Study Guide - ANSWER KEY
advertisement
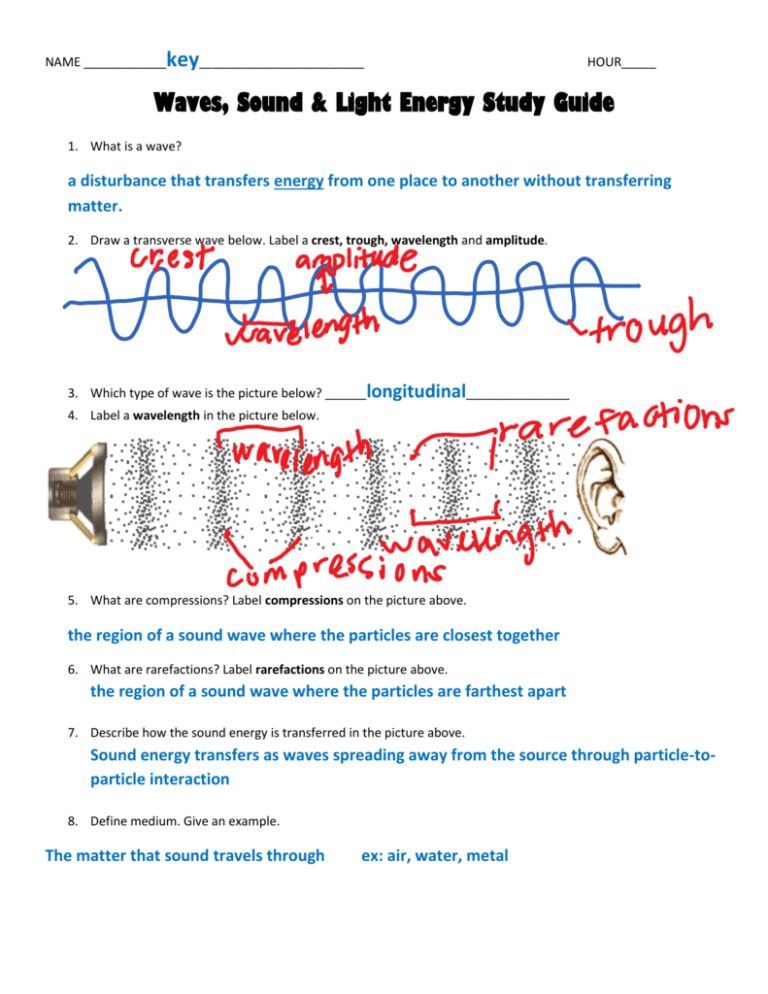
NAME ____________ key________________________ HOUR_____ Waves, Sound & Light Energy Study Guide 1. What is a wave? a disturbance that transfers energy from one place to another without transferring matter. 2. Draw a transverse wave below. Label a crest, trough, wavelength and amplitude. 3. Which type of wave is the picture below? ______longitudinal_______________ 4. Label a wavelength in the picture below. 5. What are compressions? Label compressions on the picture above. the region of a sound wave where the particles are closest together 6. What are rarefactions? Label rarefactions on the picture above. the region of a sound wave where the particles are farthest apart 7. Describe how the sound energy is transferred in the picture above. Sound energy transfers as waves spreading away from the source through particle-toparticle interaction 8. Define medium. Give an example. The matter that sound travels through ex: air, water, metal 9. Fill in the table below with the correct type of waves. Transverse or Longitudinal? Light or Sound? Longitudinal Sound Transverse Light 10. Define frequency. The number of wavelengths that pass by a point in a second. 11. Define amplitude. The height of the wave 12. Draw a wave that shows loud and quiet sounds. Label loud and quiet on your wave. 13. Draw a wave that shows high pitch and low pitch. Label the high pitch and low pitch on your wave. 14. The longer the wavelength, the ___lower_____ the pitch. 15. The shorter the wavelength, the ____ higher______ the pitch. 16. The taller the amplitude, the _____ louder______ the sound. 17. The shorter the amplitude, the ______ quieter______ the sound. 18. The longer the wavelength, the _______ lower ______ the frequency. 19. The shorter the wavelength, the ______ higher_____ the frequency. 20. The higher the frequency, the ______ higher______ the pitch. 21. The lower the frequency, the ____ lower _____ the pitch. 22. Unit for frequency: ___ Hertz____ (_Hz_) 23. Unit for loudness: ___ Decibels___ (_dB_) 24. What is the difference between pitch and loudness? The pitch is how low or high a sound is perceived and loudness is the intensity of a sound. 25. Which does sound travel the fastest through: solid, liquid or gas? WHY? Sound travels the fastest through a solid because the particles are the closest together and the particle to particle interaction can happen the fastest. 26. What are electromagnetic waves? Waves that can travel through empty space and through matter. 27. Label each type of radiation on the Electromagnetic Spectrum in the correct order according to wavelength on the picture below. 28. Which type of wave has the highest frequency, the highest energy and the shortest wavelength? Gamma Rays 29. Which type of wave has the lowest frequency, the lowest energy and the longest wavelength? Radiowaves 30. Which type of wave is strong enough to cause a chemical reaction/change? Ultraviolet Waves 31. Which types of waves are used for communication? __Radiowaves_ & __Microwaves_ 32. Which type of wave is given off from all vibrating molecules in all matter? _Infrared Waves_ 33. Which type of wave used in cell phones, radar guns, GPS, and satellites? _Microwaves_ 34. Which type of wave can pass through skin and muscles but not through your bones? _X-Rays_ 35. Which type of wave is produced when the nucleus of an atom is changed? _Gamma Rays_ 36. Which is the only type of wave that we can see? _Visible Light_ 37. Which three types of waves are emitted from