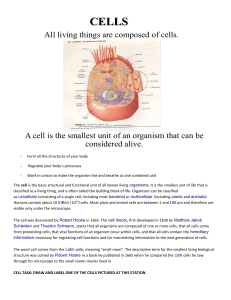
Guided Notes-Nucleic Acids

AK-GUIDED NOTES-NUCLEIC ACIDS-STRUCTURE & FUNCTION
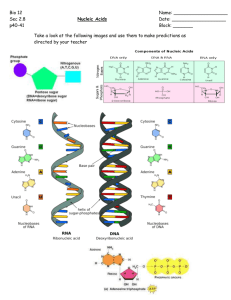
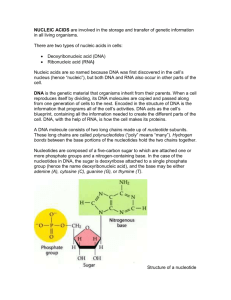
What are nucleic acids?
What are the two major types of nucleic acids?
What are the three components of a nucleotide, the nucleic acid monomer?
How are the three components of a nucleotide connected?
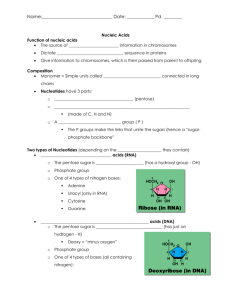
What are the two major classes of nucleotides?
How do the two classes of nucleotides differ?
What is the difference between ribose and deoxyribose sugar?
How many different ribonucleotides do cells use?
How is each of these four ribonucleotides different?
What are the two groups of nitrogenous bases?
How many different deoxyribonucleotides do cells use?
How is each of these four deoxyribonucleotides different?
Do ribonucleotides have any nitrogenous bases that are different than deoxyribonucleotides nitrogenous bases? If so what?
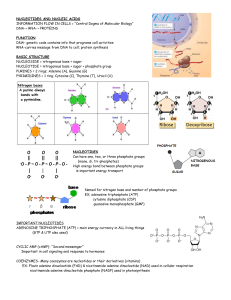
What forms when nucleotides are linked together by dehydration synthesis?
What links together in the process of dehydration synthesis between two nucleotides?
What is the resulting nucleic acid when the nucleotides involved contain the sugar ribose?
What is the name of the covalent bond formed between nucleotides by the process of dehydration synthesis & catalyzed by enzymes?
What is the resulting nucleic acid when the nucleotides involved contain the sugar deoxyribose?
What does the chain of phosphodiester bonds create?
What extends from sugar phosphate backbone?
Does the sugar-phosphate backbone of a nucleic acid have a direction? Explain
How do scientists always write the sequence of bases found in an RNA or
DNA strand? Why?
What forms the primary structure of nucleic acids? What is it analogous to?
How many chains of nucleotides are found in RNA? DNA?
What are the base pairing rules?
What is complementary?
What is antiparallel?
What is the structure of DNA?
What are the two basic functions of
DNA?
What is the information stored and transmitted in DNA?
What is the function of RNA?