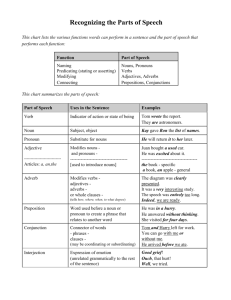
grammar-scope
advertisement
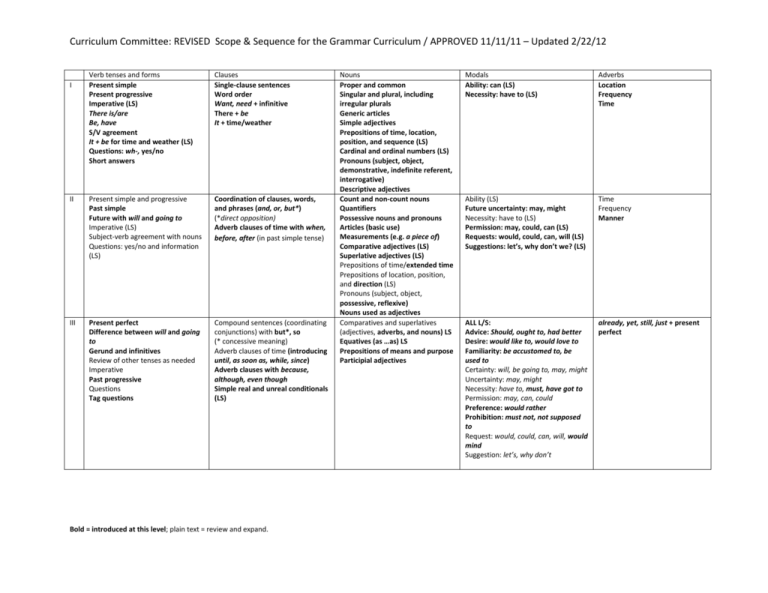
Curriculum Committee: REVISED Scope & Sequence for the Grammar Curriculum / APPROVED 11/11/11 – Updated 2/22/12 Verb tenses and forms Present simple Present progressive Imperative (LS) There is/are Be, have S/V agreement It + be for time and weather (LS) Questions: wh-, yes/no Short answers Clauses Single-clause sentences Word order Want, need + infinitive There + be It + time/weather II Present simple and progressive Past simple Future with will and going to Imperative (LS) Subject-verb agreement with nouns Questions: yes/no and information (LS) Coordination of clauses, words, and phrases (and, or, but*) (*direct opposition) Adverb clauses of time with when, before, after (in past simple tense) III Present perfect Difference between will and going to Gerund and infinitives Review of other tenses as needed Imperative Past progressive Questions Tag questions Compound sentences (coordinating conjunctions) with but*, so (* concessive meaning) Adverb clauses of time (introducing until, as soon as, while, since) Adverb clauses with because, although, even though Simple real and unreal conditionals (LS) I Bold = introduced at this level; plain text = review and expand. Nouns Proper and common Singular and plural, including irregular plurals Generic articles Simple adjectives Prepositions of time, location, position, and sequence (LS) Cardinal and ordinal numbers (LS) Pronouns (subject, object, demonstrative, indefinite referent, interrogative) Descriptive adjectives Count and non-count nouns Quantifiers Possessive nouns and pronouns Articles (basic use) Measurements (e.g. a piece of) Comparative adjectives (LS) Superlative adjectives (LS) Prepositions of time/extended time Prepositions of location, position, and direction (LS) Pronouns (subject, object, possessive, reflexive) Nouns used as adjectives Comparatives and superlatives (adjectives, adverbs, and nouns) LS Equatives (as …as) LS Prepositions of means and purpose Participial adjectives Modals Ability: can (LS) Necessity: have to (LS) Adverbs Location Frequency Time Ability (LS) Future uncertainty: may, might Necessity: have to (LS) Permission: may, could, can (LS) Requests: would, could, can, will (LS) Suggestions: let’s, why don’t we? (LS) Time Frequency Manner ALL L/S: Advice: Should, ought to, had better Desire: would like to, would love to Familiarity: be accustomed to, be used to Certainty: will, be going to, may, might Uncertainty: may, might Necessity: have to, must, have got to Permission: may, can, could Preference: would rather Prohibition: must not, not supposed to Request: would, could, can, will, would mind Suggestion: let’s, why don’t already, yet, still, just + present perfect Curriculum Committee: REVISED Scope & Sequence for the Grammar Curriculum / APPROVED 11/11/11 – Updated 2/22/12 IV Review of past, present, and future tenses in levels I-III, as needed: present simple, past simple, present perfect (RW); present and past progressive (LS); will and going to Past perfect (in appropriate adverb clauses and indirect speech) Adjective clauses (subject, object, object of a preposition, restrictive and non-restrictive) Noun clauses (direct and indirect speech, question words, whether/if, as objects and objects of a preposition, whether or not, as adjective complements) Clause combination and punctuation of simple, compound, and complex sentences Comparative and superlative adjectives (LS) Count and non-count nouns (LS) ALL L/S Advice: should, ought to, had better Certainty: all forms Desire: would love/like to Expectation: be supposed to Impossibility: cannot, could not (+future) Intention: be going to Necessity: must, have (got) to Preference: would rather Prohibition: must not Familiarity: be accustomed to, be used to Willingness: will Sentence (adverbial) transitions, as needed, specifically for compare/contrast, description, and summary V Review functions of verb tenses Gerunds and infinitives Habitual actions with would, used to Passive voice Causative verbs (make, let) Future perfect [reading only] Perfect progressives [reading only] Questions (LS) Adverb clauses, adding purpose (in order to, so that) Reduced adjective clauses Adjective clauses of place, time, and reason; and with quantities Real and unreal (present and past) conditionals (LS in EAP; RW in GenV) Reduced adverb clauses [not in Gen V; EAPV for reading purposes] Punctuation of simple, compound, and complex sentences Noun clauses with wish, whatever Correlative conjunctions Adverb clauses [reduced clauses for reading purposes] Conditional (real and unreal; implied and with inversion) Noun clauses (as subjects for reading only); complement noun clauses (EAP) Subjunctive noun clauses and nonfinite clauses of urging/ recommendation Wh- clefts (i.e. wh- noun clauses as subjects) – LS Punctuation of simple, compound, and complex sentences Parallelism Articles Review of all functions listed previously, with a new focus on RW including: Past and passive verb forms after certain modal verbs, and all tenses with semi-modals And with the addition of: Unfulfilled (past): was going to Sentence (adverbial) transitions, as needed, specifically for persuasion and argument, cause/effect Modals for hedging and boosting claims Sentence (adverbial) transitions VI Review verb tenses, passive voice as needed Subject-verb agreement (complex cases) Gerunds and infinitives Subject-verb inversion Questions (LS) Bold = introduced at this level; plain text = review and expand. Prepositions (as particles or complements of verbs) Articles, countability of nouns (in depth) Equatives, comparatives, rather than