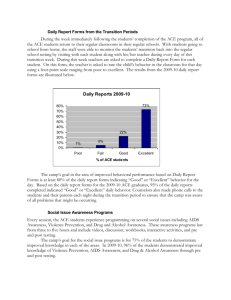
Quiz #1
advertisement

Quiz #1: Chapter 1 – Human Anatomy ACE’s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals 1) When comparing the medial epicondyle of the humerus to the lateral epicondyle of the humerus, which of the following statements is correct? a. b. c. d. The medial epicondyle is more toward the front of the body than the lateral epicondyle The medial epicondyle is more toward the back of the body than the lateral epicondyle The medial epicondyle is more toward the midline of the body than the lateral epicondyle The medial epicondyle is more away from the midline of the body than the lateral epicondyle Explanation c. The medial epicondyle is more toward the midline of the body than the lateral epicondyle The term “medial” means “toward the midline of the body,” while the term “lateral” means “away from the midline of the body.” ACE’s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals, p. 2 2) Which of the following is NOT one of four types of tissue found in the human body? a. b. c. d. Muscular Nervous Epithelial Vascular Explanation d. Vascular The four primary types of tissue are muscular, nervous, connective, and epithelial. ACE’s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals, p. 3 3) Which of the four components of blood carries hormones, food materials, ions, and gases throughout the body? a. b. c. d. Plasma Red blood cells White blood cells Platelets Explanation a. Plasma The liquid component of blood, called plasma, is responsible for carrying hormones, plasma proteins, food materials (e.g., carbohydrates, amino acids, lipids), ions (e.g., sodium, chloride, bicarbonate), and gases (e.g., oxygen, nitrogen, carbon dioxide) throughout the body. ACE’s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals, p. 3–4 4) When blood is flowing through the heart, where does it go after passing through the tricuspid valve? a. b. c. d. Right atrium Left atrium Right ventricle Left ventricle Explanation c. Right ventricle Blood passes through the tricuspid valve on its way from the right atrium to the right ventricle. ACE’s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals, p. 6 5) The average person’s breathing rate through the nose is equal to 20 to 30 liters per minute while at rest. a. True b. False Explanation b. False Humans normally breathe approximately 5 to 6 liters of air per minute through the nose when at rest, but use the mouth as the primary passageway for air when ventilation is increased to approximately 20 to 30 liters per minute during exercise. ACE’s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals, p. 8 6) Which of the following movements takes place in the frontal plane? a. b. c. d. Depression of the scapulae Flexion at the elbow Extension at the hip Supination at the wrist Explanation a. Depression of the scapulae The movements that take place in the frontal plane are as follows: Abduction Adduction Elevation Depression Inversion Eversion ACE’s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals, p. 21 7) Which of the following statements about flexibility is CORRECT? a. b. c. d. As people age, flexibility naturally increases due to decreased collagen levels. Males are generally more flexible than females. Collagen is made up of proteins that limit motion and resist stretch. The build-up of scar tissue after injury often increases flexibility. Explanation c. Collage is made up proteins that limit motion and resist stretch. Structures containing large amounts of collagen tend to limit motion and resist stretch. Thus, collagen fibers are the main constituents of tissues such as ligaments and tendons that are subjected to a pulling force. Regarding the other options, flexibility decreases with aging, females are generally more flexible than males, and scar tissue limits flexibility. ACE’s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals, p. 30 & 32 8) Which pair of shoulder muscles is BEST strengthened by shoulder shrugs performed with resistance? a. b. c. d. Rhomboid major and rhomboid minor Pectoralis minor and serratus anterior Levator scapulae and trapezius Teres major and latissimus dorsi Explanation c. Levator scapulae and trapezius These two muscles that act at the shoulder girdle to elevate the scapula are effectively targeted by shoulder shrugs. ACE’s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals, p. 35 & 38 9) The birddog is an effective exercise for which of the following muscles that act at the trunk? a. b. c. d. Multifidi Erector spinae Rectus abdominis Transverse abdominis Explanation a. Multifidi The multifidi, which contribute to spinal stability during trunk extension, rotation, and side-bending, are effectively targeted by the birddog. ACE’s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals, p. 43 10) Which category of hip muscles is primarily responsible for hip adduction? a. b. c. d. Anterior muscles Posterior muscles Medial muscles Lateral muscles Explanation c. Medial muscles The medial hip muscles (i.e., those hip muscles closer to the midline of the body), including the pectineus, adductor brevis, adductor longus, gracilis, and adductor magnus, are primarily responsible for hip adduction. ACE’s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals, p. 44 Quiz #2: Chapter 2 – Exercise Physiology ACE’s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals 1) Which of the following is NOT a benefit of regular physical activity? a. b. c. d. Decreased anxiety and depression Improved lipid profile Improved glucose control Increased diastolic blood pressure Explanation d. Increased diastolic blood pressure Some of the benefits of regular exercise include improved cardiovascular function, lowered systolic and diastolic blood pressure, decreased body weight and fat mass, improved lipid profile, improved glucose control, decreased anxiety and depression, enhanced feelings of well-being, decreased incidence of several cancers (e.g., colon, breast, prostate), and decreased incidence of osteoporosis. ACE’s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals, p. 67–68 2) Cardiac output is defined as the amount of blood pumped during each heart beat. a. True b. False Explanation b. False The amount of blood pumped during each heartbeat is called the stroke volume. Cardiac output is the product of stroke volume and heart rate, and therefore is defined as the amount of blood pumped per minute. ACE’s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals, p. 70 3) Very little of the __________ a person consumes is used for energy production. a. b. c. d. Fat Carbohydrate Protein Fiber Explanation c. Protein Of the three macronutrients, relatively little protein is used for energy production except in extreme cases of caloric restriction. Protein is principally used in the growth and repair of tissue or is excreted. ACE’s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals, p. 71–72 4) Which of the primary energy systems supplies enough energy for no more than 10 seconds of all-out exertion? a. b. c. d. Phosphagen system Anaerobic glycolysis Aerobic glycolysis Beta oxidation Explanation a. Phosphagen The total amount of ATP and creatine phosphate (CP) stored in muscle is very small, and thus the amount of energy available for muscular contraction is extremely limited. There is probably enough energy available from the phosphagens for only about 10 seconds of all-out exertion, if there were not continual resynthesis of ATP. ACE’s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals, p. 72 5) Low-intensity exercise is the best way to lose weight because it burns a higher percentage of fat than exercise at a higher intensity. a. True b. False Explanation b. False During high-intensity exercise, the total number of calories burned is much higher than during lowintensity exercise, and negates the higher percentage coming from fat. During low-intensity bouts, a higher percentage of calories is coming from fat, but the total number of fat calories is less than during high-intensity workouts. It is important to remember that the total number of calories burned is what determines weight loss, regardless of the source of those calories. ACE’s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals, p. 76 6) At what stage of an exercise bout are phosphagen stores being replenished, remaining lactate being removed from the blood, and the metabolic rate decreasing? a. b. c. d. Immediately after the commencement of exercise As the body approaches steady state During steady-state training After the cessation of exercise Explanation d. After the cessation of exercise The energy produced after the cessation of exercise (excess postexercise oxygen consumption – EPOC) is used to replenish the depleted phosphagens, to eliminate accumulated lactate if it has not already been cleared from the blood, and to restore other homeostatic conditions (e.g., thermoregulation, tissue resynthesis). As the body returns to normal temperature, the metabolic rate will return to normal. ACE’s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals, p. 79 7) Which of the following is an adaptation specifically seen with regular weightbearing exercise? a. b. c. d. Increase in respiratory capacity Improved cardiac output efficiency Increase in bone density Improved lean body mass Explanation c. Increase in bone density The concept of the SAID principle is that the body will adapt to the specific challenges imposed upon it, as long as the program progressively overloads the system being trained. Studies have shown that weightbearing exercise promotes improved bone density, which is a key factor in the prevention of osteoporosis, particularly in women. ACE’s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals, p. 81–82 8) Which hormone promotes triglyceride breakdown to aid in maintaining blood glucose? a. b. c. d. Vasopressin Cortisol Norepinephrine Estrogen Explanation b. Cortisol Cortisol is a glucocorticoid and plays a major role in maintaining blood glucose during prolonged exercise by promoting protein and triglyceride breakdown. Cortisol is also a major stress hormone and is elevated when the body is under too much stress, either from too much exercise or inadequate regeneration. ACE’s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals, p. 84 9) Replacing body fluid as it is lost is an important guideline to follow whether exercising in the heat or in the cold. a. True b. False Explanation a. True Replacing body fluids as they are lost is important when exercising in either the heat or the cold. In the cold, fluid loss may not be as obvious as when exercising in the heat. However, when exercising in cold air, large amounts of water are lost from the body during respiration. ACE’s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals, p. 86 & 89 10) Which of the following is NOT one of the primary symptoms of altitude sickness? a. b. c. d. Shortness of breath Profuse sweating Headache Nausea Explanation b. Profuse sweating While shortness of breath, headache, and nausea (along with lightheadedness) are all symptoms of altitude sickness, profuse sweating is one of the primary symptoms of heat exhaustion. ACE’s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals, p. 87 & 89 Quiz #3: Chapter 3 – Fundamentals of Applied Kinesiology ACE’s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals 1) Which of Newton’s laws of motion is described as follows? A body at rest will stay at rest and a body in motion will stay in motion (with the same direction and velocity) unless acted upon by an external force. a. b. c. d. Law of gravity Law of reaction Law of inertia Law of acceleration Explanation c. Law of inertia Newton’s first law of motion, known as the law of inertia, states that a body at rest will stay at rest and that a body in motion will stay in motion (with the same direction and velocity) unless acted upon by an external force. In addition, a body’s inertial characteristics are proportional to its mass, which is why it is harder to start (or stop) moving a heavy object than a lighter one. ACE’s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals, p. 106 2) Which of the following is an example of a multiplanar movement from the anatomical position? a. b. c. d. Depression of the scapulae Pronation of the forearm Dorsiflexion of the ankle Opposition of the thumb Explanation d. Opposition of the thumb Opposition of the thumb is a movement unique to primates and humans that follows a semicircle toward the little finger. Each of the other movements is uniplanar. ACE’s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals, p. 109 3) Assuming a client is lifting the same amount of weight, he or she can create more resistance by moving the weight closer to the working joint. a. True b. False Explanation b. False To create more resistance with the same amount of weight, move the weight farther from the working joint. To lessen the resistance as fatigue occurs, move the weight closer to the working joint. ACE’s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals, p. 112 4) A muscle with which of the following muscle arrangements has the LOWEST force production, but the HIGHEST speed of contraction? a. b. c. d. Unipennate Bipennate Multipennate Longitudinal Explanation d. Longitudinal Penniform muscles, which include unipennate, bipennate, and multipennate muscles, are designed for higher force production than longitudinal muscles. Longitudinal muscles are long and thin and have parallel fibers that run in the same direction as the length of the muscle. This type of fiber arrangement allows for speed of contraction. ACE’s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals, p. 112–113 5) Static balance exercises often involve _______________. a. b. c. d. Widening the base of support Narrowing the base of support Shifting the line of gravity outside the base of support Shifting the line of gravity through rotary motion Explanation b. Narrowing the base of support To work on static balance with a client or class participant, the fitness professional can make the individual’s base of support narrower to stimulate adaptation to the imposed demand. Widening the base of support lessens the balance challenge. ACE’s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals, p. 115–116 6) What muscles are strengthened when a client performs side-lying leg lifts with the lower leg? a. b. c. d. Adductors Abductors Internal rotators External rotators Explanation a. Adductors During side-lying leg lifts (lower leg), the adductors work concentrically in the upward phase and eccentrically in the downward phase. ACE’s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals, p. 121 7) The soleus, gastrocnemius, and plantaris are located in which compartment of the lower leg? a. b. c. d. Anterior tibial compartment Posterior tibial compartment Deep posterior compartment Superficial posterior compartment Explanation d. Superficial posterior compartment The soleus, gastrocnemius, and popliteus are all located in the superficial posterior compartment of the lower leg and serve as primary plantarflexors