Organic Chemistry201
advertisement
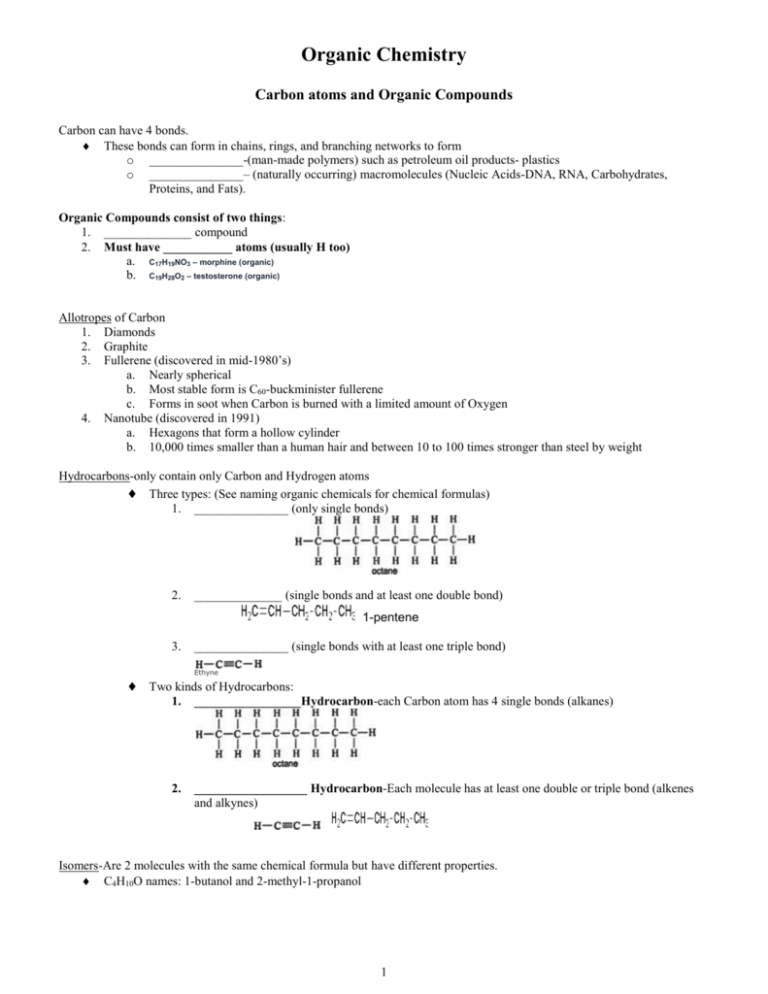
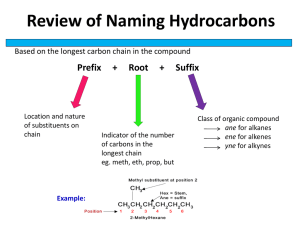
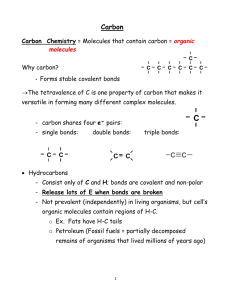
Organic Chemistry Carbon atoms and Organic Compounds Carbon can have 4 bonds. These bonds can form in chains, rings, and branching networks to form o _______________-(man-made polymers) such as petroleum oil products- plastics o _______________– (naturally occurring) macromolecules (Nucleic Acids-DNA, RNA, Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Fats). Organic Compounds consist of two things: 1. ______________ compound 2. Must have ___________ atoms (usually H too) a. C17H19NO3 – morphine (organic) b. C19H28O2 – testosterone (organic) Allotropes of Carbon 1. Diamonds 2. Graphite 3. Fullerene (discovered in mid-1980’s) a. Nearly spherical b. Most stable form is C60-buckminister fullerene c. Forms in soot when Carbon is burned with a limited amount of Oxygen 4. Nanotube (discovered in 1991) a. Hexagons that form a hollow cylinder b. 10,000 times smaller than a human hair and between 10 to 100 times stronger than steel by weight Hydrocarbons-only contain only Carbon and Hydrogen atoms Three types: (See naming organic chemicals for chemical formulas) 1. _______________ (only single bonds) 2. ______________ (single bonds and at least one double bond) 1-pentene 3. _______________ (single bonds with at least one triple bond) Ethyne Two kinds of Hydrocarbons: 1. _________________Hydrocarbon-each Carbon atom has 4 single bonds (alkanes) 2. __________________ Hydrocarbon-Each molecule has at least one double or triple bond (alkenes and alkynes) Isomers-Are 2 molecules with the same chemical formula but have different properties. C4H10O names: 1-butanol and 2-methyl-1-propanol 1 Naming and Uses of Organic Compounds First you need to determine the functional group. Note: You can name organic compounds by their IUPAC name or Common name. 1. Alkanes: Family of saturated hydrocarbons. Cn H2n + 2 Molecules that contain only H and C that are connected by single bonds and with –ane ending. Ex. Methane: CH4 (1 Carbon and 4 Hydrogens) Tetrahedral structure, with bond angles of 109.5 degrees. cyclo-A prefix added to an Alkane means a ring is included in the chemical formula Others:2-14 (IUPAC Names) CH3CH3 Ethane CH3CH2CH3 Propane CH3(CH2)2CH3 Butane CH3(CH2)3CH3 Pentane CH3(CH2)4CH3 Hexane CH3(CH2)5CH3 Heptane ____________ Group: If a H atom is removed from an alkane, a partial structure that remains is an________. Alkyl groups are named by replacing the –_____ending of the parent alkane with an –_________ending. Ex. Methyl: -CH3 Others: -CH2CH3 Ethyl -CH2CH2CH3 Propyl -CH2(CH2)2CH3 Butyl -CH2(CH2)3CH3 Pentyl -CH2(CH2)4CH3 Hexyl The alkyl groups are often used to determine the common names of compounds. ____ represents an alkyl group 2. Alkenes: Family of unsaturated hydrocarbons with Carbon=Carbon double bonds. Cn H2n Since fewer H’s than in alkanes they are unsaturated with an –________ending. Ex. Ethylene (IUPAC name is ethene): H2C=CH2 Ex. Propylene (IUPAC name is propene): CH3CH=CH2 Trigonal planar structure with bond angles of about 120 degrees. Benzene is a aromatic hydrocarbon organic ring with C6H6 3. Alkynes: Family of unsaturated hydrocarbons with CarbonCarbon triple bonds. Cn Hn alkynes use the suffix: -__________ Line drawing representation would be RCCH Ex. Propyne: CH3CCH Has sp hybrid, linear structure with bond angles of 180 degrees. Ex. Acetylene (IUPAC name is ethyne): H-CC-H Used to prepare acetic acid Other Functional Groups (9 total) 1. Esters : common in plants and responsible for some distinctive flavors and scents (like____________) O ║ C˗O Flavor of pineapple is caused by ethyl butyrate 2. Amines: Family of organic derivatives of ____________, ____________. Amines are named by adding the ending –________to the name of the hydrocarbon from which it is derived. Organic bases contain nitrogen with unshared pair of electrons. Line drawing representation would be R-NH2 2 Ex. Methylamine H3C-NH2 and Ethanamine