Terminology and Concepts Liquid and Solid States (Part 3). - E
advertisement

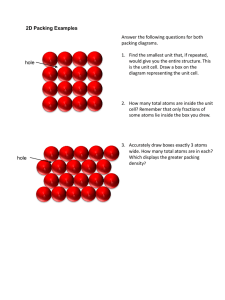
STPM Chemistry Form 6 Notes – Terminology and Concepts: Liquid and Solid States (Part 3) Four types of lattice points: 1. Lattice point at the corner of the unit cell (1/8) 2. Lattice point on the edge of the unit cell (1/4) 3. Lattice point on the face of the unit cell (1/2) 4. Lattice point in the centre of the unit cell (1) Coordination number – the number of atoms, molecules or ions (called the nearest neighbours) that surrounds a given atom, molecule or ion in a crystal lattice. A) Simple cubic cell Example: Caesium chloride & Polonium Sphere touches six other spheres. Four sphere in its own layer, one sphere above the layer and one sphere below the layer. Coordination number = 6 Unit cell contains in total one atom (8 corners x 1/8 = 1) B) Body-centre cubic lattice Example: Sodium, Barium, Potassium, Iron, Manganese, Chromium & Vanadium Sphere touches eight other spheres. Second layer are placed in the hollows between the spheres in the first layer. Each sphere atom is in contact with four atoms in the layer above and four atoms in the layer below. Coordination number = 8 Unit cell contains in total of two lattice points per unit cell (8 corners x 1/8 + 1 = 2) C) Close-packed structures Example: Sodium chloride Unit cell contains in total of four atoms per unit cell (8 corners x 1/8) + (6 faces x 1/2) i) Cubic close packing (ABCABCABC) / Face-centered cubic / Simple cubic close packing Thomas Harriot (1585) first pondered the mathematics of the cannonball arrangement or cannonball stack, which has a face-centered cubic lattice. Sphere touches twelve other spheres. First layer of spheres is packed as closely and each sphere atom is in contact with six other atoms. Second layer of spheres is placed on top of the first layer, so that each sphere in the second layer rests on the hollows between the spheres in the first layer. Each sphere atom is in contact with six atoms in its own layer, three spheres (atoms) in the layer above and three spheres (atoms) in the layer below. Coordination number = 12 ii) Hexagonal close packing (ABABABABA) Sphere touches twelve other spheres. First layer and the second layer of spheres are packed in the same way as cubic close packing. (Difference = the third layer of spheres is placed on top of the first layer) Coordination number = 12