Seventh Grade Syllabus 2nd nine weeks October 16
advertisement

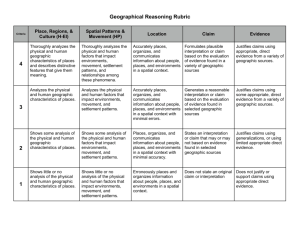
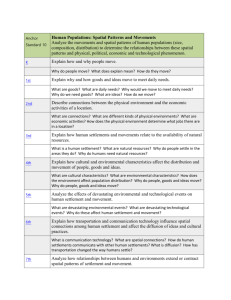
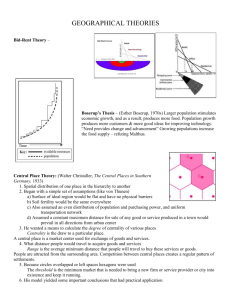
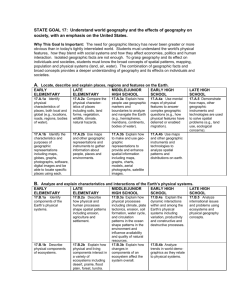
Seventh Grade Syllabus 2nd nine weeks October 16-October 30—Determine how people organize economic systems to address basic economic questions regarding which goods and services will be produced, how they will be distributed, and who will consume them. I.e. Capitalism, communism, feudalism. Use economic concepts to explain historical and current developments and issues in global, national, and state contexts. Increase in oil prices resulting from supply and demand. November 3-15—appraise the relationship between the consumer and the marketplace in the economy of the United States regarding scarcity, opportunity cost, trade-off decision making, and the stock market. Describe effects of government policies on the free market, identify laws protecting rights of consumers, and avenues of recourse when those rights are violated, compare economic systems, including market, command, and traditional. November 17-25-Apply principles of money management to the preparation of a personal budget that addresses housing, transportation, food, clothing, medical expenses, insurance, checking and savings accounts, loans, investments, credit, and comparison shopping. December 1-December 12-Describe individual and civic responsibilities of the citizens of the United States. Respect for rights of others, self-discipline, negotiation, compromise, fiscal responsibility…respect for law, patriotism, and participation in political processes. Differentiate rights, privileges, duties, and responsibilities between citizens and non-citizens. Explain how U.S. citizenship is acquired by immigrants. Explain character traits that are beneficial to individuals and society…honesty, courage, compassion, civility, loyalty Students will be given Unit Tests after each unit is completed. The students will also be given the opportunity to research and write a paper on a topic within any of the themes that are discussed this 9 weeks. The paper will be modeled on the 5 paragraph essay. This paper will be due on December 19. The students will also be given the opportunity participate in discussions related to various themes, participate in role-play simulations, and problem solving situations relevant to the past and present. 7th grade Syllabus Third 9 Weeks January 6-January 30-Describe in spatial terms using maps and other geographic representations, tools, and technologies. Explain the use of map essentials, including type, projections, scale, legend, distance, direction, grid, and symbols. Type examples…reference, thematic, planimetric, topographic, globe and map projections, aerial photographs, satellite images… Distance…fractional, graphic, and verbal scales Direction…lines of latitude and longitude, cardinal and intermediate directions Identifying geospatial technologies to acquire, process, and report information from a spatial perspective. Examples…Google Earth, GPS systems, geographic information system, satellite-remote sensing, aerial photography. Utilize maps to explain relationships and environments among people and places, including trade patterns, governmental alliances, and immigration patterns. Apply mental maps to answer geographic questions, categorize geographic organization of people, places, and environments using special maps. Examples…urban land usage patterns, distribution and linkage of cities, migration patterns, population-density patterns, spread of cultural traits, spread of diseases. February 2-February 13-Determine how regions are used to describe the organization of the Earth’s surface Identify physical and human features used as criteria for mapping regions…landforms, climates, bodies of water, resources. Language, religion, culture, economy, and government. Interpret processes and reasons for regional change: land use, urban growth, population change, natural disasters, and trade. Analyze interactions among regions to show transitional relationships, including flow of commodities and Internet connectivity…winter produce to Alabama from Chile and California, and poultry from Alabama to other countries. Compare how culture and experience influence perceptions of places and regions, language, religion, ethnicity, iconography, symbology, stereotypes. Explain globalization and its impact in all regions of the world. February 17-February 27-Compare geographic patterns in the environment that result