Weather Test #1 Study Guide
advertisement

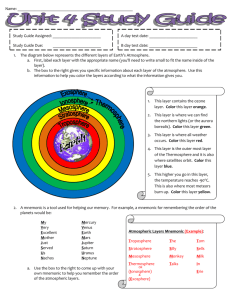
Name:__________________________________ Weather Test #1 Study Guide 1. List the layers of the atmosphere from lowest to highest: Troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere, exosphere 2. List the layers of the atmosphere from highest to lowest: Exosphere, thermosphere, mesosphere, stratosphere, troposphere 3. Which layer are the statements below about? a. Weather = troposphere g. Where we live =troposphere b. Ozone Layer =stratosphere h. Highest altitude = exosphere c. Meteoroids burn up = mesosphere i. Lowest altitude =troposphere d. Coldest layer =mesosphere j. Middle layer = mesosphere e. Hottest layer = thermosphere k. Highest pressure =troposphere f. l. Spaceships and satellites fly around in = Lowest pressure = exosphere thermosphere/exosphere 4. What is the protective layer that protects us from harmful ultraviolet rays from the sun? ozone layer 5. What are the two most common gases in the atmosphere? Nitrogen and oxygen 6. Define air pressure: the force exerted by the gases pushing on an object. (Greatest at sea level) 7. What is altitude: height 8. Put the following steps in the correct order: Condensation, Evaporation, Runoff/Ground, Precipitation evaporation, condensation, precipitation, and runoff/ground 9. Clouds form as a result from condensed water vapor 10. Define the following terms: a. Precipitation: the falling of water droplets to the ground b. Condensation: when water vapor turns into a liquid when cooled. The water droplets may sit in clouds until enough has collected to form millions of raindrops. c. Evaporation: when liquid water turns into water vapor (gas) when heated. The water vapor rises. d. Surface Water Flow/Run off: Water that we can easily see moving across Earth’s surface. (rivers and lakes) e. Ground Water Flow: Water that soaks into the ground 11. List 5 types of precipitation: freezing rain, hail, snow, sleet, rain. 12. The process of water leaving plants’ leaves is called transpiration 13. What drives the water cycle? The sun’s energy 14. Clouds at medium or low altitude, spread out layers, and form precipitation = stratus 15. Clouds at medium altitude, puffy looking, white signal fair weather, dark signals thunderstorms. Cumulonimbus 16. Clouds at high altitude, wispy looking, can consist of ice crystals, signal fair weather =cirrus 17. What does the stem nimbus mean? rain 18. Cumulonimbus clouds are also called thunderstorms 19. Clouds that form when condensation occurs at or near the ground =fog 20. What does the stem alto mean? Middle level clouds Examples: Altostratus and Altocumulus 21. Define weather: condition of the atmosphere at a certain time and place. Includes temperature, wind, precipitation, and cloud cover. 22. Define humidity: amount of water vapor in the air 23. Define air mass: a body of air that has the same properties throughout. 24. Describe the properties of the air mass that form: a. Polar/Over Ocean =cold and wet b. Polar/Over Land = cold and dry c. Tropical/Over Water=hot and wet d. Tropical/Over Land=hot and dry 25. What forms when a cold air mass and a warm air mass meets? a front 26. List the four types of fronts: warm front, cold front, occluded front, and stationary front 27. When a warm air mass slides over a cold air mass a warm front occurs. a. What types of clouds are formed? stratus b. Describe the weather formed? long periods of rain and warmer temperatures 28. When a cold air mass pushes a warm air mass up a cold front occurs. a. What types of clouds are formed? Cumulonimbus b. Describe the weather formed? Rain, thunderstorms, cooler temperatures, and severe weather 29. When a cold air mass meets a warm air mass and doesn’t move a stationary front occurs. 30. When a warm air mass gets pushed up by 2 surrounding cold air masses an occluded front occurs. 31. Warm air rises(rises/sinks) and cold air sinks (rises/sinks) 32. High pressure systems signal fair weather Winds circulate in which direction: clockwise 33. Cold pressure systems signal rainy/stormy weather Winds circulate in which direction? counterclockwise 34. Application/Diagrams: Atmospheric Layers, Water Cycle, Cloud Types, and Fronts Only cirrus, stratus, cumulus, and cumulonimbus 35. Short Answer: a. Explain the connection between convection and the water cycle. How do they relate? b. What step in the water cycle affects your life the most? Explain. c. Draw the symbols for the different types of fronts. (Cold Front, Warm Front, Stationary Front, and Occluded Front)