Notes 4-1: Cells
advertisement
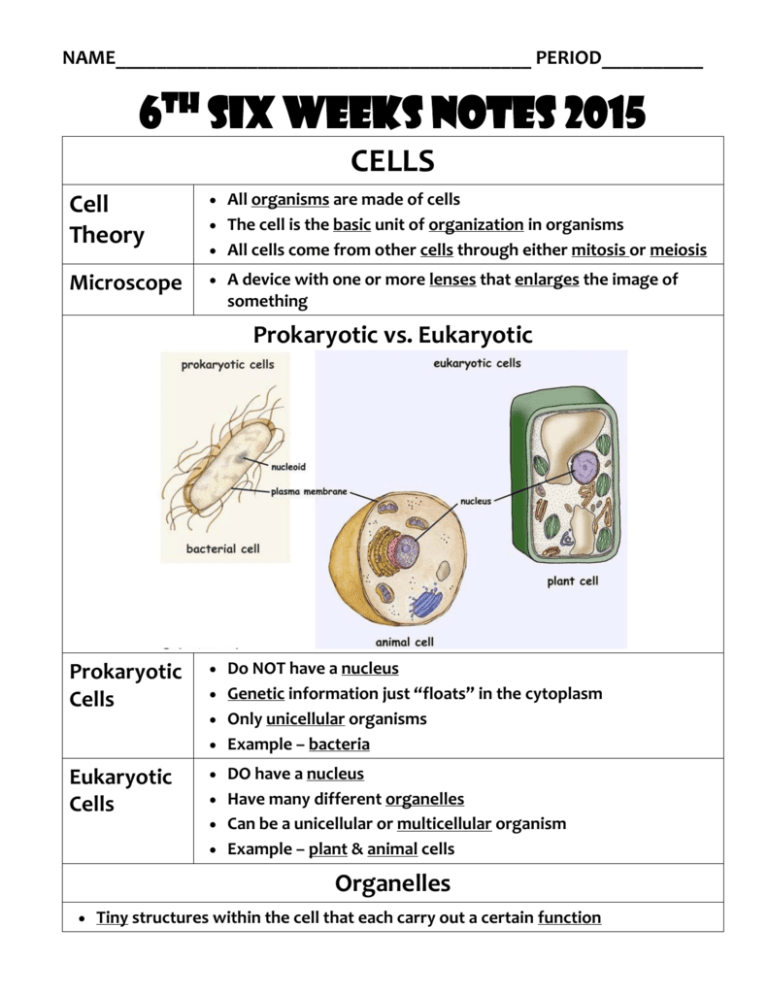
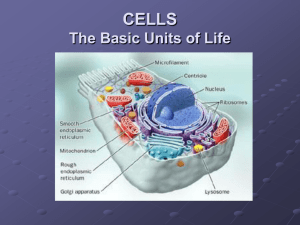
NAME_________________________________________ PERIOD__________ 6th Six weeks notes 2015 CELLS Cell Theory All organisms are made of cells Microscope A device with one or more lenses that enlarges the image of The cell is the basic unit of organization in organisms All cells come from other cells through either mitosis or meiosis something Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Prokaryotic Cells Do NOT have a nucleus Genetic information just “floats” in the cytoplasm Only unicellular organisms Example – bacteria Eukaryotic Cells DO have a nucleus Have many different organelles Can be a unicellular or multicellular organism Example – plant & animal cells Organelles Tiny structures within the cell that each carry out a certain function CELL DIAGRAMS Animal Cell Plant Cell Organelles found in BOTH Plant & Animal Cells Cell Outer covering of the cell Membrane Controls the movement of substances into and out of the cell Made of lipids (fats) Osmosis Movement of water across the cell membrane Diffusion Movement of other substances, such as oxygen, across the cell Cytoplasm Jelly-like substance that cells are filled with Nucleus Brain of the cell Does not require energy membrane Substances move based on the concentration inside the cell vs. outside the cell (move from higher to lower) Does not require energy Controls all of the cell’s activities Contains the DNA Mitochondria Produces energy for the cell by breaking down food Ribosomes Make proteins for the cell Usually found just outside the nucleus attached to the endoplasmic reticulum Stores water and other waste materials Vacuoles MUCH LARGER in plant cells Helps plant cells to maintain their SHAPE Organelles ONLY found in Plant Cells Cell Wall Tough rigid outer covering that protects plant cells and gives Chloroplast Uses sunlight, water and carbon dioxide to make food them shape Made of cellulose Give plants their green color CELL REPRODUCTION: Mitosis vs. Meiosis Parent Cell Daughter Cells Mitosis Parent cell makes a COPY of itself Both daughter cells have the same exact DNA For unicellular organisms, mitosis is used for asexual reproduction For multicellular organisms, mitosis is used for GROWTH Meiosis Parent cell divides TWICE Parent cells genes are shuffled around FOUR daughter cells each have only HALF the parents genes For multicellular organisms, this form of sexual reproduction creates genetically UNIQUE offspring Organic vs. Inorganic Compounds Organic Inorganic Come from living organisms Involved in all biochemical activities MUST contain carbon atoms bonded to other Carbon atoms Can also contain Hydrogen, Oxygen, Sulfur, Phorsphorus and Nitrogen Ex: Sugars-C12H22O12, Vitamins-C29H50O2, Hormones-C19H28O2, Amino Acids-C6H12N2O4S2, Nucleic Acids-C6H14N2O2 DO NOT come from organisms Can contain any elements Any substance that is NOT organic Ex: Water-H2O, Carbon Dioxide-CO2, Salt-NaCl, Oxygen gas-O2 Biomolecules Monomers Single molecules that can be joined together to form a larger more complex molecule Ex: monosaccharides, amino acids, nucleotides Polymers Compound made up of several monomers Ex: poly-saccharides, lipids, proteins, DNA Carbohydrates Consist of elements C, H, & O ONLY Examples: Sugars & starches Main energy source for all living things Plants use carbohydrates (cellulose) for structure Monosaccharides Made of a single sugar molecule like glucose & Disaccharides Made of two sugar molecules like lactose & fructose Monomer of other complex carbohydrates sucrose Polysaccharides Made of many sugar molecules Lipids Consist of elements C, H, O & sometimes P Types – fatty acids, triglycerides, phospholipids, & sterols Fatty Acid Tryglyceride like starch or cellulose (what plant cell walls are made of) Polymers Examples: Fats, oils & waxes Can also be used to store energy NOT water soluble Cell membranes are made of phospholipids Vitamins, enzymes & hormones are also lipids Vitamin A (retinol) Proteins Nucleic Acids Consist of elements C, H, O, & N Polymer chain of amino acids Different combinations of amino acids form different proteins Each protein has a specific job in an organism such as: o Regulating cell processes o Transporting substances into or out of cells o Forming bones, muscles & other tissues o Fighting diseases Have complex folded structures Consist of elements C, H, O, N, & S Store & transmit genetic or hereditary information Polymers of individual molecules called nucleotides Two kinds of nucleic acids: DNA and RNA Order of the individual nucleotides in a DNA or RNA molecules determines the traits in an organism Parts of a Microscope A few of the Organisms found in both plant and animal cells