Unit 4 Climate and Natural Hazards Study Guide ANSWER KEY

Name:_________________________________________Date: ________________ Period:______________
Climate and Natural Hazards Test Study Guide ANSWER KEY
Complete each question either on the backside of this sheet or on a separate piece of paper. Reminder in order to get points on your test, the study guide must be 100% completed.
1.
What is the difference between weather and climate?
Weather is happening right now, and climate is temperature and precipitation over time.
2.
List the contributing factors that make up weather.
Weather consists of temperature, precipitation, cloudiness, humidity, pressure, and visibility.
3.
List the contributing factors that make up climate.
Location, altitude, topography and latitude
4.
How does an increase in greenhouse emissions affect our climate?
If there is an increase in greenhouse gases, it can cause climate change, as well as effecting ocean currents.
5.
Define global warming.
Global warming is when the climate changes to a warmer average temperature over a period of time, because of greenhouse gasses.
6.
Define Natural Hazard.
A Natural Hazard is Natural events causing great loss of life or property damage
7.
What is a tornado?
A tornado is a violently rotating column of air that is in contact with both the surface of the earth and the clouds.
8.
How does it form?
A change in wind direction and speed creates a horizontal rotation in the lower atmosphere. Strong updrafts tilt the rotating air from a horizontal to a vertical position. A tornado forms with the rotating winds.
9.
Which natural hazard causes the most injuries or deaths in the United States per year?
Tornadoes
10.
What should you do in the event of a tornado warning?
In the event of a tornado warning, a person should take cover in the lowest most interior part of a sturdy shelter.
11.
Where do tornadoes occur most?
Tornadoes most occur in the plain states in the United States
12.
When is tornado season?
Tornado season occurs in the spring to early summer (April to June)
13.
What are hurricanes?
Violent cyclonic storm that develops in the tropical region with wind speeds that are greater than 74 mph
14.
How do hurricanes form?
Warm ocean temperatures cause rotation in the clouds, when mixed with a lowpressure system North or South of Equator.
Name:_________________________________________Date: ________________ Period:______________
15.
When is hurricane season?
Hurricane season goes from June 1 st to November 30 th
16.
What should you do in the event of a hurricane?
In the event of a hurricane, people should evacuate the affected area until the storm has passed.
17.
What is a Tsunami?
The sudden displacement of huge amounts of water, as a result of an undersea earthquake.
18.
How can a tsunami form? earthquakes can cause the sudden movement of the ocean floor at a tectonic plate boundary and can cause the water above to surge upwards then fall back.
Volcanic eruptions, landslides, and meteorites can cause a tsunami as well.
19.
Where do most tsunamis occur?
The Pacific “Ring of Fire” is the most common place for tsunamis to happen, due to the number of volcanic eruptions and earthquakes.
20.
Where are tsunamis monitored?
The countries that monitor tsunamis are located along the Pacific Coast.
21.
The destructive power of a tsunami comes from what?
The wave’s momentum and wavelength
22.
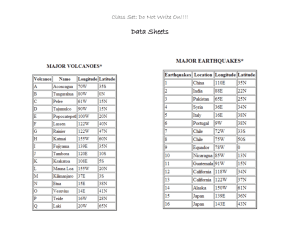
What are volcanoes?
A volcano is a mountain that forms when molten rock, called magma, forced to the Earth’s surface.
23.
What causes them to explode violently?
Density differences within the magma causes the violent eruptions.
24.
What else can cause violent explosions?
Silica and water contained in the magma
25.
What are three types of volcanoes?
Shield volcano, cinder cone volcano, and a composite volcano
26.
Where are most volcanoes found on Earth?
Most volcanoes are formed where two plates meet. Most are located around the
Pacific Ring of Fire is a string of volcanoes and sites of seismic activity, or earthquakes, around the edges of the Pacific Ocean.
27.
What should you do in the event of a volcanic eruption?
In the event of a volcanic eruption, you should evacuate the area and take shelter
28.
What are earthquakes?
Earthquakes are the trembling or shaking movement of the earth's surface.
29.
What causes earthquakes?
As tectonic plates push, pull or scrape against each other, stress builds up along faults near the plates edges.
30.
Where do most earthquakes occur?
Most earthquakes take place near the edges of tectonic plates
31.
Identify three different faults.
Strike – slip, reverse and normal fault
32.
Define magnitude
The strength of the natural hazard
33.
Define frequency
Name:_________________________________________Date: ________________ Period:______________
The amount of natural hazards to occur in a certain amount of time
34.
Explain the relationship between magnitude and frequency in earthquakes.
The greater the magnitude, the lower the frequency in earthquakes. The lower the magnitude the higher the frequency in earthquakes.
35.
What is the pacific ring of fire?
The Pacific Ring of Fire is a string of volcanoes and sites of seismic activity, or earthquakes, around the edges of the Pacific Ocean.