
relation on N × N defined by
R= { (a , b) , (c ,d): if a + d = b + c}. Show that R is an
equivalence relation.
4. Let A=R-{3} & B=R-{1}. Consider the function
f:A→B defined by f(x)=(
𝑥−2
) .show that f is one-one &
𝑥−3
onto, hence find 𝑓 −1 .
5. If f: 𝑅 → 𝑅 be defined as f(x)= 10x +7. Find the
function g:𝑅 → 𝑅. Such that gof(x)=fog(x)=𝐼𝑅 .
6. Prove that:
tan−1 (
7. Prove that : tan−1 (
cos 𝑥
1+sin 𝑥
Following system of
equations:
𝒙 + 𝟐𝒚 − 𝟑𝒛 = 4
𝟐𝒙 + 𝟑𝒚 + 𝟐𝒛 = 𝟐
3𝑥 − 3𝑦 − 4𝑧 = 11
B.
4𝑥 + 3𝑦 + 2𝑧 = 60
𝑥 + 2𝑦 + 3𝑧 = 45
6𝑥 + 2𝑦 + 3𝑧 = 70
C.
3𝑥 − 2𝑦 + 3𝑧 = 8
𝑥
2
2
√1+𝑥−√1−𝑥
)
√1+𝑥+√1−𝑥
8. Using matrices, Solve the
A.
𝜋
) = − , 𝑥𝜖 (
𝜋
1
2
2
−𝜋 𝜋
2
, ).
2
= − cos−1 𝑥.
2𝑥 + 𝑦 − 𝑧 = 1
4𝑥 − 3𝑦 + 2𝑧 = 4
9. Using properties determinants, solve the following
for x:
𝑥 − 2 2𝑥 − 3
3𝑥 − 4
|𝑥 − 4 2𝑥 − 9 3𝑥 − 16| = 0
𝑥 − 8 2𝑥 − 27 3𝑥 − 64
10. Using matrix method, sole the following system of
equations:
2 3 10
+ +
=4
𝑥 𝑦
𝑧
4 6 5
− + =1
𝑥 𝑦 𝑧
6 9 20
+ −
=2
𝑥 𝑦
𝑧
Where
𝑥, 𝑦, 𝑧 ≠ 0.
11. Find the relationship between 'a' and 'b' so that
the function 'f' defined by:
𝑎𝑥 + 1 𝑖𝑓 𝑥 ≤ 3
𝑓 (𝑥 ) = {
𝑖𝑠 𝑐𝑜𝑛𝑡𝑖𝑛𝑢𝑜𝑢𝑠 𝑎𝑡 𝑥 = 3.
𝑏𝑥 + 3 𝑖𝑓 𝑥 > 3
12. Find value of x
−1 (
sin
13. Find value:
1 − 𝑥 ) − 2 sin−1 𝑥 =
𝑥
𝑥−𝑦
𝑦
𝑥+𝑦
tan−1 ( ) − tan−1
𝜋
2
14.
15. Using properties of determinants, solve the
following for x:
16. Using properties of determinants, solve the
following for x:
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
28.
29.
30.
31.
32.
33.
34.
35.
36.
37.
38.
39.
40.
41.
42.
43.
44.
Computer Science
1. What is token? Classify its type.
2. Define Iteration Statement. Classify it with example.
3. Define Conditional Statement. Classify it with example.
4. Write the input and output statements for all data types.
5. Write the programme for following.
a. To print Fibonacci series.
b. To print prime number series.
6. Create a class with all types of constructors, destructor and two member functions.
7. Write a code to explain inline function.
8. Explain the logic for following
a. Bubble sort
b. Selection sort
c. Insertion sort
d. Merge sort
Hindi
HOLIDAYS HOMEWORK OF HISTORY
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Map work from history book 1st ,2nd &3rd in map file.
Key points from 1st&2nd book in a small copy.
Eassy type questions from book 1st [all chapters] in HW copy.
Learn 1st ,2nd ,&3rd chapters from book 1st.
Prepare PPT from history book [1,2,3]- any one.
HOLIDAY HOMEWORK CLASS XII[IIND SHIFT]
GEOGRAPHY
1. Do all the practical till chapter 4 in practical file.
2. Prepare one PPT on the chapter given to you.
3. Do all the diagrams & maps till chapter 4 of fundamental of
human geography.
4. Syllabus for 1st unit test is from 1 to 5 chapters of fundamental of
human geography.
Political Science
Q.1Why did the two superpowers need smaller allies during the Cold War? Define
in details.
Q.2Identify the princely states marked in the Indian map, Mention the major
problem faced in the integration of any one of these states into the Indian union.
Q.3 POLITICAL PARTIES AND DEMOCRATIC GOVERNANCE: A CASE
STUDY OF PARTY FORMATION IN INDIA SINCE 1950.
Q.4 Make a power point Presentation on Cold war era and Post Cold war era.
Q.5 Make Project on Parliamentary Presidential form of government (define its
merits demerits) and make a list of the countries of the world which type of
governments countries are having’.
Q.6What was Shock Therapy? Was this the best way to make a transition
from communism to capitalism?
Q.7 Draw a map and how many counties were having Communist form of
government and how many countries were having Democratic government.