of the ankle joint. ACE’s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals, p. 123 8) When evaluating a new client’s posture, a personal trainer notices a long outward curve of the thoracic spine with an accentuated lumbar curve and a backward shift of the upper trunk. What postural deviation does this client have? a. b. c. d. Kyphosis Lordosis Flat back Sway back Explanation d. Sway back Sway-back posture is a long outward curve of the thoracic spine with an accentuated lumbar curve and a backward shift of the upper trunk. It is often accompanied by rounded shoulders, a sunken chest, and a forward-tilted head. If an individual has this postural abnormality and cannot actively assume a neutralspine posture, the fitness professional should refer him or her to a physician. ACE’s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals, p. 128 9) Which of the following muscles plays a vital role (with the mulitfidi) in providing feedback to the central nervous system about spinal joint position before dynamic forces in the extremities destabilize the spine? a. b. c. d. Transverse abdominis Rectus abdominis Internal obliques External obliques Explanation a. Transverse abdominis Coactivation of the transverse abdominis and multifidi muscles occur before any movements of the limbs. Specifically, these two muscles are activated an average of 30 milliseconds before shoulder movement and 110 milliseconds before leg movement. What is the importance of this temporal pattern of trunk muscle recruitment? The transverse abdominis and multifidi muscles are thought to play a vital role in providing feedback about spinal joint position, and thus forewarn the central nervous system about impending dynamic forces to be created in the extremities that may destabilize the spine. ACE’s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals, p. 133 10) “Shoulder girdle” is the formal term for the _______________. a. S/C joint b. A/C joint c. S/T articulation d. G/H joint Explanation c. S/T articulation Shoulder girdle is the formal term for scapulothoracic (S/T) articulation, which consists of the muscles and fascia connecting the scapula to the thorax. ACE’s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals, p. 134 Quiz #4: Chapter 4 – Nutrition ACE’s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals 1) Carbohydrates, which are the body’s preferred energy source, contain how many kilocalories per gram? a. b. c. d. 2 kcal/g 4 kcal/g 7 kcal/g 9 kcal/g Explanation b. 4 kcal/g Made up of chains of sugar molecules, carbohydrates contain about 4 kcal/g. Proteins also contain 4 kcal/g, while fat contains 9 kcal/g and alcohol contains 7 kcal/g. ACE Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals, p. 160 2) Contributing to cell membrane function, making bile acids essential for fat absorption, metabolizing fat-soluble vitamins, and making vitamin D are all functions of which nutrient? a. b. c. d. Protein Carbohydrate Cholesterol Omega-3 fatty acids Explanation c. Cholesterol Cholesterol, a fat-like, waxy, rigid four-ring structure, plays an important role in cell membrane function. It also helps to make bile acids (which are important for fat absorption), metabolize fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K), and make vitamin D and some hormones such as estrogen and testosterone. ACE Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals, p. 162 3) Which of the following MUST be consumed in the diet? a. b. c. d. Vitamin K Biotin Vitamin D Folate Explanation d. Folate Vitamins must be consumed through food with only three exceptions: vitamin K and biotin can also be produced by normal intestinal flora (bacteria that live in the intestines and are critical for normal gastrointestinal function), and vitamin D can be self-produced with sun exposure. ACE Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals, p. 162 4) A client who just found out she is pregnant asks what foods to eat to increase her intake of folic acid. What would be the BEST response? a. b. c. d. Green leafy vegetables, organ meats, dried peas, beans, and lentils Citrus fruits, berries, and vegetables Green leafy vegetables, fruit, dairy, and grain products Milk, liver, eggs, and peanuts Explanation a. Green leafy vegetables, organ meats, dried peas, beans, and lentils These foods are the best sources of folate, or folic acid. Citrus fruits, berries, and vegetables are good sources of vitamin C; green leafy vegetables, fruit, dairy, and grain products are good sources of vitamin K; and milk, liver, eggs, and peanuts are good sources of choline. ACE Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals, p. 164 5) Which of the following minerals has a recommended dietary allowance (RDA) that is more than twice as high for women than it is for men? a. b. c. d. Zinc Iron Phosphorus Copper Explanation b. Iron The RDA for iron for women is 18 mg, while it is only 8 mg for men. Iron plays an essential role in hemoglobin formation, improves blood quality, and increases resistance to stress and disease. ACE Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals, p. 165 6) A client must achieve a 1,000-calorie deficit per day in order to lose 1 lb per week. a. True b. False Explanation b. False 3,500 calories = 1 lb. Therefore, a 1,000 calorie per day deficit will lead to a loss of 2 lb per week. The Dietary Guidelines recommend that those trying to lose weight aim for a 500-calorie deficit per day, achieved through decreased caloric intake and/or increased physical activity. Over the course of a week, the 3,500 calorie deficit should lead to a loss of 1 pound. For optimal long-term success and overall health, gradual weight loss of no more than 1 to 2 pounds per week is best. ACE Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals, p. 174 7) Which of the following is NOT among the 10 insights gleaned from the experiences of the National Weight Control Registry? a. b. c. d. Eat breakfast Be mindful Avoid the scale Be optimistic Explanation c. Avoid the scale While it is not advisable to become obsessive about weight to the nearest 0.01 pounds, people who maintain their weight loss keep tabs on the scale, weighing themselves at least once per week. ACE Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals, p. 176 8) In most cases, athletic performance will improve when the individual is on a low-fat diet where fat intake is below 15% of total calories. a. True b. False Explanation b. False The American Dietetic Association recommends that athletes consume a comparable proportion of food from fat as the general population—that is, 20 to 25% of total calories. There is no evidence of a performance benefit from a very low-fat diet (<15% of total calories) or from a high-fat diet (>30% of total calories). ACE Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals, p. 182 9) A client with which of the following conditions should receive comprehensive nutrition counseling before beginning an exercise program? a. b. c. d. Osteoporosis Hyponatremia Hypertension Diabetes Explanation d. Diabetes It is especially important for people with diabetes to balance nutrition intake with exercise and insulin or other medications in order to maintain a regular blood sugar level throughout the day. All individuals with diabetes who have not already had a comprehensive nutrition consultation prior to beginning an exercise program should be referred to a registered dietitian for an evaluation and nutrition education. ACE Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals, p. 188 10) A client who is also a high school soccer player is interested in using the glycemic index to guide him as he “refuels” after practices and matches. Which of the following would be the BEST snack choice? a. b. c. d. Dried fruit Rye bread Oatmeal Strawberries Explanation a. Dried fruit High-GI carbohydrates, including dried fruit, are best for refueling. Rye bread is a medium-GI carbohydrates, while oatmeal and strawberries are low-GI carbohydrates. ACE Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals, p. 179 Quiz #5: Chapter 5 – Physiology of Training ACE’s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals 1) The sinoatrial node (SA node), which is sometimes called the pacemaker of the heart, is located in which chamber of the heart? a. b. c. d. Right atrium Right ventricle Left atrium Left ventricle Explanation a. Right atrium The SA node is located on the posterior wall of the right atrium, while the atrioventricular node (AV node) is located on the floor of that same chamber. ACE’s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals, p. 214 2) Which of the following is NOT a method the body uses to preserve blood volume during steady-state exercise? a. b. c. d. Increasing heart rate Increasing stroke volume Increasing vasoconstriction in non-working muscles Releasing vasopressin and aldosterone Explanation b. Increasing stroke volume The following changes take place to preserve blood volume: A progressive increase in heart rate at steady-state exercise to maintain cardiac output and offset the small decrease in stroke volume associated with the fluid loss A compensation in blood pressure via further vasocontriction in the non-exercising regions to maintain peripheral resistance and blood pressure A release of hormones—antidiuretic hormone, or vasopressin, and aldosterone—to help reduce water and sodium losses from the body ACE’s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals, p. 216 3) Tidal volume decreases after an exerciser crosses the second ventilatory threshold (VT2). a. True b. False Explanation a. True During submaximal exercise (before reaching VT2), ventilation increases linearly with oxygen consumption and carbon dioxide production. This occurs primarily through an increase in tidal volume (i.e., the volume of air inhaled and exhaled per breath). At higher or near-maximal intensities, the frequency of breathing becomes more pronounced and minute ventilation rises disproportionately to the increases in oxygen consumption. Tidal volume decreases as breathing rate increases. ACE’s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals, p. 217 4) What hormone dilates the respiratory passages and reduces digestive activity and bladder emptying during physical activity? a. b. c. d. Insulin Norepinephrine Epinephrine Cortisol Explanation c. Epinephrine In addition to its effects on the cardiovascular and metabolic systems, epinephrine dilates the respiratory passages to aid in moving air into and out of the lungs, and reduces digestive activity and bladder emptying during exercise. ACE’s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals, p. 218 5) Which slow-acting hormone stimulates the mobilization of free fatty acids from adipose tissue, mobilizes glucose synthesis in the liver, and decreases the rate of glucose utilization in the cells? a. b. c. d. Growth hormone Glucagon Insulin Cortisol Explanation d. Cortisol Cortisol is a glucocorticoid released from the adrenal cortex that stimulates free fatty acid (FFA) mobilization from adipose tissue, mobilizes glucose synthesis in the liver (i.e., gluconeogenesis), and decreases the rate of glucose utilization by the cells. Its effect is slow, however, allowing other fastacting hormones such as epinephrine and glucagon to primarily deal with glucose and FFA mobilization. ACE’s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals, p. 219 6) What is the only macronutrient whose stored energy generates adenosine triphosphate (ATP) anaerobically? a. b. c. d. Protein Fat Cholesterol Carbohydrate Explanation d. Carbohydrate Carbohydrate serves as the major food fuel for the metabolic production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is a chemical compound required for all cellular work. Importantly, carbohydrate is the only macronutrient whose stored energy generates ATP anaerobically. This is crucial during maximal exercise that requires rapid energy release above levels supplied by aerobic metabolism. ACE’s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals, p. 220 7) Which mechanism of thermoregulation is the major contributor during exercise? a. b. c. d. Convection Radiation Evaporation Excretion Explanation c. Evaporation Though evaporation accounts for only 20% of thermoregulation while at rest, it accounts for approximately 80% of thermoregulation during exercise. ACE’s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals, p. 225 8) What is the primary advantage of the increase in blood volume that results from chronic cardiorespiratory exercise? a. b. c. d. Decreased cardiac stress Improved VO2max Enhanced oxygen delivery to working muscles Reduced work environment for the heart Explanation c. Enhanced oxygen delivery to working muscles A physical-performance advantage of reduced blood viscosity, which is direct result of the increased blood volume, is that it enhances oxygen delivery to the active skeletal muscles, because the blood flows more easily through the vessels, including the capillaries. The other three choices are associated with increases in heart size and volume. ACE’s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals, p. 227 9) During what phase of the general adaptation syndrome will a client see progressive increases in muscle size and strength? a. b. c. d. Shock phase Adaptation phase Alarm phase Exhaustion phase Explanation b. Adaptation phase The adaptation phase, or resistance phase, generally begins around weeks four through six and represents major muscular adaptations (biochemical, mechanical, and structural). This phase is characterized by progressive increases in muscle size and strength. ACE’s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals, p. 232 10) An individual is using a resistance band to perform very short-duration (less than 2 seconds per stretch) hamstring stretches in sets of eight repetitions. What flexibility-training technique is this person using? a. b. c. d. Ballistic stretching Dynamic stretching Proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation Active isolated stretching Explanation d. Active isolated stretching Active isolated stretching follows a design similar to a traditional strength-training workout. Instead of holding stretches for 15 to 30 seconds at a point of resistance (i.e., mild discomfort), stretches are never held for more than two seconds. The stretch is then released, the body segment returned to the starting position, and the stretch is repeated for several repetitions. ACE’s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals, p. 243 Quiz #6: Chapter 1 – Role and Scope of Practice for the Personal Trainer ACE’s Personal Trainer Manual, 4th Edition 1) Most health benefits occur with at least __________ a week of moderate-intensity physical activity, such as brisk walking. Additional benefits occur with more physical activity. a. b. c. d. 60 minutes 75 minutes 150 minutes 180 minutes Explanation c. 150 minutes Most health benefits occur with at least 150 minutes a week of moderate-intensity physical activity, such as brisk walking. Additional benefits occur with more physical activity. