Introduction to Earth Science Unit Test Study Guide Format
advertisement

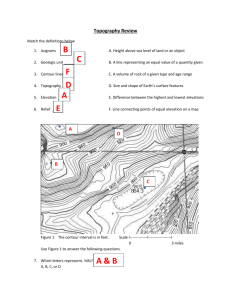
Name KEY Date Period Introduction to Earth Science Unit Test Study Guide Format: 34 Total Question Topics: Observation vs. Inference 18 Multiple Choice 15 Free Response/ Diagram Interpretation 1 Graphing *MC and Free Response are mixed throughout the test Earth Spheres Fields of Sciences Pos. /Neg. Feedback Longitude/ Latitude Geography (general descriptions and locations; from project) Topography Graphing 1. Describe what each field of science study. a. Geology: the study of the physical earth (rocks, minerals, etc.), the process of Earth, and Earth’s history. b. Meteorology: the study of Earth’s atmosphere, weather and climate c. Oceanography: the study of Earth’s ocean d. Astronomy: the study of the Universe (planets, stars, galaxies, etc.) 2. Define each sphere. a. Biosphere: all of Earth’s living organisms (plants, animals, bacteria, etc.) b. Geosphere: the physical solid earth c. Hydrosphere: all of Earth’s water (water cycle, oceans, lakes, rivers, etc) d. Atmosphere: all the gasses surrounding the solid Earth e. Cryosphere: Earth’s Ice (Polar Ice Caps, icebergs, glaciers) 3. Give an examples of the spheres connect to each other. a. Biosphere- Geosphere: animals burrow into the soil to hibernate to for shelter b. Hydrosphere- Atmosphere: Ocean evaporate into water vapor into the atmosphere c. Geosphere- Atmosphere: Wind can erode soil away d. Hydrosphere- Geosphere: Rivers carve out canyons 4. Explain Positive Feedback and give one example. Positive feedback is when a system is always moving away from the equilibrium. Example: Cotton Candy machine, formation of a hurricane 5. Explain Negative Feedback and give one example. Negative feedback is when a system always goes back to the equilibrium (back to Normal). Example: Photosynthesis of plants and respiration of animals. 6. What type of feedback loop is the picture depicting? Explain why. This is a positive feedback loop because as when there is a large population, more babies will be born which then adds more to the population. The population size never goes back to the beginning (equilibrium). 7. What type of feedback loop is the picture depicting? Explain why. This is a negative feedback loop because as the temperature of the body increases the body releases sweat which will bring the body’s temperature down to equilibrium. (Back to Normal). 8. Label the following graphs Positive Feedback or Negative Feedback. 9. Positive Feedback Negative Feedback A. Which direction do latitude lines run? Sideways B. Which direction do longitude lines run? Up and down C. Imaginary line that divides the Northern Hemisphere from the Southern Hemisphere: Equator D. Imaginary line that is 0⁰ longitude: Prime Meridian 10. Explain why Australisia is the correct term for the continent. Australisia is the correct term to describe the continents because then New Zealand and New Guinea and the other surrounding Pacific Islands around Australia are included. 11. Use the map below to answer the following questions. a. What is the contour interval? 50 elevation between each contour line) (The amount of b. What is the elevation of point D? 200 12. Draw the elevation profile below of the diagram above (from question 11). 13. How would you determine the direction of a river’s flow based on a topographical map? The river always flows from higher elevation to lower elevation. 14. How do you determine the steepness of elevation on a topographical map? Steepness is based on how close or far apart the contour lines are to each other. The closer the lines are to each other the steeper the slope is. 15. Name the one major river running through each continent. a. Europe: Danube b. North America: Mississippi or Colorado C. Asia: Yangtze E. South America: Amazon 16. Identify the continent/ region each Sea is located in. a. Gulf of Mexico: North America b. Arabian Sea: between Asia (India) and Africa C. Coral Sea: Australia D. Japan Sea: Asia (between China and Japan) 17. Write 2 observations about the classroom. The desks are grouped together. 18. Make 2 inferences based on your observations. The class will work on an assignment in small groups.