CH3CH2-NH2 Found in _____________ –coffee drinks and soft drinks 3. Amides: O ║ C-N The amides are an important functional group and are present in a number of types of drugs molecules (local anesthetics, antiarrhythmics, etc). It is also the key linking in proteins and peptide drug products. Suffix ending: -amide Example: O ║ H- C-NH2 formamide or methanamide 4. Alcohols: -OH 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Example: Ethanol (liquor) is used as a _____________ for many flavorings: vanilla extract Halide: -Group 17 elements Example: Freon-11 which is a _____________ Ketones: Example-Acetone (propanone) used for ______________________________________ O ║ C Aldehyde: Example- _______________ extract (benzaldehyde) O ║ C˗H Ether: -O- are used in ________________ Carboxylic Acid: Family of the most useful building blocks for synthesizing other molecules. O ║ Line drawing representation would be C R OH They are named by adding the ending –________ acid to the name of the hydrocarbon from which the acid is derived. Ex. HCOOH is methanoic acid, which is also known as formic acid. Found in ___________ Derivatives of carboxylic acid are: O ║ C R X Acid halide (X=F, Cl, Br, or I) With ending –________________ Ex. Acetyl chloride (from acetic acid) where the R is CH3 and the X is Cl. Ex. Acetic anhydride where both the R’s are replaced with CH 3. O O ║ ║ C C R O R Acid anhydride: With ending anhydride Crude Oil Crude Oil is formed from the _________ remains of plants and animals that have been _________ and _________ under _______________ for ___________ of years. Crude Oil is a complex ______________ of mainly ___________ that can be separated into ___________ by the technique of fractional distillation. (It is not useful in its natural form so it must be refined before commercially useful products are produced by the petrochemical) The hydrocarbon liquids must be completely ________________________ in each other. When the temperature is high enough, the ____________ energy of a particular hydrocarbon molecule will be able to escape the __________________________ forces in the liquid and become a gas. o The _______________________ forces of the ______________ atoms are much weaker than the strong Carbon atoms in the hydrocarbon so it will ______________ without decomposing. 3 A ________________ is a mixture of hydrocarbon liquids with a narrow boiling point range depending on the molecules involved. Within each fraction obtained from crude oil the hydrocarbon molecules will have similar number of _____________ atoms and similar _______________ properties. _____________________ is a process in which large hydrocarbon molecules are broken down into smaller and more useful ones. Cracking is used on natural gas (mainly ______________) and liquid fuels. Three common types are _____________ (uses water), ________________ (uses fine powdered ______________), and _________________ (uses Hydrogen, platinum on silica or alumina) Examples of Crude Oil ( )-% of Crude Oil Number of Carbon atoms in the Hydrocarbon molecule fraction 1 to 4 Boiling point Uses Less than ___________ __________ or Propane gas fuel, feed stock for other organic chemicals __________ 6-10 25-75 oC 75 to 190 oC Paraffin, Kerosene (10-15%) 10-16 190-250 oC Diesel oil, Gas oil (15-20%) ___________ 250-________ oC Residue-fuel oil, lubricating oils, waxes, and bitumen (40-50%) 20-70 Bitumen-over ______ ______________ Car gas Valuable raw material ___________ to make more petrol and alkenes Less flammable than petrol ___________ domestic heating oil ____________ aircraft jet fuel Truck fuel, Central heating fuel ___________ more petrol and alkenes products Liquid fuel for ships and power stations, lubricants, mineral oils, candle wax, clear wax and polishes Fuel Gas, liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), Refinery Gases (1-2 %) Gasoline-Petrol Naphtha (20-40%) ____________-Water repellent solid at room temperatures that readily melts. Used for road repairs, road resurfacing, and roofing products 4