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, Chapter 1, p. 4 2) Which of the following accounts for the unique position that personal trainers hold in the allied healthcare continuum? a. They are able to provide detailed dietary planning to combat chronic illnesses b. They are at the top of the allied healthcare pyramid due to the extended time they spend with clients c. They are able to show clients how to exercise effectively while following physicians’ general recommendations d. They are licensed professionals who can prescribe specific exercise programs Explanation c. They are able to show clients how to exercise effectively while following physicians’ general recommendations While other members of the allied healthcare continuum might also give patients or clients guidelines for general exercise (e.g., “try to walk up to 30 minutes per day, most days of the week”), few of them actually teach clients how to exercise effectively. This is where personal trainers hold a unique position in the allied healthcare continuum. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, Chapter 1, p. 6 3) What is the primary purpose of a fitness certification? a. b. c. d. To protect the public from harm To prove mastery of the profession To increase one’s earning potential To provide hands-on experience Explanation a. To protect the public from harm The primary purpose of a certification is to protect the public from harm by assessing if the professional can perform the job in a safe and effective manner. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 7 4) Which of the following is NOT part of the definition of “scope of practice”? a. b. c. d. The legal range of services that professionals in a given filed can provide The code of ethics that must be adhered to while in the workplace The setting in which the services can be provided Guidelines or parameters that must be followed Explanation b. The code of ethics that must be adhered to while in the workplace A scope of practice defines the legal range of services that professionals in a given field can provide, the settings in which those services can be provided, and the guidelines or parameters that must be followed. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 7 5) According the general scope of practice for fitness professionals, personal trainers can rehabilitate clients who are recovering from musculoskeletal injuries. a. True b. False Explanation b. False Personal trainers can design exercise programs once clients have been released from rehabilitation, but they cannot “rehabilitate” clients after injury. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 8 6) As a general rule, ACE recommends that candidates allow __________ of study time to adequately prepare for the ACE Personal Trainer Certification Exam. a. b. c. d. 1 to 3 months 3 to 6 months 6 to 9 months 9 to 12 months Explanation b. 3 to 6 months As a general rule, ACE recommends that candidates allow three to six months of study time to adequately prepare for the ACE Personal Trainer Certification Exam. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 10 7) Diagnosing the cause of a client’s lordosis posture and prescribing an exercise program to treat it is within a personal trainer’s scope of practice. a. True b. False Explanation b. False Fitness professionals must never “diagnose” a client’s condition or “prescribe” any treatment. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 11 8) To renew certification for a new two-year cycle, ACE-certified Professionals must complete a minimum of _____ hours of continuing education credits and maintain a current certificate in ________________ and, if living in North America, automated external defibrillation. a. b. c. d. 10; cardiopulmonary resuscitation 20; risk management 20; cardiopulmonary resuscitation 30; risk management Explanation c. 20; cardiopulmonary resuscitation ACE certifications are valid for two years from the date earned, expiring on the last day of the month. To renew certification for a new two-year cycle, ACE-certified Professionals must complete a minimum of 20 hours of continuing education credits and maintain a current certificate in cardiopulmonary resuscitation and, if living in North America, automated external defibrillation. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 12 9) What should a personal trainer do if a client insists on using dietary supplements despite the trainer’s assurance that his or her fitness goals can be met without them? a. Refer the client to the health club’s sales team b. Refer the client to a registered dietitian or physician c. Check that the facility’s insurance policy covers the sale of these products d. Stop training the client until he or she agrees to stop using these products Explanation b. Refer the client to a registered dietitian or physician The personal trainer can help the client understand that fitness goals can be reached without supplements and that supplements can have negative and potentially harmful side effects. If a client insists on using dietary supplements, the personal trainer should refer the client to a qualified physician or registered dietitian for guidance. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 14 10) Which of the following is an appropriate response to a client who mentions being sore following a weekend tennis tournament? a. b. c. d. Recommending the use of over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications Recommending the use of a creatine supplement prior to his or her next tournament Providing deep tissue massage to help relieve the soreness Discussing the proper technique for icing the affected areas Explanation d. Discussing the proper technique for icing the affected area Discussing the proper technique for icing the affected area is the appropriate response. The other options all fall outside the ACE scope of practice. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 15 Quiz #7: Chapter 2 – Principles of Adherence and Motivation ACE’s Personal Trainer Manual, 4th Edition 1) Adherence is defined as the psychological drive that gives behavior direction and purpose. a. True b. False Explanation b. False For the purposes of a fitness professional, exercise adherence refers to voluntary and active involvement in an exercise program. Motivation is defined as the psychological drive that gives behavior direction and purpose. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 26 2) More than ____% of people who start a new program will drop out within the first six months. a. b. c. d. 25 50 60 75 Explanation b. 50 More than 50% of people who start a new program will drop out within the first six months. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 26–27 3) Which of the following is NOT one of the three primary categories of potential determinants for physical activity? a. b. c. d. Personal attributes Physical attributes Environmental factors Physical-activity factors Explanation b. Physical attributes The potential determinants for physical activity can be broken down into three categories: • Personal attributes • Environmental factors • Physical-activity factors ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 27 4) General trends reveal that members of which of the following populations are MOST LIKELY to be performing higher levels of physical activity in unsupervised settings? a. b. c. d. Older adults Men Those with fewer years of education Those in a lower socioeconomic bracket Explanation b. Men Men demonstrate higher and more consistent activity adherence than women. Lower levels of physical activity participation are seen with increasing age, fewer years of education, and low income. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 27 5) What is arguably the most important and influential personal attribute variable when predicting adherence to physical activity? a. b. c. d. Activity history Obesity level Cardiovascular disease status Social support network Explanation a. Activity history Activity history is arguably the most important and influential personal attribute variable. In supervised exercise programs, past program participation is the most reliable predictor of current participation. This relationship between past participation and current participation is consistent across gender, obesity, and coronary heart disease status. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 27–28 6) ________________ is the most common excuse for not exercising and for dropping out of an exercise program. a. b. c. d. Perceived lack of time Lack of access to facilities Lack of social support Lack of improvement Explanation a. Perceived lack of time Perceived lack of time is the most common excuse for not exercising and for dropping out of an exercise program. The perception of not having enough time to exercise is likely a reflection of not being interested in or enjoying the activity, or not being committed to the activity program. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 28 7) Which of the following individuals is MOST LIKELY to adhere to a supervised physical-activity program? a. A highly motivator beginner who elects to begin a vigorous-intensity exercise program b. An individual who perceives his health to be poor and had been encouraged by his doctor to exercise c. An obese man who is motivated by a fear of adverse health conditions that are common in his family d. A middle-aged man who has prehypertension but believes he has personal control over his health Explanation d. A middle-aged man who has prehypertension but believes he has personal control over his health A belief in personal control over health outcomes is a consistent predictor of unsupervised exercise activity participation among healthy adults. Regarding the other options, the drop-out rate in vigorousintensity exercise programs is almost twice as high as in moderate-intensity activity programs; those who perceive their health to be poor are unlikely to start or adhere to an activity program; and obese individuals are typically less active than normal-weight individuals, and are less likely to adhere to supervised exercise programs. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 27–29 8) Which of the following terms is defined as the belief in one’s own capabilities to successfully engage in a behavior? a. b. c. d. Intrinsic motivation Self-efficacy Extrinsic motivation Locus of control Explanation b. Self-efficacy Self-efficacy is defined as the belief in one’s own capabilities to successfully engage in a behavior. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 30 9) When developing SMART goals, which of the following types of goals should be AVOIDED? a. b. c. d. Long-term goals Outcome goals Negative goals Performance goals Explanation c. Negative goals Setting negative goals puts the focus on the behavior that should be avoided, not the behavior to be achieved. It is important that the client is thinking about achievement, not avoidance. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 33 10) What is the most important tool when dealing with a client who is at risk for relapse? a. b. c. d. Enhancing the client’s assertiveness Developing a system of social support Planning ahead and being prepared Signing behavioral contracts Explanation c. Planning ahead and being prepared The most important tool in dealing with a relapse is planning ahead and being prepared. Personal trainers should educate their clients about the potential occurrence of a relapse and prepare them in advance, so that they are able to get back on track with their activity programs soon after experiencing a relapse. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 34 Quiz #8: Chapter 3 – Communication and Teaching Techniques ACE’s Personal Trainer Manual, 4th Edition 1) Which of the following presents the four stages of the client–trainer relationship in their proper order? a. b. c. d. Investigation, planning, action, rapport Rapport, investigation, planning, action Rapport, planning, investigation, action Planning, rapport, investigation, action Explanation b. Rapport, investigation, planning, action The four stages of the client–trainer relationship, in their proper order, are rapport, investigation, planning, and action. The rapport stage involves setting a foundation of mutual understanding and trust; the investigation stage involves reviewing the client's health and fitness data and history; the planning stage involves designing an exercise program in partnership with the client; and the action stage is when the client begins exercising. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 40 2) A loud, tense voice communicates confidence and professionalism when speaking to a new client. a. True b. False Explanation b. False A loud, tense voice tends to make people nervous. Personal trainers should try to develop a voice that is firm and confident to communicate professionalism. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 42 3) Which of the following body positions may be interpreted by a client as aggressiveness on the part of the trainer? a. b. c. d. Standing with an open body position Seated while leaning slightly forward Standing with hands on hips Seated behind a desk with legs crossed Explanation c. Standing with hands on hips An open, well-balanced, erect body position communicates confidence, while a rigid, hands-on-hips stance may be interpreted as aggressive. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 42 4) What personality style does a client have if he scores high on the sociability scale and low on the dominance scale? a. b. c. d. Deliberator Director Collaborator Expressor Explanation c. Collaborator Collaborators are high on the sociability scale and low on the dominance scale. They tend to be emotionally open, relationship oriented, and favor relationships over results. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 43 5) When working with a client whose personality style is classified as “expressor,” which of the following approaches would be the BEST option for a personal trainer? a. b. c. d. Offer incentives and rewards; stimulate the client’s thoughts and provoke ideas Be clear, concise, and business-like; appeal to the need for action and problem-solving Be candid, open and patient, personally interested and supportive, and goal oriented Provide consistent, accurate follow-ups; supply information to supply the need for detail Explanation a. Offer incentives and rewards; stimulate the client’s thoughts and provoke ideas Offering incentives and rewards, stimulating the client’s thoughts, and provoking ideas are effective techniques when working with “expressors.” The other techniques listed are more effective when working with other common personality styles. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 43 6) A personal trainer who is seeking clarification from a client by trying to restate the main points and feelings in a client’s communication is using which method of effective listening? a. b. c. d. Encouraging Paraphrasing Reflecting Summarizing Explanation c. Reflecting The personal trainer can use the listening technique of reflecting to demonstrate understanding or seek clarification by trying to restate the main points and feelings in the client’s communication. The client can correct a conclusion if it is wrong, or explore the reflection in more depth if it is correct. Reflections should help to move the conversation in productive directions as well as indicate effective listening. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 47 7) “I will perform a full-body resistance-training workout twice every week” is an example of which type of goal? a. b. c. d. SMART goal Process goal Product goal Time-bound goal Explanation b. Process goal A process goal is something that the client does, as opposed to something he or she achieves. Process goals are easy to track and provide short-term successes. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 48 8) Motivational interviewing is most commonly done during which stage of the client–trainer relationship? a. b. c. d. Rapport Investigation Planning Action Explanation c. Planning Motivational interviewing refers to a method of speaking with people in a way that motivates them to make a decision to change their behavior. Motivational interviewing may help clients feel the need to become more active and make a decision to start exercising. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 50–51 9) The three components of properly phrased feedback are BEST presented in what order? a. Correct errors; provide reinforcement for what was done well; motivate clients to continue practicing and improving b. Provide reinforcement for what was done well; correct errors; motivate clients to continue practicing and improving c. Motivate clients to continue practicing and improving; provide reinforcement for what was done well; correct errors d. Correct errors; motivate clients to continue practicing and improving; provide reinforcement for what was done well Explanation b. Provide reinforcement for what was done well; correct errors; motivate clients to continue practicing and improving Feedback should do three things: • Provide reinforcement for what was done well • Correct errors • Motivate clients to continue practicing and improving The correcting of errors, which may be seen as the more “negative” point, should be sandwiched between reinforcement and motivation. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 54 10) Clients who are beginning the basics of a particular movement and are ready for specific feedback are in which stage of motor learning? a. b. c. d. Cognitive Associative Autonomous Affective Explanation b. Associative In the associative stage of learning, clients begin to master the basics and are ready for more specific feedback that will help them refine the motor skill. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 58 Quiz #9: Chapter 4 – Basics of Behavior Change and Health Psychology ACE’s Personal Trainer Manual, 4th Edition 1) Which behavioral theory model is based on a prediction that people engage in a health behavior depending on the perceived threat they feel regarding a health problem? a. b. c. d. Transtheoretical model of behavioral change Health belief model Self-efficacy model Stages-of-change model Explanation b) Health belief model The health belief model predicts that people will engage in a health behavior (e.g., exercise) based on the perceived threat they feel regarding a health problem and the pros and cons of adopting the behavior. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 64 2) What is the most influential source of self-efficacy information? a. b. c. d. Past performance experience Imaginal experience Vicarious experience Emotional state Explanation a) Past performance experience Past performance experience is the most influential source of self-efficacy information. Personal trainers should ask clients about their previous experiences with exercise, fitness facilities, and personal trainers. These previous experiences will strongly influence self-efficacy. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 66 3) People with low self-efficacy are more likely to choose non-challenging tasks that are easy to accomplish. a. True b. False Explanation a) True People with low self-efficacy will be more likely to choose non-challenging tasks that are nonthreatening and easy to accomplish. They will display minimal effort to protect themselves in the face of a challenge—since failing when not working hard will be a lesser blow to their self-efficacy than failing when doing their best—and, if faced with too many setbacks, they are likely to lose faith, give up, and drop out of the program. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 67 4) A prospective client tells you that he has been going for 2-mile walks a couple of times each week for the past two months, and that he joined the gym because he is finally ready to adopt a more structured workout regimen. What is this individual’s stage of change? a. b. c. d. Contemplation Preparation Action Maintenance Explanation b) Preparation The preparation stage is marked by some physical activity, as individuals are mentally and physically preparing to adopt an activity program. Activity during the preparation stage may be a sporadic walk, or even a periodic visit to the gym, but it is inconsistent. People in the preparation stage are ready to adopt and live an active lifestyle. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 67 5) Which of the following intervention strategies would be LEAST APPROPRIATE when working with someone in the precontemplation stage? a. Make inactivity a relevant issue b. Provide information about the risks of being inactive and the benefits of being active c. Provide information from multiple sources (e.g., news, posters, pamphlets, general healthpromotion material) d. Introduce different types of exercise activities to find something the individual enjoys Explanation d) Introduce different types of exercise activities to find something the individual enjoys This intervention is most appropriate for someone in the preparation stage. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 69 6) ________________ involves the number of pros and cons perceived about adopting and/or maintaining an activity program. a. b. c. d. Processes of change Self-efficacy Operant conditioning Decisional balance Explanation d. Decisional balance One of the four components of the transtheoretical model, decisional balance refers to the number of pros and cons that an individual perceives about adopting and/or maintaining an activity program. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 69 7) Which of the following occurs when a positive stimulus that once followed a behavior is removed and the likelihood that the behavior will reoccur is decreased? a. b. c. d. Positive reinforcement Negative reinforcement Extinction Punishment Explanation c) Extinction Extinction occurs when a positive stimulus that once followed a behavior is removed and the likelihood that the behavior will reoccur is decreased. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 73 8) A client leaves a gym bag on the front seat of his car each morning as a reminder to work out on his way home from work. What behavior-change strategy is he using? a. b. c. d. Stimulus control Observational learning Shaping Operant conditioning Explanation a) Stimulus control Stimulus control refers to making adjustments to the environment to increase the likelihood of healthy behaviors. Simple and effective stimulus-control strategies may include choosing a gym that is in the direct route between home and work; keeping a gym bag in the car that contains all the required items for a workout; having workout clothes, socks, and shoes laid out for early morning workouts; and writing down workout times as part of a weekly schedule. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 74 9) When should behavior contracts and written agreements be revised or updated? a. b. c. d. Whenever the client has a relapse into inactivity After the client finishes his final purchased workout Never; they should be permanent documents When goals are met or programs are modified Explanation d) When goals are met or programs are modified It is important that a written agreement is reviewed and adjusted at all program-modification points. Similarly, the behavior contract must be revised and updated as goals are met and programs are modified. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 74 10) After several months of working with a client, a personal trainer notes that the client’s self-efficacy and ability levels have improved. How should this affect the amount of external feedback the trainer provides to the client? a. b. c. d. The trainer should increase the amount of external feedback The amount of feedback should not change The trainer should taper the amount of external feedback The trainer should immediately stop providing external feedback Explanation c) The trainer should taper the amount of external feedback As self-efficacy and ability build, trainers should taper off the amount of external feedback they provide, encouraging the clients to start providing feedback for themselves. Clients must learn to reinforce their own behaviors by providing internal encouragement, error correction, and even punishment. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 75 Quiz #10: Chapter 5 – Introduction to the ACE Integrated Fitness Training Model ACE’s Personal Trainer Manual, 4th Edition 1) The following list presents the four phases of the functional movement and resistance training component of the ACE IFT Model in their proper order. • Stability and mobility training • Movement training • Load training • Performance training a. True b. False Explanation a. True The proper order of the four phases of the functional movement and resistance training component of the ACE IFT Model is as follows: stability and mobility training, movement training, load training, and performance training. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 86 2) During what phase of the functional movement and resistance training component of the ACE IFT Model is the application of external resistance to functional movement patterns a primary focus? a. b. c. d. Stability and mobility training Movement training Load training Performance training Explanation c) Load training The focus of phase 3, or load training, is on applying external resistances, or loads, to functional movement patterns. Phase 3 applies the traditional resistance-training methodology for endurance, hypertrophy (or strength-endurance), and strength to the client’s particular goals. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 88 3) A client who is in the load-training phase of functional movement and resistance training will be working in the anaerobic-endurance training phase of cardiorespiratory training. a. True b. False Explanation a. False While these two phases both represent phase 3 of their respective training components, it is important to understand that each client will progress from one phase to the next according to his or her unique needs, goals, and available time to commit to training. Many clients will be at different phases of the two training components based on their current health and fitness levels. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 86 4) It is essential that personal trainers conduct assessments of muscular strength and endurance before a new client begins a stability and mobility training program. a. True b. False Explanation b) False No assessments of muscular strength or endurance are required prior to designing and implementing an exercise program during this phase. Assessments that should be conducted early in this phase include basic assessments of posture, balance, movement, and range of motion of the ankle, hip, shoulder complex, and thoracic and lumbar spine. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 89 5) During which phase of the functional movement and resistance training component of the ACE IFT Model should assessments of muscular strength and endurance be introduced? a. b. c. d. Phase 1 Phase 2 Phase 3 Phase 4 Explanation c) Phase 3 During phase 3, or load training, assessments of muscular strength and endurance are introduced to facilitate program design and quantify progress. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 90 6) No assessments are recommended during the aerobic-base training phase of cardiorespiratory training. a. True b. False Explanation a) True No assessments are recommended during the aerobic-base training phase, since many of the clients who start in this phase will be unfit and may have difficulty completing an assessment of this nature. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 93 7) What is a PRIMARY goal of introducing interval training during phase 2 of a client’s cardiorespiratory training program? a. b. c. d. To improve aerobic endurance by raising the intensity of exercise To add variety to the program to avoid boredom To help the client exercise at intensities beyond the first ventilatory threshold To increase the client’s adherence to the program by improving his or her mood state Explanation a) To improve aerobic endurance by raising the intensity of exercise The goal of interval training will be to improve aerobic endurance by raising the intensity of exercise performed at VT1, and to improve the client’s ability to utilize fat as a fuel source. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 93 8) A client who is in phase 3 of the cardiorespiratory training component of the ACE IFT Model is beginning to utilize the three-zone training model based on ventilatory threshold. Approximately what percentage of his time should be spent training between VT1 and VT2? a. b. c. d. >80% 70–80% 10–20% <10% Explanation d) <10% The full cardiorespiratory exercise program should be composed of: • Zone 1 (at or below VT1): 70–80% of training time • Zone 2 (between VT1 and VT2): <10% of training time • Zone 3 (at or above VT2): 10–20% of training time ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 94 9) Clients working in the anaerobic-power training phase of the ACE IFT Model generally have goals related to _____________. a. b. c. d. Long-duration, moderate-intensity events requiring great endurance Long-duration events of a nearly constant speed and intensity Short-duration, high-intensity efforts during longer endurance events Short-duration, high-intensity events requiring explosive power but little endurance Explanation c. Short-duration, high-intensity efforts during longer endurance events Clients working in this phase of cardiorespiratory training will be training for competition and have specific goals that relate to short-duration, high-intensity efforts during longer endurance events, such as speeding up to stay with a pack in road cycling. