G485 Module 2 Notes - Mr Matheson`s Physics.com
advertisement
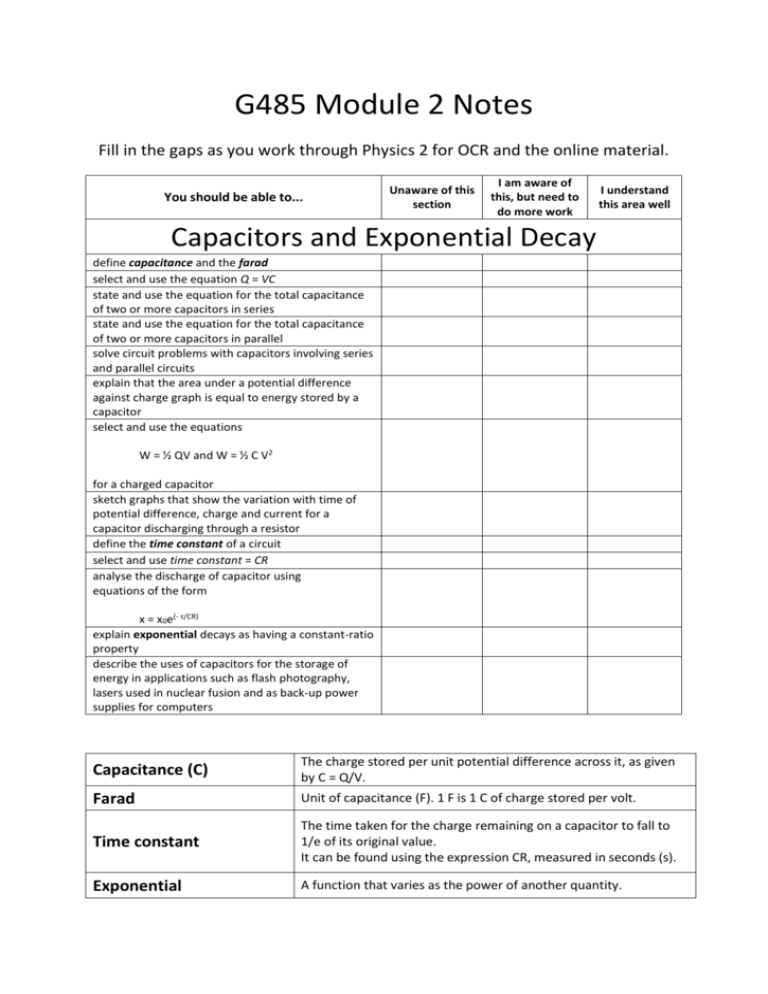
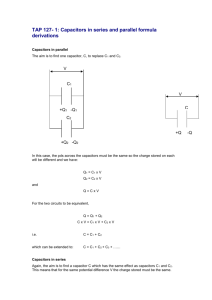
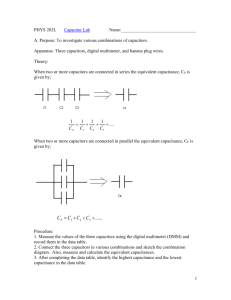
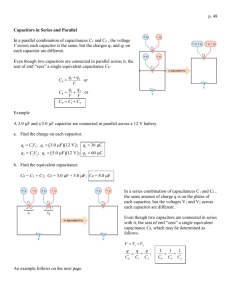
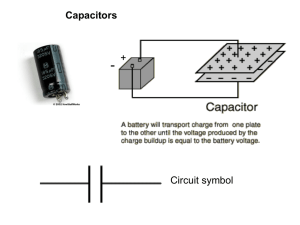
G485 Module 2 Notes Fill in the gaps as you work through Physics 2 for OCR and the online material. You should be able to... Unaware of this section I am aware of this, but need to do more work I understand this area well Capacitors and Exponential Decay define capacitance and the farad select and use the equation Q = VC state and use the equation for the total capacitance of two or more capacitors in series state and use the equation for the total capacitance of two or more capacitors in parallel solve circuit problems with capacitors involving series and parallel circuits explain that the area under a potential difference against charge graph is equal to energy stored by a capacitor select and use the equations W = ½ QV and W = ½ C V2 for a charged capacitor sketch graphs that show the variation with time of potential difference, charge and current for a capacitor discharging through a resistor define the time constant of a circuit select and use time constant = CR analyse the discharge of capacitor using equations of the form x = x0e(- τ/CR) explain exponential decays as having a constant-ratio property describe the uses of capacitors for the storage of energy in applications such as flash photography, lasers used in nuclear fusion and as back-up power supplies for computers Capacitance (C) The charge stored per unit potential difference across it, as given by C = Q/V. Farad Unit of capacitance (F). 1 F is 1 C of charge stored per volt. Time constant The time taken for the charge remaining on a capacitor to fall to 1/e of its original value. It can be found using the expression CR, measured in seconds (s). Exponential A function that varies as the power of another quantity. Construction of a Capacitor Capacitors are electrical components that They are constructed from s electric charge. plates that are separated by a The two main types of capacitors are ceramic capacitors (above right) and capacitors (above left). Charging a Capacitor Draw a circuit with a capacitor being charged by a single cell. . Stored Charge (add your notes here) Capacitance On the side of a capacitor you will find its capacitance, and indicator of the amount of stored charge it can hold. Capacitance = _____________ C = _____ Capacitance is defined as: The unit for capacitance is named after so is called the Farad. 1 farad is equal to 1F is a LARGE capacitance, typical capacitors usually have a value of Answer SAQs 3 and 4, page 160 3) 4) Energy Stored in a Capacitor If an experiment is carried out where a capacitor is charged then discharged (as you did in class) the following graph is plotted: Copy Figure 11.5 The gradient shows the: The area under the line represents: The energy stored by a capacitor, W, is equal to: W= Derivation Work is done to charge a capacitor (which will then be equal to the energy stored by it). This can be derived as follows: There are 3 equations that can be used for calculating W, in terms of QV, QC or CV. . . . Answer SAQs 7 and 8, page 161 7) 8) Capacitors in Parallel Draw fig 11.9 page 163 There are 3 rules for capacitors in parallel: . . . SAQ 12 Page 163 12) Capacitors in Series Draw fig 11.10 page 163 There are 3 rules for capacitors in series: . . . SAQ 14 Page 163 14) Capacitor Series Parallel SAQs 20 and 21 page 167 20) 21) Resistor