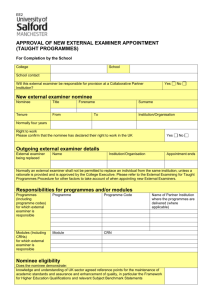
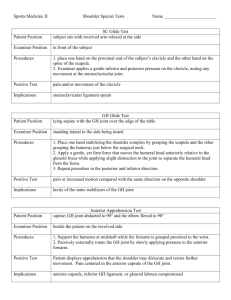
Hand and Wrist Special Tests
advertisement
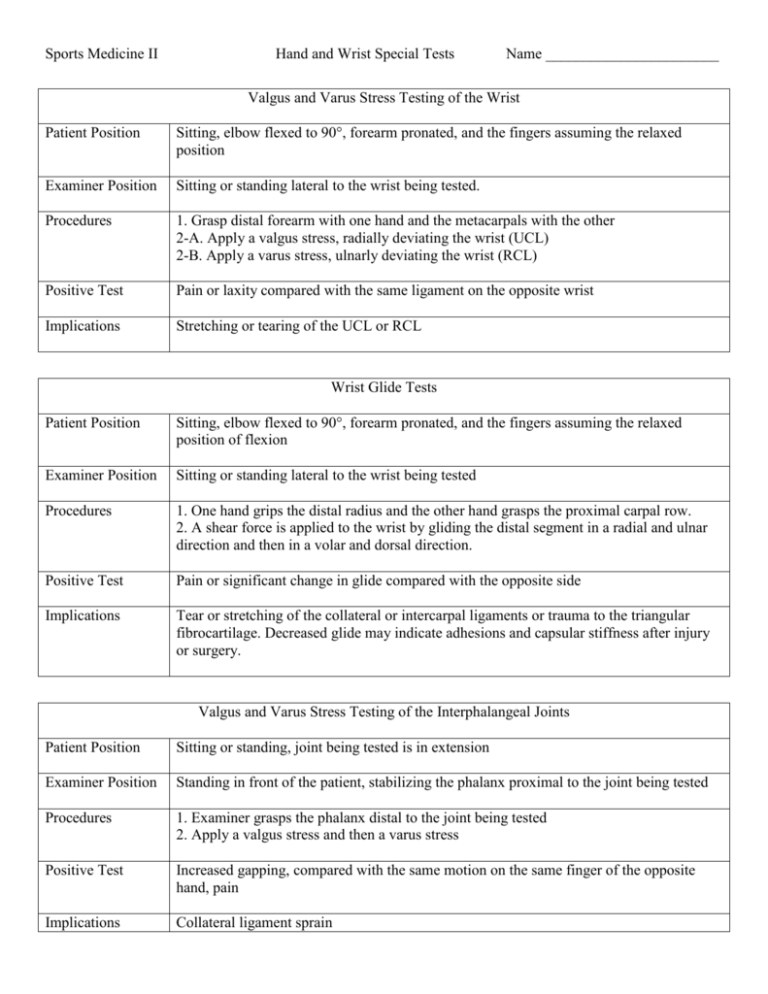
Sports Medicine II Hand and Wrist Special Tests Name _______________________ Valgus and Varus Stress Testing of the Wrist Patient Position Sitting, elbow flexed to 90°, forearm pronated, and the fingers assuming the relaxed position Examiner Position Sitting or standing lateral to the wrist being tested. Procedures 1. Grasp distal forearm with one hand and the metacarpals with the other 2-A. Apply a valgus stress, radially deviating the wrist (UCL) 2-B. Apply a varus stress, ulnarly deviating the wrist (RCL) Positive Test Pain or laxity compared with the same ligament on the opposite wrist Implications Stretching or tearing of the UCL or RCL Wrist Glide Tests Patient Position Sitting, elbow flexed to 90°, forearm pronated, and the fingers assuming the relaxed position of flexion Examiner Position Sitting or standing lateral to the wrist being tested Procedures 1. One hand grips the distal radius and the other hand grasps the proximal carpal row. 2. A shear force is applied to the wrist by gliding the distal segment in a radial and ulnar direction and then in a volar and dorsal direction. Positive Test Pain or significant change in glide compared with the opposite side Implications Tear or stretching of the collateral or intercarpal ligaments or trauma to the triangular fibrocartilage. Decreased glide may indicate adhesions and capsular stiffness after injury or surgery. Valgus and Varus Stress Testing of the Interphalangeal Joints Patient Position Sitting or standing, joint being tested is in extension Examiner Position Standing in front of the patient, stabilizing the phalanx proximal to the joint being tested Procedures 1. Examiner grasps the phalanx distal to the joint being tested 2. Apply a valgus stress and then a varus stress Positive Test Increased gapping, compared with the same motion on the same finger of the opposite hand, pain Implications Collateral ligament sprain Test for Laxity of the Collateral Ligaments of the Thumb Patient Position Sitting or standing Examiner Position Standing in front of the patient Procedures 1. Examiner stabilizes the first metacarpal with one hand and its proximal phalanx with the other. 2. While stabilizing the first metacarpal with the thumb slightly abducted and extended, the examiner applies a valgus stress to the ulnar collateral ligament. 3. Test is repeated with the joint in varying degrees of flexion to evaluate the dorsal capsule of the joint. Positive Test The ulnar side of the first metacarpophalangeal joint gaps farther than the uninjured side or the patient describes pain (or both) Implications Stretching or tearing of the ulnar collateral ligament Phalen’s Test Patient Position Sitting or standing Examiner Position Standing in front of the patient Procedures 1. Patient places dorsal aspect of both hands in full contact so that both wrists are maximally flexed. 2. Apply a steady compressive force through the subject’s forearms so that the wrists are maximally flexed for 1 minute. Positive Test Numbness and tingling in the fingers (due to compression of median nerve) Implications Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Finkelstein’s Test Patient Position Sitting or standing Examiner Position Standing in front of patient Procedures 1. Patient makes a fist around the thumb. 2. Examiner grasps the patient’s forearm and fist with the patient’s thumb in the examiner’s thenar eminence. 3. While stabilizing the patient’s forearm, ulnarly deviate the patient’s wrist. Positive Test Pain over the abductor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis brevis tendons Implications Tenosynovitis (de Quervain’s disease) Tap Test Patient Position Sitting or standing Examiner Position In front of patient Procedures 1. Patient extends affected finger. 2. Examiner applies a firm tap to the end of the finger being tested. Positive Test Pain Implications Fracture Compression Test Patient Position Sitting or standing Examiner Position In front of patient Procedures 1. Examiner holds the distal phalanx and applies compression along the long axis of the bone of the finger being tested. Positive Test Pain Implications Fracture Tinel’s Sign Patient Position Sitting with hand palm up on table Examiner Position Sitting beside patient Procedures 1. Examiner taps on the volar aspect of the subject’s wrist over the area of the carpal tunnel. Positive Test Tingling, paresthesia, or pain by the subject in the area of the thumb, index finger, middle finger, and radial one-half of the ring finger. Implications Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, compression of the median nerve Murphy’s Sign Patient Position Sitting or standing Examiner Position Standing in front of the subject Procedures 1. Subject makes a fist. 2. Examiner notes the position of the third metacarpal. Positive Test Third metacarpal is level with second and fourth metacarpal Implications Dislocated lunate