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 95 10) What is the most important goal when working with special-population clientele? a. To provide them with initial positive experiences that promote adherence through easily achieved initial successes b. To move them through the various phases of the ACE IFT Model with the ultimate goal of improving fitness and performance c. To reach the stage of resistance training during which external loads are introduced, as this will improve their performance of activities of daily living d. To teach them the importance of daily exercise and continuing with their programs even during times of illness or discomfort Explanation a. To provide them with initial positive experiences that promote adherence through easily achieved initial successes The most important goal with all clients is to provide them with initial positive experiences that promote adherence through easily achieved initial successes. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 95 Quiz #11: Chapter 6 – Building Rapport and the Initial Investigation Stage ACE’s Personal Trainer Manual, 4th Edition 1) The first objective when meeting a prospective client is to gather information on the client’s goals and objectives. a. True b. False Explanation b) False The first objective when meeting a prospective client is to first build a foundation for a personal relationship with the individual; gathering information on the client’s goals and objectives is secondary. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 100 2) Which of the following is NOT one of the primary purposes of a pre-participation screening? a. Identifying the absence or presence of known disease b. Identifying the individual’s stage of behavioral change c. Identifying individuals with medical contraindications who should be excluded from exercise or physical activity d. Identifying those individuals with medical conditions who should participate in medically supervised programs Explanation b) Identifying the individual’s stage of behavioral change The purposes of the pre-participation screening include the following: Identifying the presence or absence of known cardiovascular, pulmonary, and/or metabolic disease, or signs or symptoms suggestive of cardiovascular, pulmonary, and/or metabolic disease Identifying individuals with medical contraindications (health conditions and risk factors) who should be excluded from exercise or physical activity until those conditions have been corrected or are under control Detecting at-risk individuals who should first undergo medical evaluation and clinical exercise testing before initiating an exercise program Identifying those individuals with medical conditions who should participate in medically supervised programs ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 105 3) Which of these follow-up actions would be most appropriate for an individual who answers “yes” to the following questions on the PAR-Q? “Is your doctor currently prescribing drugs (for example, water pills) for your blood pressure or heart c condition?” “In the past month, have you had chest pain when you were not doing physical activity?” a. b. c. d. Slowly and progressively start becoming more physically active Take part in a fitness appraisal before beginning exercise Talk with a doctor before beginning to exercise or undergoing a fitness appraisal Delay becoming much more physically active until feeling better Explanation c) Talk with a doctor before beginning to exercise or undergoing a fitness appraisal If a person answers “yes” to one or more questions on the PAR-Q, he or she should talk with a doctor by phone or in person BEFORE starting to become much more physically active or BEFORE having a fitness appraisal. He or she should also tell the doctor about the PAR-Q and which questions were answered YES. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 106 4) Which of the following is considered a positive risk factor for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease? a. b. c. d. Body mass index of 28 kg/m2 HDL cholesterol of 66 mg/dL Serum cholesterol of 195 mg/dL Systolic blood pressure of 143 mmHg Explanation d) Systolic blood pressure of 143 mmHg Systolic blood pressure > 140 mmHg and/or diastolic blood pressure > 90 mmHg, confirmed by measurements on at least two separate occasions, is considered to be a positive risk factor for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 108 5) For which of the following clients would a medical exam and graded exercise test be recommended before training begins? a. b. c. d. Low-risk client wanting to perform moderate exercise Low-risk client wanting to perform vigorous exercise Moderate-risk client wanting to perform moderate exercise High-risk client wanting to perform moderate exercise Explanation d) High-risk client wanting to perform moderate exercise A medical exam and GXT before exercise are recommended for moderate-risk clients engaged in vigorous exercise and high-risk clients engaged in moderate or vigorous exercise. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 109 6) Which of the following documents represents a client’s voluntary abandonment of the right to file a lawsuit against the personal trainer? a. b. c. d. Informed consent form Release of liability waiver Behavioral contract Medical release form Explanation b) Release of liability waiver This document is used to release a personal trainer from liability for injuries resulting from a supervised exercise program, and represents a client’s voluntary abandonment of the right to file a lawsuit. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 110 7) After how long a period of inactivity following an injury does disuse atrophy in the muscles surrounding the injury begin? a. b. c. d. Two hours Two days Two weeks Two months Explanation b. Two days Disuse atrophy of the muscles surrounding an injury may begin after just two days of inactivity. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 117 8) Which of these medications causes a dose-related decrease in a person’s resting, exercise, and maximal heart rates? a. b. c. d. Beta blockers Antihistamines Antidepressants Diuretics Explanation a) Beta blockers Beta blockers inhibit the effects of catecholamines (epinephrine and norepinephrine) throughout the body and reduce resting, exercise, and maximal heart rates. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 120 9) Which medication has no primary affect on heart rate, but can cause dangerous cardiac arrhythmias due to water and electrolyte imbalances? a. b. c. d. ACE inhibitors Calcium channel blockers Diuretics Bronchodilators Explanation c) Diuretics Diuretics are medications that increase the excretion of water and electrolytes through the kidneys. They have no primary effect on the heart rate, but they can cause water and electrolyte imbalances, which may lead to dangerous cardiac arrhythmias. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 121 10) Which of the following must be included as part of every client’s pre-participation screening? a. b. c. d. Body-composition testing Movement screens Static posture assessment Health-risk appraisal Explanation d) Health-risk appraisal Regardless of the assessments selected and how the assessment timelines are structured, trainers should remember that a health-risk appraisal must be included as a pre-participation screen. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 121–122 11) Which of the following is NOT cause to immediately stop a cardiorespiratory exercise test? a. b. c. d. Leg cramping Complaints of severe fatigue Nausea and lightheadedness Heavy breathing due to intense exercise Explanation d) Heavy breathing due to intense exercise While shortness of breath, wheezing, and difficult or labored breathing are on the list of symptoms that call for an immediate end to an exercise test, heavy breathing due to the intensity of the exercise is not. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 122 12) Which of the following is NOT a reason that the average resting heart rate for women is higher than that of men? a. b. c. d. Smaller heart chamber size Lower sympathetic drive Lower blood volume Lower hemoglobin levels Explanation b) Lower sympathetic drive The higher values found in the female RHR are attributed in part to: • Smaller heart chamber size • Lower blood volume circulating less oxygen throughout the body • Lower hemoglobin levels in women ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 125 13) _______________ represents the pressure that is exerted on the artery walls as blood remains in the arteries during the filling phase of the cardiac cycle. a. b. c. d. Resting blood pressure Maximal blood pressure Systolic blood pressure Diastolic blood pressure Explanation d) Diastolic blood pressure Diastolic blood pressure represents the pressure that is exerted on the artery walls as blood remains in the arteries during the filling phase of the cardiac cycle, or between beats when the heart relaxes. It is the minimum pressure that exists within one cardiac cycle. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 125 14) A client’s blood-pressure reading is 124/78 mmHg. How should the personal trainer classify this client? a. b. c. d. Normal Prehypertension Stage 1 hypertension Stage 2 hypertension Explanation b) Prehypertension Individuals are classified as prehypertensive when systolic blood pressure is 120–139 mmHg or diastolic blood pressure is 80–89 mmHg. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 128 15) Which of the following statements about the ratings of perceived exertion scale is CORRECT? a. When using ratings of perceived exertion, men tend to underestimate exertion, while women tend to overestimate exertion. b. When using the 0–10 scale, an RPE of 6 corresponds to a heart rate of 60 bpm c. When using the 6–20 scale, an RPE of 11 is considered “somewhat hard” d. Most deconditioned individuals find using the RPE scale to be very easy and intuitive Explanation a. When using ratings of perceived exertion, men tend to underestimate exertion, while women tend to overestimate exertion. Regarding the other choices, the 0–10 RPE scale does not directly correspond with heart rate, an RPE of 11 on the 6–20 scale is considered “fairly light,” and most deconditioned individuals find using the RPE scale difficult, as they find any level of exercise to be fairly hard. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th edition, p. 129 Quiz #12: Chapter 7 – Functional Assessments: Posture, Movement, Core, Balance, and Flexibility ACE’s Personal Trainer Manual, 4th Edition 1) Which of the following is a non-correctible factor related to postural deviations? a. b. c. d. Side dominance Structural deviations Lack of joint stability Lack of joint mobility Explanation b. Structural deviations The non-correctible factors related to postural deviations are as follows: • Congenital conditions (e.g., scoliosis) • Some pathologies (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis) • Structural deviations (e.g., tibial or femoral torsion, femoral anteversion) • Certain types of trauma (e.g., surgery, injury, amputations) The other choices are correctible factors. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 136 2) When designing an exercise program for a beginning exerciser, it is best to focus on enhancing muscular strength before shifting the focus to improving the client’s posture. a. True b. False Explanation b. False Given the propensity many individuals have toward poor posture, an initial focus of trainers should be to restore stability and mobility within the body and attempt to “straighten the body before strengthening it.” ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 137 3) Barring structural differences in the skeletal system, a pronated ankle ________________. a. b. c. d. Forces internal rotation of the tibia and slightly less internal rotation of the femur Causes a lengthening of the calf muscles and limits ankle dorsiflexion Has little effect on the rest of the body’s kinetic chain Moves the calcaneus into inversion, lifting the inside of the heel slightly off the ground Explanation a. Forces internal rotation of the tibia and slightly less internal rotation of the femur Ankle pronation forces internal rotation at the knee and places additional stresses on some knee ligaments and the integrity of the joint itself. Additionally, as pronation tends to move the calcaneus into eversion, this may actually lift the outside of the heel slightly off the ground (moving the ankle into plantarflexion). In turn, this may tighten the calf muscles and potentially limit ankle dorsiflexion. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 140 4) The coupling relationship between tight __________ and __________ is defined as the lower-cross syndrome. a. b. c. d. Rectus abdominis; hamstrings Hip flexors; erector spinae Rectus abdominis; erector spinae Hip flexors; hamstrings Explanation b. Hip flexors; erector spinae Tight or overdominant hip flexors are generally coupled with tight erector spinae muscles, producing an anterior pelvic tilt. This coupling relationship between tight hip flexors and erector spinae is defined as the lower-cross syndrome. A posterior pelvic tilt is caused by tightness in the rectus abdominis and hamstrings. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 142 5) Which pelvic tilt screen may be invalid if the individual exhibits well-developed gluteal muscles? a. b. c. d. The relationship of the ASIS and PSIS The appearance of lordosis in the lumbar spine The alignment of the pubic bone to the ASIS The degree of flexion or hyperextension in the knees Explanation b. The appearance of lordosis in the lumbar spine This technique may be invalid if an individual exhibits well-developed gluteal muscles, which will create a larger space and a perception of increased lordosis. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 143 6) An elevated shoulder may present with an overdeveloped or tight upper trapezius muscle. a. True b. False Explanation a. True An elevated shoulder may present with an overdeveloped or tight upper trapezius muscle, while a depressed shoulder may present with more forward rounding of the scapula. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 144–145 7) When performing a shoulder screen and observing the client from a posterior view, a trainer notices an outward protrusion of the vertebral borders, but not the inferior angles, of the scapulae. What deviation is most likely being observed? a. b. c. d. Scapular protraction Kyphosis Sway-back posture Winged scapulae Explanation a. Scapular protraction Noticeable protrusion of the vertebral (medial) border outward is termed “scapular protraction,” while noticeable protrusion of the inferior angle and vertebral (medial) border outward is termed “winged scapulae.” ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 145 8) What is the objective of conducting clearing tests prior to the performance of movement screens? a. b. c. d. To determine the client’s health and fitness level To identify any movements that exacerbate pain To identify clients who are unable to perform basic movements without losing balance To address any static postural deviations prior to introducing movement Explanation b. To identify any movements that exacerbate pain Prior to administering any movement screens, trainers should screen their clients for any potential contraindications associated with pain by using basic clearing tests. The objective when conducting clearing tests is to ensure that pain is not exacerbated by movement. Any client who exhibits pain during a clearing test should be referred to his or her physician and should not perform additional assessments for that part of the body. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 150 9) During the hurdle step screen, you observe that the client exhibits an anterior tilt with a forward torso lean. What muscles should you suspect of being underactive or weak? a. b. c. d. Stance-leg hip flexors Gluteus medius and maximus Hip adducts and tensor fascia latae Rectus abdominis and hip extensors Explanation d. Rectus abdominis and hip extensors If a client exhibits an anterior tilt with a forward torso lean, he or she likely has overactive or tight stance-leg hip flexors and underactive or weak rectus abdominis and hip extensors. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 154 10) During the Thomas Test, you observe that when the client holds the back and sacrum flat, the back of the lowered thigh touches the table, but the knee does not flex to 80 degrees. What muscle(s) should you suspect of being tight? a. b. c. d. Rectus femoris Iliopsoas Primary hip flexors Hamstrings Explanation a. Rectus femoris When a client is unable to flex the knee to 80 degrees, a personal trainer should suspect tightness in the rectus femoris, which does not allow the knee to bend. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 161 11) In your notes regarding a client performing the external and internal shoulder rotation tests, you recorded that the client displayed potential tightness in the infraspinatus and teres major. What might you have observed during the test that led to that conclusion? a. b. c. d. Client externally rotated the forearms 90 degrees to touch the mat Client displayed discrepancies between arms when externally rotating the forearms Client internally rotated the forearms 70 degrees toward the mat Client displayed discrepancies between arms when internally rotating the forearms Explanation d. Client displayed discrepancies between arms when internally rotating the forearms If a client displays an inability to internally rotate the forearm 70 degrees, or shows discrepancies between the limbs, there are two possible reasons: potential tightness in the lateral rotators of the arm (i.e., infraspinatus and teres minor) or the joint capsule and ligaments may be tight and limit rotation. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 165 12) Which of the following is NOT a reason to stop a client while he or she is performing the sharpened Romberg test? a. b. c. d. The client’s feet move on the floor The client’s eyes open The client exceeds 30 seconds with good postural control The client’s arms move from the folded position Explanation c. The client exceeds 30 seconds with good postural control During the sharpened Romberg test, the trainer should continue to time the client’s performance until one of the following occurs: the client loses postural control and balance, the client’s feet move on the floor, the client’s eyes open, the client’s arms move from the folded position, or the client exceeds 60 seconds with good postural control. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 167 13) A male client performs the stork-stand balance test and is able to hold the position for 46 seconds. How would you rate this client’s performance? a. b. c. d. Excellent Good Fair Poor Explanation b. Good A male client who is able to hold the stork-stand position for 41 to 50 seconds is categorized as “good.” ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 168 14) Apley’s scratch test is usually performed in conjunction with which of the following pairs of tests? a. b. c. d. Sharpened Romberg test and stork-stand balance test Thomas test and passive straight-leg raise test Shoulder flexion-extension test and internal-external rotation test of the humerus Blood pressure cuff test and muscle-length test Explanation c. Shoulder flexion-extension test and internal-external rotation test of the humerus Apley’s scratch test involves multiple and simultaneous movements of the scapulothoracic and glenohumeral joints in all three planes. This represents a challenge in evaluating shoulder movement and identifying movement limitations. To identify the source of the limitation, trainers can first perform various isolated movements in single planes to locate potentially problematic movements. Consequently, the scratch test is completed in conjunction with the shoulder flexion-extension test and the internal-external rotation test of the humerus. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 162 15) Which of the following joint movements from the anatomical position has an average range of motion of 0 degrees in healthy adults? a. b. c. d. Lumbar rotation Elbow extension Subtalar inversion Hip extension Explanation b. Elbow extension While elbow flexion has an average range of motion of 145 degrees, extension is not possible at the elbow. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 158 Quiz #13: Chapter 8 – Physiological Assessments ACE’s Personal Trainer Manual, 4th Edition 1) During a treadmill test, a client complains of leg cramping but feels that she will be able to finish the test. What is the MOST appropriate course of action? a. Monitor her progress closely and stop the test if her pain worsens b. Allow her to complete the test, as treadmill tests measure cardiorespiratory fitness, not muscular endurance c. Stop the test immediately and possibly refer the client to her primary healthcare professional d. Have her rest for a few minutes and rehydrate before continuing the test from the stopping point Explanation c. Stop the test immediately and possibly refer the client to her primary healthcare professional During the administration of any exercise test involving exertion, trainers must always be aware of identifiable signs or symptoms that merit immediate test termination and possible referral to a qualified healthcare professional. These symptoms include: • Onset of angina, chest pain, or angina-like symptoms • Significant drop (>10 mmHg) in systolic blood pressure (SBP) despite an increase in exercise intensity • Excessive rise in blood pressure (BP): SBP >250 mmHg or diastolic blood pressure (DBP) >115 mmHg • Excess fatigue, shortness of breath, or wheezing (does not include heavy breathing due to intense exercise) • Signs of poor perfusion: lightheadedness, pallor (pale skin), cyanosis (bluish coloration, especially around the mouth), nausea, or cold and clammy skin • Increased nervous system symptoms (e.g., ataxia, dizziness, confusion, syncope) • Leg cramping or claudication • Subject requests to stop • Physical or verbal manifestations of severe fatigue • Failure of testing equipment ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 174 2) Which of the following is NOT one of three sites used when performing skinfold measurements on a male client? a. b. c. d. Chest Thigh Abdomen Triceps Explanation d. Triceps For men, the three skinfold sites are the chest, thigh, and abdomen. The triceps, thigh, and suprailium are the three skinfold sites for women. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 178 3) After performing skinfold measurements with a male client, his body-fat percentage is calculated to be 26%. How would you rank this client in terms of body-fat percentage? a. b. c. d. Athlete Fitness Average Obese Explanation d. Obese In males, a body-fat percentage of 25% or higher is considered obese. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 184 4) _______________ provides an objective ratio describing the relationship between body weight and height. a. b. c. d. BMI DEXA MRI NIR Explanation a. BMI BMI, or body mass index, is an anthropometric measure that provides an objective ratio describing the relationship between body weight and height. The other three options are forms of body-composition assessment. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 185 5) Which of these assessments measures a client’s anaerobic capacity? a. b. c. d. Which of these assessments measures a client’s anaerobic capacity? Vertical jump test Kneeling overhead toss 300-yard shuttle run Explanation d. 300-yard shuttle run This test assesses anaerobic capacity or the highest rate of sustainable power over a predetermined distance. The other three tests assess a client’s anaerobic power, which involves a single repetition or event and represents the maximal amount of power the body can generate. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 235 6) What is the waist-to-hip ratio threshold at which a female client’s health is considered at risk? a. b. c. d. 0.79 0.82 0.86 0.95 Explanation c. 0.86 A female client’s health is considered at risk when her WHR is at or above 0.86. For men, that threshold is 0.95. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 188 7) Measuring VO2max in a laboratory involves the collection and analysis of _______________ during maximal exercise. a. b. c. d. Blood oxygen levels Exhaled air Core temperature Caloric expenditure Explanation b. Exhaled air VO2max, an excellent measure of cardiorespiratory efficiency, is an estimation of the body’s ability to use oxygen for energy, and is closely related to the functional capacity of the heart. Measuring VO2max in a laboratory involves the collection and analysis of exhaled air during maximal exercise. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 189 8) A personal trainer can accurately estimate VO2max from a client’s heart-rate response to exercise. a. True b. False Explanation a. True Research demonstrates that as workload increases, so do heart rate and oxygen uptake. In fact, heart rate and oxygen uptake exhibit a fairly linear relationship to workload. This relationship allows the personal trainer to accurately estimate VO2max from the heart-rate response to exercise with fairly good accuracy. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 189 9) If an activity requires a functional capacity of 6 METs, what is the total oxygen consumption of someone performing that activity? a. 0.6 mL/kg/min b. 6 mL/kg/min c. 10.5 mL/kg/min d. 21 mL/kg/min Explanation d. 21 mL/kg/min 1 MET is equal to 3.5 mL/kg/min, so 6 METs = 6 x 3.5 mL/kg/min = 21 mL/kg/min ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 191 10) Which of the following types of physiological assessment is contraindicated for a client with asthma? a. b. c. d. Cycle ergometer test Treadmill test Ventilatory threshold test Step test Explanation c. Ventilatory threshold test This type of testing is not recommended for: • Individuals with certain breathing problems [asthma or other chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)] • Individuals prone to panic/anxiety attacks, as the labored breathing may create discomfort or precipitate an attack • Those recovering from a recent respiratory infection ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 202 11) The end-point of the VT2 threshold test is determined by the client’s ability to recite the Pledge of Allegiance, or another memorized group of phrases. a. True b. False Explanation b. False The end-point of the talk test for VT1 (not the VT2 threshold test) is determined by the client’s ability to recite the Pledge of Allegiance, or another memorized group of phrases. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 202 12) Individuals who are short in stature may not be good candidates for which type of testing? a. b. c. d. Cycle ergometer tests Treadmill tests Ventilatory threshold tests Step tests Explanation d. Step tests Individuals who are short in stature are not good candidates for step testing, as they may have trouble with the step height, especially during the McArdle step test. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 208 13) Which of the three tests included in McGill’s torso muscular endurance test battery is a timed test involving a static, isometric contraction of the anterior muscles, stabilizing the spine until the individual exhibits fatigue and can no longer hold the assumed position? a. Trunk flexor endurance test b. Trunk lateral endurance test c. Trunk extensor endurance test Explanation a. Trunk flexor endurance test The flexor endurance test is the first in the battery of three tests that assesses muscular endurance of the deep core muscles. It is a timed test involving a static, isometric contraction of the anterior muscles, stabilizing the spine until the individual exhibits fatigue and can no longer hold the assumed position. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 217 14) A male client who weighs 190 pounds has a one-repetition maximum of 225 pounds on the bench press exercise. His relative strength for this exercise is __________. a. b. c. d. 225 pounds 0.84 35 pounds 1.18 Explanation d. 1.18 Relative strength is the maximum force a person is able to exert in relation to his or her body weight and is calculated using the formula: Relative strength = Absolute strength/Body weight, where Absolute strength is defined as the one-repetition maximum. In this case, Relative strength = 225 pounds/190 pounds = 1.18 ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 221 15) A competitive soccer player, whose sport requires an ability to accelerate, decelerate, change direction, and then accelerate again, is interested in completing an assessment to serve as a baseline against which he can measure future improvements. Which test will BEST measure these sports skills? a. b. c. d. 300-yard shuttle run 40-yard dash Pro agility test Margaria-Kalamen stair climb Explanation c. Pro agility test The pro agility test quickly and simply measures an individual’s ability to accelerate, decelerate, change direction, and then accelerate again. In fact, the National Football League and USA Women’s Soccer Team use this assessment as part of their battery of tests. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 237 Quiz #14: Chapter 9 – Functional Programming for Stability-Mobility and Movement ACE’s Personal Trainer Manual, 4th Edition 1) Which of the following joints favors stability over mobility? a. b. c. d. Ankle Knee Thoracic spine Glenohumeral Explanation b. Knee In terms of mobility and stability of joints along the kinetic chain, the knee favors stability over mobility, while the other three options favor mobility. