Ch. 22, 23, 24 Practice Quiz with answers
advertisement
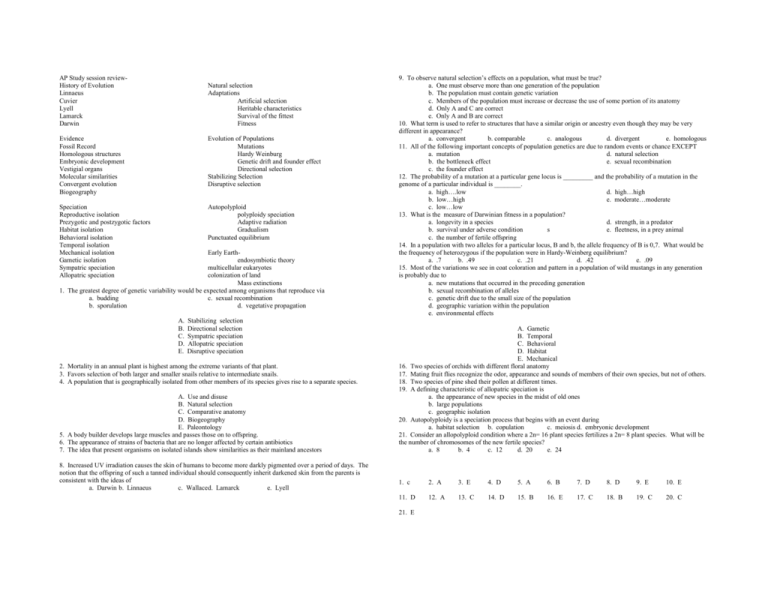
AP Study session reviewHistory of Evolution Linnaeus Cuvier Lyell Lamarck Darwin Natural selection Adaptations Artificial selection Heritable characteristics Survival of the fittest Fitness Evidence Fossil Record Homologous structures Embryonic development Vestigial organs Molecular similarities Convergent evolution Biogeography Evolution of Populations Mutations Hardy Weinburg Genetic drift and founder effect Directional selection Stabilizing Selection Disruptive selection Speciation Reproductive isolation Prezygotic and postzygotic factors Habitat isolation Behavioral isolation Temporal isolation Mechanical isolation Gametic isolation Sympatric speciation Allopatric speciation Autopolyploid polyploidy speciation Adaptive radiation Gradualism Punctuated equilibrium Early Earthendosymbiotic theory multicellular eukaryotes colonization of land Mass extinctions 1. The greatest degree of genetic variability would be expected among organisms that reproduce via a. budding c. sexual recombination b. sporulation d. vegetative propagation A. B. C. D. E. Stabilizing selection Directional selection Sympatric speciation Allopatric speciation Disruptive speciation 2. Mortality in an annual plant is highest among the extreme variants of that plant. 3. Favors selection of both larger and smaller snails relative to intermediate snails. 4. A population that is geographically isolated from other members of its species gives rise to a separate species. A. Use and disuse B. Natural selection C. Comparative anatomy D. Biogeography E. Paleontology 5. A body builder develops large muscles and passes those on to offspring. 6. The appearance of strains of bacteria that are no longer affected by certain antibiotics 7. The idea that present organisms on isolated islands show similarities as their mainland ancestors 8. Increased UV irradiation causes the skin of humans to become more darkly pigmented over a period of days. The notion that the offspring of such a tanned individual should consequently inherit darkened skin from the parents is consistent with the ideas of a. Darwin b. Linnaeus c. Wallaced. Lamarck e. Lyell 9. To observe natural selection’s effects on a population, what must be true? a. One must observe more than one generation of the population b. The population must contain genetic variation c. Members of the population must increase or decrease the use of some portion of its anatomy d. Only A and C are correct e. Only A and B are correct 10. What term is used to refer to structures that have a similar origin or ancestry even though they may be very different in appearance? a. convergent b. comparable c. analogous d. divergent e. homologous 11. All of the following important concepts of population genetics are due to random events or chance EXCEPT a. mutation d. natural selection b. the bottleneck effect e. sexual recombination c. the founder effect 12. The probability of a mutation at a particular gene locus is _________ and the probability of a mutation in the genome of a particular individual is ________. a. high….low d. high…high b. low…high e. moderate…moderate c. low…low 13. What is the measure of Darwinian fitness in a population? a. longevity in a species d. strength, in a predator b. survival under adverse condition s e. fleetness, in a prey animal c. the number of fertile offspring 14. In a population with two alleles for a particular locus, B and b, the allele frequency of B is 0,7. What would be the frequency of heterozygous if the population were in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium? a. .7 b. .49 c. .21 d. .42 e. .09 15. Most of the variations we see in coat coloration and pattern in a population of wild mustangs in any generation is probably due to a. new mutations that occurred in the preceding generation b. sexual recombination of alleles c. genetic drift due to the small size of the population d. geographic variation within the population e. environmental effects A. Gametic B. Temporal C. Behavioral D. Habitat E. Mechanical 16. Two species of orchids with different floral anatomy 17. Mating fruit flies recognize the odor, appearance and sounds of members of their own species, but not of others. 18. Two species of pine shed their pollen at different times. 19. A defining characteristic of allopatric speciation is a. the appearance of new species in the midst of old ones b. large populations c. geographic isolation 20. Autopolyploidy is a speciation process that begins with an event during a. habitat selection b. copulation c. meiosis d. embryonic development 21. Consider an allopolyploid condition where a 2n= 16 plant species fertilizes a 2n= 8 plant species. What will be the number of chromosomes of the new fertile species? a. 8 b. 4 c. 12 d. 20 e. 24 1. c 2. A 3. E 4. D 5. A 6. B 7. D 8. D 9. E 10. E 11. D 12. A 13. C 14. D 15. B 16. E 17. C 18. B 19. C 20. C 21. E 21.