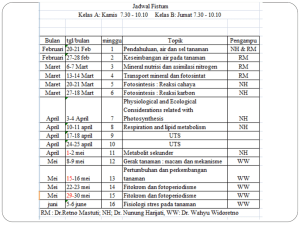
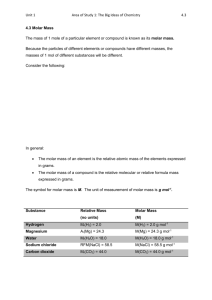
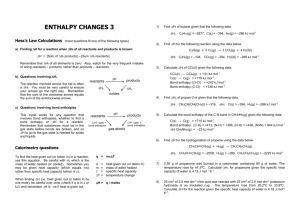
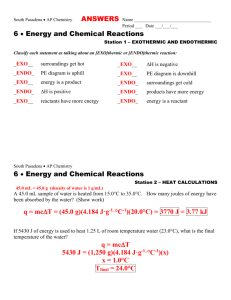
CEM214 SemTest 1 March 2011
advertisement

QWAQWA CAMPUS / QWAQWA KAMPUS CEM 214 UNIVERSITEIT VAN DIE VRYSTAAT UNIVERSITY OF THE FREE STATE SEMESTER TEST 1 Sat, 19 March 2011 ASSESSOR / ASSESSOR: Mrs MA Mokoena MODERATOR:/ MODERATOR: Prof AS Luyt TYD /TIME : 1UUR/1 Hour PUNTE / MARKS: 50 ANSWER ALL QUESTIONS AND SHOW ALL CALCULATIONS WITH AN INK PEN -- NO PENCILS OR "TIPPEX" ALLOWED / PAPER CONSIST OF 2 PAGE(S) AND 4 QUESTIONS. Question 1 1. 2 mol of nitrogen gas is heated at constant pressure from 298 K to 373 K. Calculate S, given the temperature variation of Cp,m of N2 as : Cp,m /J K-1 mol-1= 27.296 + 5.23 x 10-3 (T/K) -0.042 x 10-7 (T/K) 2 2. Estimate the molar combustion enthalpy of ethanol CH3OH (l), [10] by using the appropriate average bond energy data. Assume that the standard enthalpy of vaporization of methanol 35.3 kJmol-1 and that of liquid water 44 kJmol-1 the work done, H, U and the amount of heat transferred kJ mol-1. Use T = 298 K and show all steps. [7] 3. A system of one mol of Ar is expanded reversibly and isothermally at 0 oC from 22.4 L to 44.8 L. Calculate the work done, H, U and the amount of heat transferred. [7] 4. Two moles of ideal gas is reversibly cooled down at constant volume from 200K to 100K; then it expands isothermally from 10 L to 25 L. Calculate the change in pressure P during the process. [6] Bindingsenergieë/ kJ mol-1 / Bond energies /kJ mol-1 C-C 343 C=O C=C CC C-H C-O 615 812 416 351 724 C=O (in CO2) O-H O-O O=O (in O2) 799 464 144 498 MEMORUNDUM S vap 373 C p n dT 298 T T 373 27.296 5.23 x 103 (T / K ) 0.042 x 107 (T / K )2 dT S n T 298 T 1. 2 27.296 ln 2 5.239 x10 3 (T T ) 1 / 2(0.042)(T 2 T 2 ) 2 1 2 1 T1 373 2 27.296 ln 5.239 x10 3 (373 298) 1 / 2(0.042)(3732 298 2 ) 2981 _______________ 2. CH3OH(g) + 3/2O2(g) CO2(g) + 2H2O(g) ∆Ug [3xBE(C-H) + BE(C-O) + BE(O-H) + 3/2xBE(O=O)] – [2xBE(C=O) + 4xBE(H-O)] ∆Ug [3x416 + 351 + 464 + 3/2x498] kJ mol-1 - [2x799 + 4x464] kJ mol-1 ∆Ug [________+ ________ ] kJ mol-1 = ______ kJ mol-1 ∆Hg = ∆Ug + ∆(PV) waar/where ∆(PV) klein is/is small ∆Hg ∆Ug = ________ kJ mol-1 CH3CH2OH(g) + 3O2(g) 2CO2(g) + 3H2O(g) CH3OH(l) CH3CH2OH(g) _______ kJ mol-1 35.3 kJ mol-1 2H2O(g) 2H2O(l) - 88 kJ mol-1 CH3CH2OH(l) + 3O2(g) 2CO2(g) + 3H2O(l) _____ kJ mol-1 3. A system of one mol of Ar is expanded reversibly and isothermally at 0 oC from 22.4 L to 44.8 L. Calculate the work done, H, U and the amount of heat transferred. Work done = wrev = 1 mol Ar : Thus [7] Vm, 2 P dV Vm,1 1 PVm = RT; Wrev = - Vm, 2 Vm,1 = -RT ln RT dV = -RT ln V│Vm.1Vm,2 V 𝑉𝑚,2 ⁄𝑉 = RT ln 𝑚,1 𝑉𝑚,1 ⁄𝑉 = 8.3145 x 273.15 ln 22.4 ⁄44.8 𝑚,2 = _________J ∆H = Cp,m (T2-T1) = 0 ∆U = CV,m (T2-T1) = 0 So qrev = ∆U – w rev = 0 – RTln 𝑉𝑚,2 ⁄𝑉 = __________J 𝑚,1 1. Two moles of ideal gas is reversibly cooled down at constant volume from 200K to 100K; then it expands isothermally from 10 L to 25 L. Calculate the change in pressure P during the process. [6] 4. P P P dP dV dn dT V n ,T n V ,T T n ,V nRT P V dP1 dT T T n ,V dT n ,V 8.314 (100 200) Pa _________ Pa P1 nR dT nR (T2 T1 ) 2[ V V 0.02 T2 T1 nRT P dP2 dV dV V V n ,T V n ,T V2 P2 nRT V 2 dV nRT ( V1 1 1 1 1 ) [8.314 x100 K ( )]Pa 82309 Pa V2 V1 0.01 0.02 Ptot P1 P2 40739 Pa