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 247 2) Which of the following muscles exerts an upward pull on the anterior, inferior surface of the pelvis in an effort to maintain a neutral pelvic position? a. b. c. d. Erector spinae Hamstrings Rectus abdominis Hip flexors Explanation c. Rectus abdominis Maintenance of a neutral pelvic position is achieved via opposing force-couples between four major muscle groups that all have attachments on the pelvis. The rectus abdominis pulls upward on the anterior, inferior pelvis, while the hip flexors pull downward on the anterior, superior pelvis. On the posterior surface, the hamstrings pull downward on the posterior, inferior pelvis, while the erector spinae pull upward on the posterior, superior pelvis. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 250 3) When trying to meet the objective of the stability and mobility training phase by reestablishing appropriate levels of stability and mobility through the kinetic chain, a personal trainer should begin by targeting which region of the body? a. b. c. d. Lumbar spine Thoracic spine Hips Shoulders Explanation a. Lumbar spine The process begins by targeting an important proximal region of the body, the lumbar spine, which encompasses the body’s center of mass and the core. As this region is primarily stable, programming should begin by first promoting stability of the lumbar region through the action and function of the core. Once an individual demonstrates the ability to stabilize this region, the program should then progress to the more distal segments. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 251 4) After proximal stability is established in the lumbar spine, the focus of the stability and mobility training phase shifts to establishing _______________. a. b. c. d. Static balance Mobility and stability in the distal extremities Stability of the scapulothoracic spine Mobility of the pelvis and thoracic spine Explanation d. Mobility of the pelvis and thoracic spine A programming sequence that promotes stability and mobility within the body will adhere to the basic principle that proximal stability facilitates distal mobility. With this in mind, the next step after establishing stability in the lumbar spine is to address mobility of the pelvis and thoracic spine. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 252 5) Which stretching technique is MOST appropriate for deconditioned clients to perform DURING a workout? a. b. c. d. Dynamic stretching Active isolated stretching Proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation Myofascial release Explanation b. Active isolated stretching Active isolated stretching is the best choice for deconditioned clients during a workout. Dynamic stretching is only appropriate for conditioned clients and athletes, while myofascial release and proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation are more suitable during the warm-up and cool-down. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 253 6) Which stretching technique involves holding each stretch to the point of tension for 15 to 60 seconds? a. b. c. d. Dynamic stretching Static stretching Active isolated stretching Ballistic stretching Explanation b. Static stretching Static stretches should be taken to the point of tension, with clients performing a minimum of four repetitions and holding each repetition for 15 to 60 seconds. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 253 7) A skilled performance athlete who has established good flexibility would like to address functional flexibility during his pre-exercise stretching routine. What two types of stretching would be the BEST choices for this client? a. b. c. d. Active isolated stretching and dynamic stretching Dynamic stretching and ballistic stretching Static stretching and proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation Myofascial release and active isolated stretching Explanation b. Dynamic stretching and ballistic stretching Dynamic and ballistic stretches are appropriate during a pre-exercise stretching routine for athletes interested in improving their functional flexibility. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 253 8) Which of the following muscles is part of the outer layer of the core? a. b. c. d. Multifidi Diaphragm Quadratus lumborum Latissimus dorsi Explanation d. Latissimus dorsi The outermost layer consists of larger, more powerful muscles that span many vertebrae and are primarily responsible for generating gross movement and forces within the trunk. Muscles in this region include the rectus abdominis, erector spinae, external and internal obliques, iliopsoas, and latissimus dorsi. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 255 9) The strengthening of weakened muscles should begin with the performance of two to four repetitions of isometric muscle contractions, each held for five to 10 seconds at less than 50% of maximal voluntary contraction in a supported, isolated environment. a. True b. False Explanation a. True The strengthening of weakened muscles follows a progression model beginning with two to four repetitions of isometric muscle contractions, each held for five to 10 seconds at less than 50% of MVC in a supported, more isolated environment. The next progression is to dynamic, controlled ROM exercises incorporating one to three sets of 12 to 15 repetitions. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 254 10) A key role of the serratus anterior is to move the thorax toward a more fixed, stable scapulae. a. True b. False Explanation b. False During open kinetic chain (OKC) movements, a key role of the serratus anterior is to control movement of the scapulae against a more fixed ribcage. During closed kinetic chain movements, however, where the distal segment is more fixed, a key role of the serratus anterior is to move the thorax toward a more fixed, stable scapulae. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 274 11) The center of mass is generally slightly lower in men due to their increased body mass and narrower stance. a. True b. False Explanation b. False The location of the center of mass varies in individuals by body shape, size, and gender, being slightly higher in males due to greater quantities of musculature in the upper body. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 281 12) Which of the following techniques will reduce the balance challenge of an exercise? a. b. c. d. Narrowing the base of support Lowering the center of mass Looking up and down during the exercise Closing the eyes Explanation b. Lowering the center of mass Lowering the center of mass will reduce the balance challenge of an exercise, while the other choices will all increase the balance challenge. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 283 13) Standing on a single leg and taking a step mandates stability in each of the following regions EXCEPT the __________. a. b. c. d. Stance leg Hip Torso Raised leg Explanation d. Raised leg Standing efficiently on a single leg mandates stability in the stance-leg, hip, and torso, while simultaneously exhibiting mobility in the raised leg if stepping is involved. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 292 14) Which type of movement has the GREATEST need for thoracic mobility? a. b. c. d. Pushing movements Bend-and-lift movements Rotational movements Pulling movements Explanation c. Rotational movements The need for thoracic mobility is greater during rotational movements than with pushing and pulling movements, given the three-dimensional nature of the movement patterns. Performing these exercises without thoracic mobility or lumbar stability may compromise the shoulders and hips, and increase the likelihood for injury. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 304 15) Which of the following exercises BEST addresses the rotational movement pattern during the movement-training phase? a. b. c. d. Wood-chop Unilateral row Lunge Hip hinge Explanation a. Wood-chop The wood-chop is a rotational movement. The unilateral row is a pulling movement, the lunge is a single-leg movement, and the hip hinge is a bend-and-lift movement. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 304–306 Quiz #15: Chapter 10 – Resistance Training: Programming and Progressions ACE’s Personal Trainer Manual, 4th Edition 1) Which of the following terms is defined as the product of muscular strength and movement speed? a. b. c. d. Muscular endurance Muscular power Absolute strength Relative strength Explanation b. Muscular power Muscular power is the product of muscular strength and movement speed. Assuming that an individual’s movement speed remains the same, an increase in muscular strength is accompanied by a proportional increase in muscular power. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 317 2) Which of the following is a skill-related parameter that might be addressed in a client’s exercise program? a. b. c. d. Balance Flexibility Body composition Aerobic capacity Explanation a. Balance The skill-related parameters are as follows: power, speed, balance, agility, coordination, and reactivity. The other three options are health-related parameters. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 318 3) Training frequency is inversely related to both training __________ and training __________. a. b. c. d. Volume; type Type; intensity Volume; intensity Type; duration Explanation c. Volume; intensity Training frequency is inversely related to both training volume and training intensity. Less vigorous exercise sessions produce less muscle microtrauma, require less time for tissue remodeling, and can be performed more frequently. More vigorous exercise sessions produce more muscle microtrauma, require more time for tissue remodeling, and must be performed less frequently for optimum results. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 318 4) A client’s resistance-training regimen involves performing four sets of each exercise, with each set containing four repetitions. This training volume BEST addresses which training goal? a. b. c. d. Muscular hypertrophy Muscular endurance Muscular strength General muscle fitness Explanation c. Muscular strength Muscular strength is addressed with any training regimen involving the performance of two to six sets of six or fewer repetitions. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 321 5) What is the first progression made when utilizing the double-progressive training protocol? a. b. c. d. Adding resistance in 5% increments Adding repetitions to the set Adding sets to the workout Reducing the rest intervals Explanation b. Adding repetitions to the set The double-progressive strength-training protocol may be used with any repetition range. The first progression is adding repetitions, and the second progression is adding resistance in 5% increments. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 324 6) According the principle of reversibility, a client who stops performing resistance exercise will lose strength at about __________ that it was gained a. b. c. d. The same rate Twice the rate One-tenth the rate One-half the rate Explanation d. One-half the rate A client who stops performing resistance exercise will lose strength at about one-half the rate that it was gained. For example, if an individual increased his or her leg press strength by 50% over a 10-week training period, he or she would lose half of that strength gain after 10 weeks of no resistance exercise, and all of his or her strength gain after 20 weeks without training. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 326 7) After progressing to the load-training phase of the ACE IFT Model, a client has mastered the stability and mobility exercises from the previous phases and no longer needs to include them in each workout. a. True b. False Explanation b. False Regardless of the specific objective of the load-training program, it is recommended that stability and mobility exercises be included in the warm-up and cool-down activities. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 333 8) What aspect of muscular fitness is BEST addressed by a client adhering to the following regimen? • Frequency: Provide at least 72 hours recovery time between exercises for the same muscle groups • Intensity: Between 70 and 80% of maximum resistance, reaching fatigue between 50 and 70 seconds • Repetitions: Eight to 12 • Sets: Three to four sets with 30 to 60 seconds rest between successive training sets • Type: A combination of multijoint and single-joint exercises using various techniques, including breakdown training and assisted training a. b. c. d. Muscular hypertrophy Muscular strength Muscular power Muscular endurance Explanation a. Muscular hypertrophy This workout program would best address muscular hypertrophy. Muscle hypertrophy training typically involves lower weightloads and higher repetitions than muscular-strength training, but higher weightloads and lower repetitions than muscular-endurance training. The recommended training intensity for muscle hypertrophy is about 70 to 80% of maximum resistance (or a repetition range of eight to 12). ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 338 9) A plyometric exercise program BEST addresses which aspect of muscular fitness? a. b. c. d. Muscular hypertrophy Muscular strength Muscular power Muscular endurance Explanation c. Muscular power To improve the production of muscular force and power, plyometric exercise can be implemented. Plyometric exercise incorporates quick, powerful movements and involves the stretch-shortening cycle [an active stretch (eccentric contraction) of a muscle followed by an immediate shortening (concentric contraction) of that same muscle]. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 343 10) Which of the following types of plyometric drills provides the highest intensity? a. b. c. d. Multiple linear jumps Jumps in place Hops and bounds Multidirectional jumps Explanation c. Hops and bounds Hops and bounds are the most intense of the options listed. Hops involve taking off and landing with the same foot, while bounds involve the process of alternating feet during the take-off and landing. Hops and bounds emphasize horizontal speed and are performed repeatedly with no rest between actions. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 344 & 346 Quiz #16: Chapter 11 – Cardiorespiratory Training: Programming and Progressions ACE’s Personal Trainer Manual, 4th Edition 1) Most health benefits occur with at least __________ a week of moderate-intensity physical activity. a. b. c. d. 60 minutes 75 minutes 150 minutes 180 minutes Explanation c. 150 minutes Many of the recommendations from the 2008 Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans are derived from the knowledge that most health benefits occur with at least 150 minutes a week of moderateintensity physical activity and that the benefits of physical activity far outweigh the possibility of adverse outcomes. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 374 2) A client performs regular moderate- to vigorous-intensity activity at 85% of his maximum heart rate. What is his fitness classification? a. b. c. d. Poor/fair Fair/average Average/good Good/excellent Explanation c. Average/good An individual in this category will perform “habitual physical activity: Regular moderate-to-vigorous Intensity” at 80–91% of maximum heart rate and 65–80% of %HRR/VO2max or VO2R. