228 - Classroom Observation Rubric
advertisement
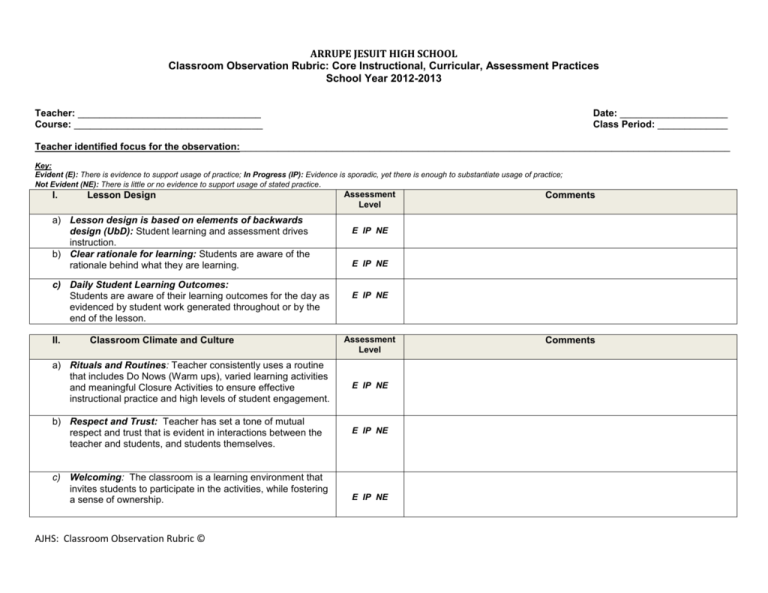
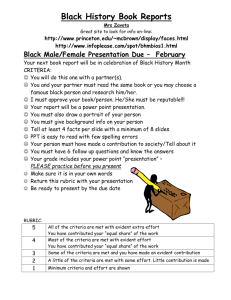
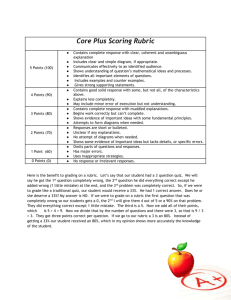
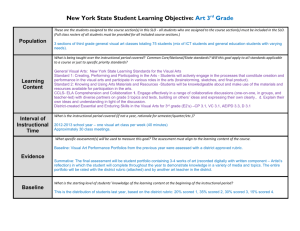
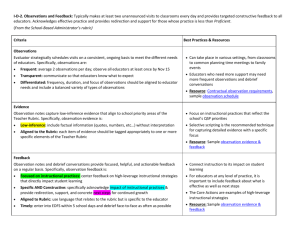
ARRUPE JESUIT HIGH SCHOOL Classroom Observation Rubric: Core Instructional, Curricular, Assessment Practices School Year 2012-2013 Teacher: __________________________________ Course: ___________________________________ Date: ____________________ Class Period: _____________ Teacher identified focus for the observation:___________________________________________________________________________________________ Key: Evident (E): There is evidence to support usage of practice; In Progress (IP): Evidence is sporadic, yet there is enough to substantiate usage of practice; Not Evident (NE): There is little or no evidence to support usage of stated practice. I. Lesson Design a) Lesson design is based on elements of backwards design (UbD): Student learning and assessment drives instruction. b) Clear rationale for learning: Students are aware of the rationale behind what they are learning. c) Daily Student Learning Outcomes: Students are aware of their learning outcomes for the day as evidenced by student work generated throughout or by the end of the lesson. II. Classroom Climate and Culture Assessment Level E IP NE E IP NE E IP NE Assessment Level a) Rituals and Routines: Teacher consistently uses a routine that includes Do Nows (Warm ups), varied learning activities and meaningful Closure Activities to ensure effective instructional practice and high levels of student engagement. E IP NE b) Respect and Trust: Teacher has set a tone of mutual respect and trust that is evident in interactions between the teacher and students, and students themselves. E IP NE c) Welcoming: The classroom is a learning environment that invites students to participate in the activities, while fostering a sense of ownership. AJHS: Classroom Observation Rubric © Comments E IP NE Comments III. Instructional Practice Assessment Level a) Student Organizational Systems: Teacher helps students to organize their materials and time for success in the course. E IP NE b) Scaffolded Instruction: Teacher carefully scaffolds instruction on a regular basis to incorporate a Gradual Release of Responsibility: Modeling/Direct Instruction (minilesson, whole-group, teacher-led instruction), Guided Practice (small-group, teacher-directed activities), and Independent Practice (independent work that allows for differentiation and teacher conferring). E IP NE c) Quality of Instruction: Instruction links directly to learning outcomes. It is succinct and to the point. Instruction is clear and easy to track. It is accompanied by visuals aids, such as written directions, diagrams, photos, film clips, text, to support student learning, particularly second language learners. E IP NE d) Differentiated Instruction: Teacher regularly differentiates instruction by process and/or product, offering additional support to struggling students and additional challenge to advanced students. This includes the use of varied learning activities that support student learning. e) Use of Time: Teacher uses time flexibly and judiciously, maximizing student progress towards the daily learning objectives. Every minute counts, and teacher makes instantaneous adjustments to the schedule when needed. f) Clear Expectations for Quality Work: Teacher establishes clear expectations for quality of student work, using rubrics, models and exemplars. Students are clear about the type of work product they are aiming for. g) Apprentice of Thinking/Reading/Writing Strategies: Teachers explicitly teach students strategies used by proficient thinkers, readers, writers, etc. Teacher “shows” students the skill or use of knowledge needed to reach learning outcomes. In other words, the teacher cognitively apprentices the student. AJHS: Classroom Observation Rubric © E IP NE E IP NE E IP NE E IP NE Comments III. Instructional Practice h) Types of Assessment: Teacher consistently uses a variety of both formal and informal assessments, e.g. student conversation in small groups, student-conferences, student note taking, written responses, homework, warm-ups, student questions, exit slips, quizzes, and tests, to measure every student’s progress towards learning outcomes. i) j) Use of Student Data/Evidence of Learning: Teacher has a system that enables him/her to use assessment data (formal and informal) to guide and adapt instruction to meet individual and whole-class needs. Homework reinforces daily learning outcomes and/or introduces outcomes for the next lesson. When based on closure activity, teacher adapts homework if necessary. Assessment Level E IP NE E IP NE E IP NE IV. Notes from Debrief Conversation (Strengths and Refinements) V. Next Steps: AJHS: Classroom Observation Rubric © Comments AJHS: Classroom Observation Rubric ©