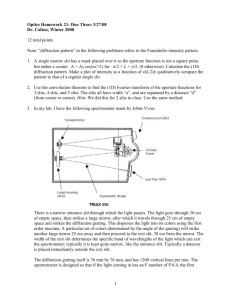
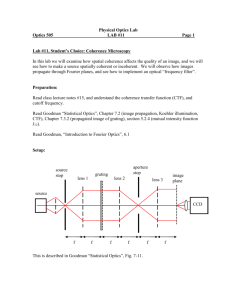
Honors Physics * Review problems for Wave Optics, Ray Optics, and
advertisement

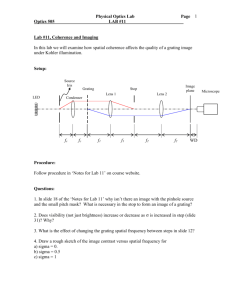
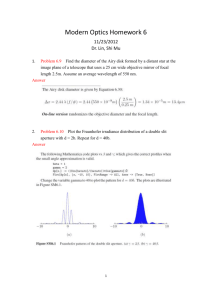
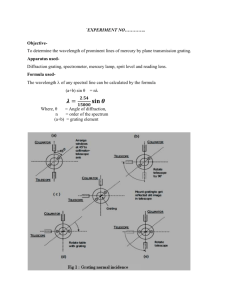
Honors Physics – Optics Review 1 - Review problems for Wave Optics & beginning of Ray Optics (Chapters 17-18.4) Remember to review the homework (you can redo homework problems as practice problems and obtain new number variables) and also work non-assigned problems from the textbook. 1. A thin film of MgF2 n=1.38 coats a piece of glass. Destructive interference is observed for the reflection of light with wavelengths of 500 nm and 625 nm. What is the thinnest film for which this can occur? 2. A helium-neon laser 633 nm illuminates a diffraction grating. The distance between the two m=1 bright fringes is 32.0 cm on a screen 2.00 m behind the grating. What is the spacing between slits of the grating? 3. A layer of benzene (n=1.5) floats on water. If the angle of incidence of the light entering the benzene from air is 60o, what is the angle the light makes with the vertical in the benzene and in the water? 4. A helium-neon laser 633 nm illuminates a single slit and is observed on a screen 1.50 m behind the slit. The distance between the first and second minima in the diffraction pattern is 4.75 mm. What is the width of the slit? 5. Alpha Centauri is one of the nearest stars to earth. Suppose radio waves of 250 nm from Alpha Centauri reach a radio telescope on earth by two separate paths. One path is a direct line to the telescope (which is located on the edge of a cliff by the Pacific Ocean). The second path is by reflection off the water in the Pacific Ocean. The first minimum of destructive interference occurs when the star is 25o above the horizon. Find the height of the cliff. (Assume that there is no phase change on reflection off the water). 6. If the distance between two slits is 0.050 mm (human hair ranges from very fine (0.017 mm) to very coarse (0.181 mm)) and the distance to a screen is 2.5 m, find the spacing between the first and second order bright fringes for yellow light of 600 nm. 7. Two radio antennas are separated by 300 m and arranged along I70 (the west/east line). They simultaneously transmit identical signals of the same wavelength. A passing car traveling west picks up the radio signals. Suppose the car is located on a frontage road at the coordinate 1000 m north of the mid-point between the antennas and 400 m west of the mid-point between the antennas. A) If the car is at the position of the second maximum, what is the wavelength of the signals? B) How much farther in the same direction must the car travel to encounter the next minimum reception? fold along the dashed line Answers: 1. 90.6 6. 3E-2 2. 7.9E-6 7. a) 55.7 3. 35, 41 b) 124 4. 2E-4 5. 148