KefB inhibits phagosomal acidification but its role is unrelated to M
advertisement

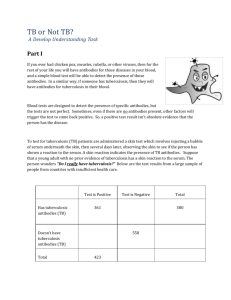
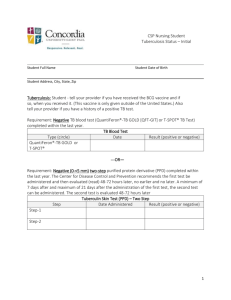
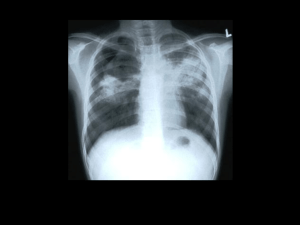
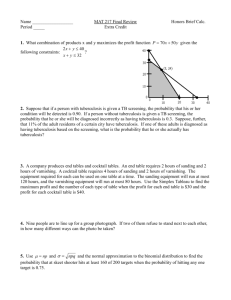
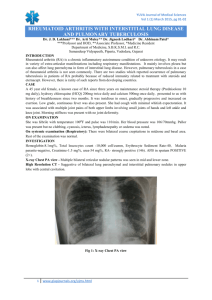
KefB inhibits phagosomal acidification but its role is unrelated to M. tuberculosis survival in host Garima Khare, P. Vineel Reddy, Pragya Sidhwani and Anil K. Tyagi* Supplementary Information for Figure 1 Given below are the original gel pictures for the confirmation of the disruption of kefB in M. tuberculosis. The portions marked as Fig 1B, 1C, 1D and 1E have been used separately in the final Figure 1. Legend to Supplementary Figure S1 Figure S1. Localization of M. tuberculosis, MtbΔkefB, MtbΔkefBComp in early endosomes by employing Rab5 antibodies. RAW 264.7 macrophages were infected with FITC labeled M. tuberculosis, MtbΔkefB, MtbΔkefBComp and latex beads (green) separately. The cells were then subjected to staining with Rab5 primary antibodies and counterstained with Texas Red labeled secondary antibodies followed by observation under confocal microscope. Representative fluorescent images depict that disruption of kefB leads to a poor accumulation of MtbΔkefB in early endosomes while the M. tuberculosis and MtbΔkefBComp were found to accumulate in Rab5 rich organelles (overlap of green and red images appears yellow as shown by arrows). Latex beads employed as control display poor colocalization with the Rab5 rich early endosomes. The scale bars depict 5 µm.