Study Guide 2
advertisement

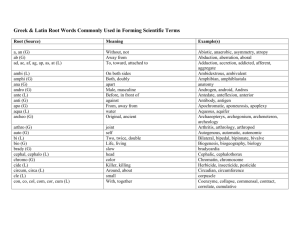
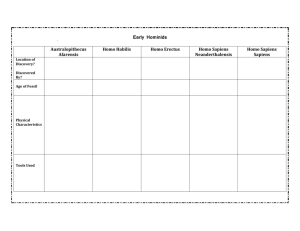
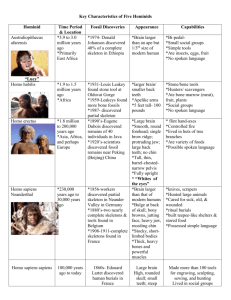
Evo Psyc Study Guide 2 Common ancestor (humans and chimpanzees) Climate change (Africa 10mybp) Reasons for bipedalism Pre-Australopiths Sahelanthropus tchadensis Orrorin tugenenis Ardipithecus kadabba Ardipithecus ramidus Foramen magnum Valgus angle Sagittal crest Austropiths A. Anamensis A. Afarensis (Lucy; Donald Johanson) A. Africanus (Dart, Tung Child) A. Sediba Robust vs. Gracile Laetoli feet Early Homo (defining characteristics) H. habilis H. rudolfensis Oldowan tools Hammerstone – core – flake Percussion Hands and tool-making, important grips Brain and tool-making, neuroscience studies Apes and tool-making (Kanzi study) Lokalalei refitting Homo erectus/ergaster Nariokotome boy – comparison to A. afarensis Erectus/ergaster distinction Important body and life style changes relative to Australopiths Relationship to H. florensiensis and H. heidelbergensis Important traits of H. heidelbergensis Acheulean tools Cognitive implications of the hand axe Cognitive implications of other remains: Mineral pigments Berekhat Ram Levallios technique Boxgrove debitage Control of fire Composite tools Neanderthals Relationship to H. sapiens and H. heidelbergensis Geographic range Physical traits relative to H. sapiens Tools (hafting; Levallois; spears; source materials) Hunting practices Lifestyle Symbolism (Chatelperronian controversy) Use of pigments Social life Campsites Hearths, use of fire Group sizes Sex role specialization Burials, religious beliefs Neanderthal language Homo sapiens Earliest fossil evidence (Omo Kibish; Herto) Possible significance of Herto defleshing Middle Paleolithic vs. Upper Paleolithic Levant findings (significance) Toba eruption and population bottleneck Modern Cognition Fortuitous mutation (Richard Klein) Expanded working memory capacity (Coolidge & Wynn) Paul Mellars and the “chosen few” Significance of Howieson’s Poort & Still Bay tool kits Blombos beads and Tsodilo Hills snake rock Models of Homo sapiens’ evolution Out of Africa: replacement Multi-regional or regional continuity Assimilation Migration of Homo sapiens Inter-breeding events (who and when) Aurignacian tools and the Upper Paleolithic Blades Ornamental tools Abstract figurines Cave art Phases in art creation: initial, second, final. Effects of and evidence for Expanded working memory capacity Alloying metals Traps and weirs Harpoons Managed foraging Abstract art Cave art and religion (shamanism) Burials and complex societies (ancestor worship)