Ecosystem Notes - Ms. Clark`s Science
advertisement

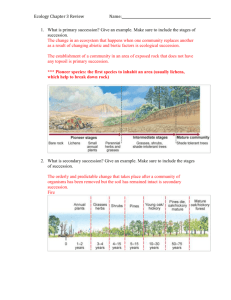
Earth Systems – Ecosystem Analysis Intro. Environment o Includes all conditions (biotic and abiotic) o Biotic – living segment o Abiotic – nonliving segment Might include external factors, i.e. ozone o Habitat Portion of environment where organism lives Described by its features Geographic, physical, chemical, biotic Described as macrohabitat or microhabitat i.e. macrohabitat could be deciduous forest i.e. microhabitat might be rotting log o Community Groups of interacting species within habitat Community Type Biome: largest geographic area with similar climax community Changes and variations within the larger community o Usually caused by formation of microclimates Created by variations in light intensity/ solar radiation Resulting variations in temp/heat Changes available soil moisture/humidity Succession o Slow predictable change in plant life Primary succession if area wiped clean Pioneer species are first species to populate area Species change as conditions change o i.e. soil moisture, shade Secondary succession if area partially disturbed o Climax community eventually reached No further change allowed by conditions Altitude and Latitude o Both cause gradual change in environment Altitude: drop 3 degrees every 1000ft Latitude: gradient exists, but not as predictable Evidence in Colorado mountains o Two treelines, top and bottom o Ecosystems change as altitude increases Grasslands on the plain o o o Dry shrubs in the foothills Trees, primarily conifers Ponderosa, douglas fir, limber pine, lodgepole Engelmann spruce, subalpine fir Colorado blue spruce throughout, (water) Decrease in size of vegetation at the top Tundra above treeline Zonation Belts/zones in biotic community on smaller scale o Caused by soil characteristics, light, moisture, slope o Changes occur horizontally Stratification Layering of biotic conditions o Changes occur over the vertical axis o Caused by changes in light, moisture i.e. deciduous forest o ground, herbaceous, shrub, understory-tree, canopy-tree Ecosystem Community and its relationship with abiotic factors Niche Functional role within an ecosystem Dimensions of the Ecosystem Temporal Things with time component i.e. population growth, succession Spatial Geographical components i.e. location, topography, stratification Physical or chemical Atmosphere Lithosphere (land, substrate) Hydrosphere (aquatic) Biotic Biosphere o Part of atmosphere, lithosphere, hydrosphere that can sustain life Biomes Large regional interaction of similar communities Usually identified by major plant types and/ or climate Earth divided into “10” biomes excluding aquatic