from processes within the atmosphere, biosphere, lithosphere, and hydrosphere of Earth’s physical systems. Compare the earth-sun relationship regarding seasons, fall hurricanes, monsoon rainfalls, and tornadoes. Explain the process that shape physical environment including long-range effects of extreme weather phenomena such as plate tectonics, glaciers, ocean and atmospheric circulation, El Nino, erosion, Describe the characteristics and physical processes that influence the spatial distribution of ecosystems and biomes on Earth’s surface. How do ecosystems vary from place to place and how they vary over time. Place to place examples, soil differences, climate, and topography. Overtime examples-alteration of natural habitat due to flood, fire, reduction of species diversity due to loss of natural habitat, reduction of wetlands due to replacement of farms, reduction of forests and farmland due to replacement of housing development, and reforestation efforts. Compare geographic issues in different regions—hurricanes, tsunamis, tornadoes, floods. March 2-13—Evaluate spatial patterns and demographic structure of population on Earth’s surface in terms of density, dispersion, growth, and mortality rates, natural increase, and doubling time. Predict reasons and consequences of migration, including push and pull factors— politics, war, famine…potential of jobs and family. 7th grade syllabus 4th 9 weeks March 16-31—spring break in the middle of this unit…Explain how cultural features, traits, and diffusion help define regions, including religious structures, agricultural patterns, ethnic enclaves, ethnic restaurants, spread of Islam. April 1-10-Illustrate how primary, secondary, and tertiary economic activities have specific functions and special patterns. Primary—forestry, agriculture, mining Secondary—manufacturing furniture, grinding coffee beans, assembling automobiles Tertiary—selling furniture, selling café latte, selling automobiles Compare one location to another for production of goods and services…fast food restaurants in highly accessible locations, medical offices near hospitals, legal offices near courthouses, and industries near transportation routes. Analyze impact of economic interdependence and globalization on places and populations…seed corn produced in Iowa and planted in South America, silicon chips manufactured in California and installed in a computer made in china that is sold in Australia. Explain why countries enter into global trade agreements…NAFTA, DR-CAFTA, EU, MERCOSUR, and ASEAN April 13-April 23-Classify spatial patterns of settlement in different regions of the world, including types and sizes of settlement patterns…types-linear, clustered, grid…Sizes-large urban, small urban, rural. Explain how human activity that resulted in the development of settlements at particular locations due to trade, political importance, or natural resources…Timbuktu near trade routes, Pittsburgh, and Birmingham near coal and iron ore deposits, Singapore near ocean transportation corridor. Describe settlement patterns in association with the location of resources…fall line settlements near waterfalls to use energy for mills. European Industrial settlements near coal seams, special arrangements of towns and cities in North American Corn Belt settlements. Describe ways in which urban areas interact and influence surrounding regions…Daily commuters from region to region, communication centers that service nearby and distant locations through radio, television, newspapers, and internet. April 27-May 8-Determine Political, Military, cultural and economic forces that contribute to cooperation and conflict among people. Identify political boundaries based on physical and human systems, rivers as boundaries between countries, streets as boundaries between local governments Identify effects of cooperation among countries in controlling territories…UN, NATO, etc. Describe the eruption of territorial conflicts over boundaries, resources, land use, and ethnic identity…India, Pakistan conflict over Jammu and Kashmir, West Bank, Sudan, Somalia Piracy, Iraq, May 11-22-explain how human systems develop in response to physical environmental conditions. Farming practices in different regions, slash-and-burn agriculture, terrace farming, center-pivot irrigation Identify types, locations, and characters of natural hazards, earthquakes, hurricanes, tornadoes, floods, mudslides. Differentiate ways people prepare for and respond to natural hazards, including storm shelters, fire and tornado drills, building codes for construction.