Masterton Practice for Acids and Bases - OPHS-AP
advertisement

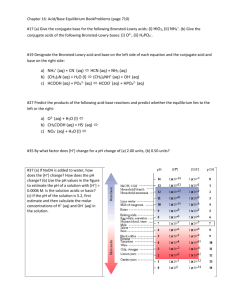
Masterton Practice for Acids and Bases 1. Classify each of the following as a strong or weak base: a. LiOH b. CH3CH2NH2 c. Ca(OH)2 d. F- 2. Show how these weak bases react with water in an equation and Kb expressions. a. BO3b. CH3NH2 c. CN3. Classify each of the following as a strong or weak acid: a. HNO3 b. HNO2 c. HC2H3O2 d. H3PO4 4. For each acid in question #3, show the appropriate dissociation and equilibrium expression. 5. a. b. c. Label the following as the acid, base, conjugate acid or conjugate base. HNO2 + H2O H3O+ + NO2H2O + S-2 HS- + OHCN- + HC2H3O2 C2H3O2- + HCN 6. For each of the equations in #5 list the conjugate acid-base pairs. 7. For hypobromous acid (Ka = 2.1 x 10-9), calculate the [H+] and pH in solutions prepared by adding the following number of moles of HBrO to water make one liter of solution. a. 1.0 mole b. 0.20 mole 8. Calculate the pH of solutions of acetic acid (Ka= 1.8 x 10-5) prepared by adding the following number of moles of acetic acid to 2.50L of water: a. 3.75 mol b. 0.700 mol 9. Lactic acid (Ka = 1.4 x 10-4) is present in sore muscles after vigorous exercise. For a 1.5M solution of lactic acid, calculate: a. [H+] b. [OH-] c. pH d. % dissoc 10. For a 0.10M solution of benzoic acid (Ka=6.6 x 10-5), calculate: a. [H+] b. [OH-] c. pH d. % dissoc 11. The pH of a solution prepared by dissolving0.150 mol of formic acid, HCHO2 to form 0.500L of solution is 2.14. Calculate the Ka of formic acid. 12. The percent dissociation of a certain weak acid in 0.10 M solution is 0.025%. Calculate the Ka of the weak acid. 13. Calculate the [OH-] and pH in a solution prepared by dissolving 0.20 mol NH3 (Kb= 1.8 x 10-5) in one liter of water. 14. Calculate the [OH-], [H+] and the pH of 0.20M solutions of each of the following amines. a. triethyamine, [(C2H5)3N, Kb=4.0 x 10-4] b. hydroxylamine (HONH2, Kb=1.1 x 10-8] 15. Calculate the pH of a 0.20 M C2H5NH2 solution (Kb = 5.6 x 10-4) 16. Calculate the percent dissociation of 0.10 M pyridine, C5H5N, Kb = 1.7 x 10-9. 17. The pH of a 0.01 M HCOOH (formic acid) is approximately a. 1 b. 3 c. 7 d. 11 e. 13 18. The pH of a 0.05 M solution of ammonia is approximately a. 1 b. 3 c. 7 d. 11 e. 13 19. The ionization constant of water at 45°C is 4.0 x 10-14. What is the pH of water at this temperature? 20. Which is the strongest acid? a. Ascorbic acid, Ka=8.0 x 10-5 b. Benzoic acid, Ka=6.5 x 10-5 c. 3-chlorobenzoic acid, Ka=1.5 x 10-4 d. 2-hydroxybenzoic acid, Ka=1.1 x 10-3 e. Chloroacetic acid, Ka=1.4 x 10-3 21. Which of the following acids has the strongest conjugate base? a. Ascorbic acid, Ka=8.0 x 10-5 b. Benzoic acid, Ka=6.5 x 10-5 c. 3-chlorobenzoic acid, Ka=1.5 x 10-4 d. 2-hydroxybenzoic acid, Ka=1.1 x 10-3 e. Chloroacetic acid, Ka=1.4 x 10-3