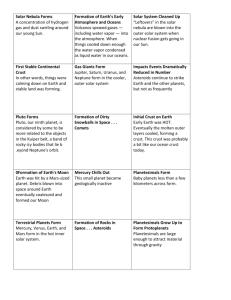
File
advertisement
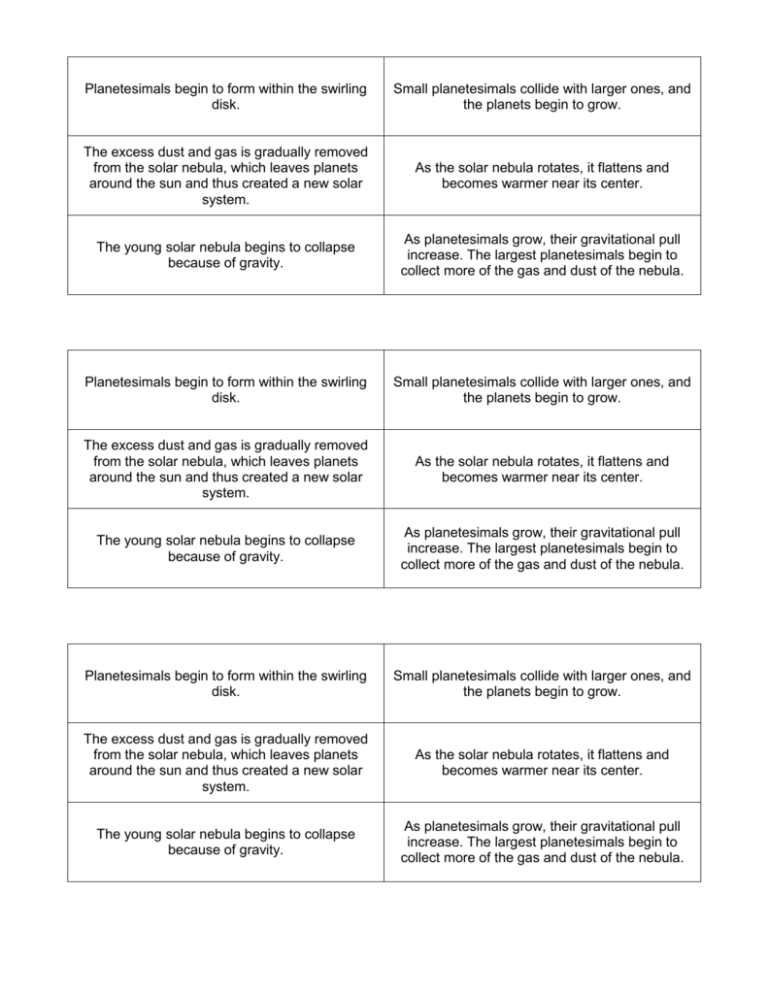
Planetesimals begin to form within the swirling disk. Small planetesimals collide with larger ones, and the planets begin to grow. The excess dust and gas is gradually removed from the solar nebula, which leaves planets around the sun and thus created a new solar system. As the solar nebula rotates, it flattens and becomes warmer near its center. The young solar nebula begins to collapse because of gravity. As planetesimals grow, their gravitational pull increase. The largest planetesimals begin to collect more of the gas and dust of the nebula. Planetesimals begin to form within the swirling disk. Small planetesimals collide with larger ones, and the planets begin to grow. The excess dust and gas is gradually removed from the solar nebula, which leaves planets around the sun and thus created a new solar system. As the solar nebula rotates, it flattens and becomes warmer near its center. The young solar nebula begins to collapse because of gravity. As planetesimals grow, their gravitational pull increase. The largest planetesimals begin to collect more of the gas and dust of the nebula. Planetesimals begin to form within the swirling disk. Small planetesimals collide with larger ones, and the planets begin to grow. The excess dust and gas is gradually removed from the solar nebula, which leaves planets around the sun and thus created a new solar system. As the solar nebula rotates, it flattens and becomes warmer near its center. The young solar nebula begins to collapse because of gravity. As planetesimals grow, their gravitational pull increase. The largest planetesimals begin to collect more of the gas and dust of the nebula.