Name Date Practice Test- Cell Division and Communication AP
advertisement
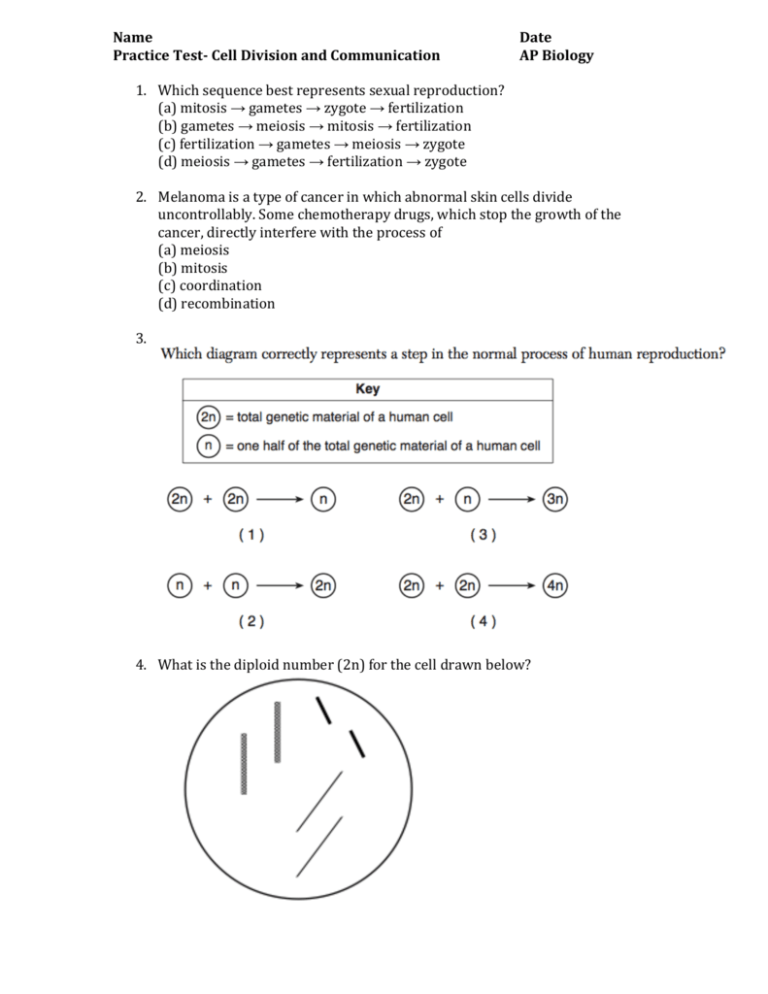
Name Practice Test- Cell Division and Communication Date AP Biology 1. Which sequence best represents sexual reproduction? (a) mitosis → gametes → zygote → fertilization (b) gametes → meiosis → mitosis → fertilization (c) fertilization → gametes → meiosis → zygote (d) meiosis → gametes → fertilization → zygote 2. Melanoma is a type of cancer in which abnormal skin cells divide uncontrollably. Some chemotherapy drugs, which stop the growth of the cancer, directly interfere with the process of (a) meiosis (b) mitosis (c) coordination (d) recombination 3. 4. What is the diploid number (2n) for the cell drawn below? 5. Draw a possible gamete that would be produced from this cell. 6. 7. 8. 9. Which of the following is true of steroid receptors? A) The receptor molecules are themselves lipids or glycolipids. B) The receptor may be inside the nuclear membrane. C) The unbound steroid receptors are quickly recycled by lysosomes. D) The concentration of steroid receptors must be relatively high in most cells. E) The receptor molecules are free to move in and out of most organelles. 10. When a neuron responds to a particular neurotransmitter by opening gated ion channels, the neurotransmitter is serving as which part of the signal pathway? A) receptor B) relay molecule C) transducer D) signal molecule E) endocrine molecule 11. Testosterone functions inside a cell by A) acting as a signal receptor that activates tyrosine kinases. B) binding with a receptor protein that enters the nucleus and activates specific genes. C) acting as a steroid signal receptor that activates ion channel proteins. D) becoming a second messenger that inhibits nitric oxide. E) coordinating a phosphorylation cascade that increases spermatogenesis. 12. Which of the following is the greatest advantage of having multiple steps in a transduction pathway? A) Many of the steps can be used in multiple pathways. B) Having multiple steps in a pathway requires the least amount of ATP. C) Having multiple steps provides for greater possible amplification of a signal. D) Each individual step can remove excess phosphate groups from the cytoplasm. E) Each step can be activated by several G proteins simultaneously. 13. Humans produce skin cells by mitosis and gametes by meiosis. The nuclei of skin cells produced by mitosis will have A) half as much DNA as the nuclei of gametes produced by meiosis. B) the same amount of DNA as the nuclei of gametes produced by meiosis. C) twice as much DNA as the nuclei of gametes produced by meiosis. D) four times as much DNA as the nuclei of gametes produced by meiosis. 14. Compared to most prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells typically have A) more DNA molecules and larger genomes. B) the same number of DNA molecules but larger genomes. C) the same number of DNA molecules and similarly sized genomes. D) fewer DNA molecules but larger genomes. E) fewer DNA molecules and smaller genomes. 15. A group of cells is assayed for DNA content immediately following mitosis and is found to have an average of 8 picograms of DNA per nucleus. How many picograms would be found at the end of S and the end of G2? A) 8; 8 B) 8; 16 C) 16; 8 D) 16; 16 E) 12; 16 16. Which is the first checkpoint in the cell cycle where a cell will be caused to exit the cycle if this point is not passed? A) G0 B) G1 C) G2 D) S E) previous M 17. Which of the following is a protein maintained at constant levels throughout the cell cycle that requires cyclin to become catalytically active? A) PDGF B) MPF C) protein kinase D) cyclin E) Cdk 18. Which of the following is true concerning cancer cells? A) They do not exhibit density-dependent inhibition when growing in culture. B) When they stop dividing, they do so at random points in the cell cycle. C) They are not subject to cell cycle controls. D) When they stop dividing, they do so at random points in the cell cycle, and they are not subject to cell cycle controls. E) When they stop dividing, they do so at random points in the cell cycle; they are not subject to cell cycle controls; and they do not exhibit