the sun? a. _Infrared Waves_ b. _Visible Light_ c. _Ultraviolet Waves_ 38. What are 4 sources of visible light? The sun, stars, light bulbs, laser pointers, lightning, fire 39. When is an object “seen”? An object is “seen” only when an object emits or reflects light to the eye. 40. What is luminous? Give an example. Objects that generate their own light. ex: the sun, stars, light bulbs 41. What is illuminated? Give an example. Objects that reflect light ex: the moon, the table, the wall 42. Explain the difference between a regular reflection and a diffuse reflection. In a regular reflection, all the light rays reflect at the same angle. In a diffuse reflection, the rays of reflect off the surface at different angles (in many different directions). 43. Which types of surfaces have a regular reflection? diffuse reflection? Regular – smooth & shiny Diffuse – rough & dull 44. What is refraction? Why does it occur? Refraction is the bending of light when light waves speed up or slow down as they pass through different substances 45. Give two examples of refraction. A straw looking disconnected in a glass of water A rainbow forming from light and water droplets 46. Define transparent. Give an example. A material that light is able to completely or almost completely pass through. Ex: glass, water 47. Define translucent. Give an example. A material that light is mostly able to pass through but is blurred or fuzzy. Ex: frosted glass, wax paper 48. Define opaque. Give an example. A material that no light is able to pass through. Ex: the wall, a car 49. What does it mean when light is absorbed (absorption)? Light transfers into the material 50. What does it mean when light is transmitted (transmission)? Light passes through the material 51. Explain why we see all the colors of the visible light spectrum when light shines through a prism or water droplet. White light is made up of all the colors of the rainbow (ROY-G-BIV). When the white light transmits through a prism or a water droplet, the light bends (refracts) and different color frequencies bend at different angles, separating all the colors in the visible light spectrum. 52. Why do we see the color blue? We see the color blue when white light hits a surface and all the colors are absorbed except blue which is reflected to our eyes. 53. What makes up the visible light spectrum? (Visible white light?) All the colors of the rainbow (Red Orange Yellow Green Blue Indigo Violet) 54. Why does a white t-shirt appear white? White light hits a white shirt and the white light reflects off the white shirt appearing white. 55. Explain how we see something that is black. We see black because all of the colors that make up white light are absorbed into the shirt. 56. Label each part of the eye: cornea, pupil, iris, lens, retina, optic nerve. 57. What does each part of the eye do or what is it used for? Optic nerve – sends signals from the retina to Pupil – the hole that light passes through; the brain enlarges or shrinks to allow more or less light in Retina – back of the eye where an image is formed; has cells (rods & cones) that absorb light and converts information into signals. Iris – the colored part of the eye where the light from outside your eye is refracted inward; protects the eye. Cornea – Lens – helps focus light to form an upside- down image on the retina 58. Does the light travel the fastest in a solid, liquid, or gas? WHY? The light travels the fastest in a gas (actually empty space) because there are less or no particles in the way to slow down the wave of light.