density-dependent inhibition when growing in culture. Use the following information to answer the questions below. The unlettered circle at the top of Figure 9.1 shows a diploid nucleus with four chromosomes that have not yet replicated. There are two pairs of homologous chromosomes, one long and the other short. One haploid set is black, and the other is gray. The circles labeled A–E show various combinations of these chromosomes. Figure 9.1 19. What is the correct chromosomal condition for one daughter nucleus at telophase of mitosis? A) A B) B C) C D) D E) E 20. What is the correct chromosomal condition for one daughter nucleus at prophase of mitosis? A) A B) B C) C D) D E) E 21. A particular cell has half as much DNA as some other cells in a mitotically active tissue. The cell in question is most likely in A) G1. B) G2. C) prophase. D) metaphase. E) anaphase. 22. If an organism is diploid and a certain gene found in the organism has 18 known alleles (variants), then any given organism of that species can/must have which of the following? A) at most, 2 alleles for that gene B) up to 18 chromosomes with that gene C) up to 18 genes for that trait D) a haploid number of 9 chromosomes E) up to, but not more than, 18 different traits 23. Which of the following is a true statement about sexual vs. asexual reproduction? A) Asexual reproduction, but not sexual reproduction, is characteristic of plants and fungi. B) In sexual reproduction, individuals transmit 50% of their genes to each of their offspring. C) In asexual reproduction, offspring are produced by fertilization without meiosis. D) Sexual reproduction requires that parents be diploid. E) Asexual reproduction produces only haploid offspring. 24. Which of the following is true of a species that has a chromosome number of 2n = 16? A) The species is diploid with 32 chromosomes per cell. B) The species has 16 sets of chromosomes per cell. C) Each cell has eight homologous pairs. D) During the S phase of the cell cycle there will be 32 separate chromosomes. E) A gamete from this species has four chromosomes. 25. Which of these is a way that the sexual life cycle increases genetic variation in a species? A) by allowing crossing over B) by allowing an increase in cell number C) by increasing gene stability D) by conserving chromosomal gene order E) by decreasing mutation frequency 26. The somatic cells of a privet shrub each contain 46 chromosomes. To be as different as they are from human cells, which have the same number of chromosomes, which of the following must be true? A) Privet cells cannot reproduce sexually. B) Privet sex cells have chromosomes that can synapse with human chromosomes in the laboratory. C) Genes of privet chromosomes are significantly different than those in humans. D) Privet shrubs must be metabolically more like animals than like other shrubs. E) Genes on a particular privet chromosome, such as the X, must be on a different human chromosome, such as number 18. 27. Which of the following might result in a human zygote with 45 chromosomes? A) an error in either egg or sperm meiotic anaphase B) failure of the egg nucleus to be fertilized by the sperm C) fertilization of a 23 chromosome human egg by a 22 chromosome sperm of a closely related species D) an error in the alignment of chromosomes on the metaphase plate E) lack of chiasmata in prophase I Refer to the drawings in Figure 10.2 of a single pair of homologous chromosomes as they might appear during various stages of either mitosis or meiosis, and answer the following questions. Figure 10.2 28. Which diagram represents metaphase II of meiosis? A) I B) II C) IV D) V E) VI 29. Which diagram(s) represent(s) anaphase II of meiosis? A) II only B) III only C) IV only D) V only E) either II or V 30. Which diagram(s) represent(s) prophase I of meiosis? A) II only B) I only C) IV only D) V only E) either II or V Answer Key: 1. D 2. B 3. (2) 4. 2n=6 5. Gamete should include one set of chromosomes: one thin solid, one thick solid, one shaded chromosome. 6. Answers will vary 7. Answers will vary 8. Meiosis I 9. B 20. B 10. D 21. A 11. B 22. A 12. C 23. B 13. C 24. C 14. A 25. A 15. D 26. C 16. B 27. A 17. E 28. E 18. E 29. D 19. E 30. C