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 377 3) During the talk test, a client is able to speak, but not very comfortably. At approximately what intensity is this client working? a. b. c. d. Below VT1 Just above VT1 Just below VT2 Above VT2 Explanation b. Just above VT1 Studies in a variety of populations have demonstrated that the talk test is a very good marker of VT1. Typically, below the VT1, people will respond to any of a number of speech-provoking stimuli (normal conversation, a structured interview, reciting a standard paragraph) by stating that they can speak comfortably. Above VT1, but below a second metabolic marker called the second ventilatory threshold (VT2), they will be able to speak, but not comfortably. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 382 4) In which zone of the three-zone training model is an individual exercising if he or she is working at a heart rate equal to his or her second ventilatory threshold? a. Zone 1 b. Zone 2 c. Zone 3 Explanation c. Zone 3 Zone 3 reflects heart rates at or above VT2, while zone 1 reflects heart rates below VT1 and zone 2 reflects heart rates from VT1 to just below VT2. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 385 5) A client is performing 250 minutes of exercise each week and has a weekly caloric expenditure of approximately 1,700 calories. What is this client’s physical fitness classification? a. b. c. d. Poor-fair Fair-average Average-good Good-excellent Explanation b. Fair-average A client in the “fair-average” category will be exercising 30–90 minutes/day and 200–300 minutes/week, and will be expending between 1,500 and 2,000 calories each week. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 386 6) Which exercise variable is it MOST appropriate for a personal trainer to manipulate in the early stages of an exercise program? a. b. c. d. Duration Intensity Frequency Type Explanation a. Duration Exercise duration is probably the most appropriate variable to manipulate initially, building the exercise session by 10%, or five to 10 minutes every week or two over the first four to six weeks. Thereafter, and once adherence is developed, trainers can implement progressions by increasing exercise frequency and then exercise intensity. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 387 7) During which cardiorespiratory training phase of the ACE IFT Model should a client be working at an RPE of 3 to 4? a. b. c. d. Phase 1 Phase 2 Phase 3 Phase 4 Explanation a. Phase 1 During phase 1, training should focus on steady-state exercise in zone 1, which can be gauged by the client’s ability to talk (below talk test threshold) and/or work at an RPE of 3 to 4 (moderate to somewhat hard). ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 394 8) During which cardiorespiratory training phase of the ACE IFT Model should a trainer administer the VT2 threshold test to determine HR at VT2? a. b. c. d. Phase 1 Phase 2 Phase 3 Phase 4 Explanation c. Phase 3 During phase 3, the focus is on designing programs to help clients who have endurance performance goals and/or are performing seven or more hours of cardiorespiratory exercise per week. This is the most appropriate time to administer the VT2 threshold test to determine HR at VT2. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 394 9) Stop-and-go game-type activities are an appropriate choice for both youth and older adult exercisers. a. True b. False Explanation b. False While youth often excel at and enjoy these activities, older adults are generally less tolerant of stop-andgo game-type activities (along with heavy training loads, rapid increases in training load, and singlemode exercise). ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 406 10) During which cardiorespiratory training phase of the ACE IFT Model should low zone 2 intervals be introduced into a client’s program? a. b. c. d. Phase 1 Phase 2 Phase 3 Phase 4 Explanation b. Phase 2 This phase of cardiorespiratory training is dedicated to enhancing the client’s aerobic efficiency by progressing the program through increased duration of sessions, increased frequency of sessions when possible, and the introduction of zone 2 intervals. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 397 Quiz #17: Chapter 13 – Mind-Body Exercise ACE’s Personal Trainer Manual, 4th Edition 1) Which form of mind-body exercise is BEST described as a form of moving meditation? a. b. c. d. Nia Yoga Tai chi Pilates Explanation c. Tai chi Tai chi, the martial art derivative of qigong, is best described as a moving meditation. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 454 2) Which type of yoga program is BEST suited for individuals who are new to yoga? a. b. c. d. Restorative yoga Integral yoga Bikram yoga Ashtanga yoga Explanation a. Restorative yoga This style of hatha yoga is perhaps most appropriate for those who are just embarking on a yoga program because of the use of props and the elementary nature of the poses. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 459 3) Which type of yoga is also known as “power yoga”? a. b. c. d. Anusara yoga Ashtanga yoga Viniyoga Kripalu yoga Explanation b. Ashtanga yoga The asanas in Ashtanga yoga are sequenced in groups of poses that range from moderate to very difficult. The sequence pace and pose difficulty is what often characterizes Ashtanga as “power yoga.” ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 462 4) Which term, also the name of a type of yoga, is synonymous with what is also called “serpent power,” or the coiled-up energy contained in the body? a. b. c. d. Bikram Kundalini Kripalu Anusara Explanation b. Kundalini Also called the yoga of awareness, kundalini yoga’s principal purpose is to awaken the serpent power (kundalini, or coiled-up energy) with postures, breath control, chanting, and meditation. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 462 5) Which form of tai chi is the most practiced in the West today? a. b. c. d. Original Chen style Chang style Yang style Wu style Explanation c. Yang style Originated by Yang Luchan in the 1800s, the Yang form is the most widely practiced form in the West today. The original Yang form consists of 108 movements (Yang Long Form); however, the Yang 24– Short Form is a popular modification practiced today. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 466 6) An older adult client who is interested in trying mind-body exercise has decided that tai chi might be the best fit for her needs and abilities. Which form of tai chi would you recommend? a. b. c. d. Original Chen style Chang style Wu style Sun style Explanation d. Sun style Because the sun style involves a higher stance than other forms, it is often the easiest for older adults to learn. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 466 7) Which contemporary form of mind-body exercise involves floor work and as well as work done on a machine called a reformer? a. b. c. d. Nia Pilates Alexander Technique Feldenkrais Method Explanation b. Pilates Pilates is based on the idea that there is a core set of postural muscles that help to keep the body balanced and are essential to providing good support to the spine. This method is divided into two modalities, floor/mat work and work on a Reformer, a piece of resistance equipment originally developed by Joseph H. Pilates. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 466–467 8) Which contemporary form of mind-body exercise includes a moderate-level aerobic component that fosters spontaneity? a. b. c. d. Nia Pilates Alexander Technique Feldenkrais Method Explanation a. Nia Unlike other mind-body exercise programs, Nia also includes a moderate-level aerobic component to address cardiorespiratory endurance. The aerobic segment is designed to foster creativity and spontaneity rather than strict adherence to standard group movement patterns. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 468 9) One of the means of objectively assessing the success of a mind-body exercise program is to record baseline and serial blood-pressure measurements. a. True b. False Explanation a. True Baseline and serial resting blood pressure measurement is also an accepted outcome measure responsive to four to six weeks of mind-body exercise—especially if the participant has a resting blood pressure in the prehypertension or higher range (i.e., >120/80 mmHg). ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 469 10) __________ is the practice of voluntary breath control, consisting of conscious inhalation, retention, and exhalation. a. b. c. d. Asana Sivananda Viniyoga Pranayama Explanation d. Pranayama In the yogic and qigong traditions, breathing functions as an intermediary between the mind and body. Pranayama (the practice of voluntary breath control, consisting of conscious inhalation, retention, and exhalation) is often practiced in conjunction with meditation and yoga asanas but can stand by itself as an important mind-body exercise method. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 463 Quiz #18: Chapter 14 – Exercise and Special Populations ACE’s Personal Trainer Manual, 4th Edition 1) Which of the following is NOT a common manifestation of atherosclerosis? a. b. c. d. Stroke Arrhythmias Angina Heart attack Explanation b. Arrhythmias Atherosclerosis is the underlying cause of cerebral and peripheral vascular diseases. Manifestations of atherosclerosis include angina, heart attack, stroke, and intermittent claudication. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 481 2) During a workout, you notice that a client displays a sudden lack of coordination and balance and, when asked, reports trouble seeing. What is the MOST likely cause of these symptoms? a. b. c. d. Myocardial infarction Claudication Diabetes Stroke Explanation d. Stroke The warning signs of a stroke are as follows: Sudden numbness or weakness of the face, arms, or legs Sudden confusion or trouble speaking or understanding others Sudden trouble seeing in one or both eyes Sudden walking problems, dizziness, or loss of balance and coordination Sudden severe headache with no known cause ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 485 3) A client’s physician provides the following guideline regarding the intensity of exercise for a new client: “An RPE of 11 to 16 (6 to 20 scale) is the preferred exercise intensity.” With which condition is this client MOST likely coping? a. b. c. d. Hypertension Cancer Type 2 diabetes Fibromyalgia Explanation c. Type 2 diabetes Individuals with type 2 diabetes can exercise at a moderate intensity of 11 to 16 on the 6 to 20 ratings of perceived exertion (RPE) scale. The other three options all require a light to moderate intensity of 9 to 13 on the RPE scale. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 493 4) A male client brings a form from his primary care physician reporting the following test results: Waist circumference: 41 inches Triglycerides: 140 mg/dL HDL cholesterol: 38 mg/dL Blood pressure: 128/80 mmHg Fasting blood glucose: 93 mg/dL This client currently has the metabolic syndrome. a. True b. False Explanation b. False The metabolic syndrome is defined as the presence of three or more of the following components: Elevated waist circumference Men >40 inches (102 cm) Women >35 inches (88 cm) Elevated triglycerides >150 mg/dL Reduced HDL cholesterol Men <40 mg/dL Women <50 mg/dL Elevated blood pressure >130/85 mmHg Elevated fasting blood glucose >100 mg/dL This client has only two of these components (elevated waist circumference and reduced HDL cholesterol). ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 494 5) A client’s physician provides the following guideline regarding the mode of exercise for a new client: “Swimming is the recommended mode of exercise; upper-body resistance-training exercises are not appropriate.” With which of the following conditions is this client MOST likely coping? a. b. c. d. Osteoporosis Arthritis Asthma Fibromyalgia Explanation c. Asthma Swimming may be particularly beneficial for individuals with asthma because it allows them to inhale the moist air just above the surface of the water. For some clients with asthma, upper-body exercises such as arm cranking, rowing, and cross-country skiing may not be appropriate because of the higher ventilation demands. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 494 6) Weightbearing and resistance-training activities are MOST important for clients with which of the following diseases or disorders? a. b. c. d. Osteoporosis Diabetes Arthritis Low-back pain Explanation a. Osteoporosis For clients with osteoporosis, the mechanical stress associated with weightbearing or resistance-training activities produces strain on bone tissue and stimulates bone deposition and resulting gains in bone mass and strength. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 502 7) For clients with which of the following diseases or disorders is it MOST important to develop a “regular” pattern of activity that does not result in post-activity malaise? a. b. c. d. Low-back pain Chronic fatigue syndrome Fibromyalgia Cancer Explanation b. Chronic fatigue syndrome When working with clients with CFS, the goal is to develop a “regular” pattern of activity that does not result in post-activity malaise. Low-intensity exercise is recommended. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 509 8) How often should low-back exercises be performed in order to yield the maximum benefit? a. b. c. d. 2–3 days/week 4–5 days/week 5–6 days/week 7 days/week Explanation d. 7 days/week While there is a common belief that exercise sessions should be performed at least three times per week, it appears that low-back exercises have the most beneficial effect when performed daily. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 511 9) When programming exercise to help a client reduce low-back pain, it is most important to focus on muscular strength, as opposed to muscular endurance. a. True b. False Explanation b. False Low-back exercises performed for maintenance of health need not emphasize strength; rather, more repetitions of less-demanding exercises will assist in the enhancement of endurance and strength. Given that endurance has more protective value than strength, strength gains should not be overemphasized at the expense of endurance. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 511 10) Overweight or obese clients who are seeking to lose weight should perform a MINIMUM of _____ minutes of moderate-intensity exercise each week. a. b. c. d. 120 150 225 240 Explanation b. 150 Individuals seeking weight loss should include exercise as a key component of their programs, and overweight and obese adults should accumulate more than 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise each week, and when possible, more than 225 minutes per week. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 511 Quiz #19: Chapter 15 – Common Musculoskeletal Injuries and Implications for Exercise ACE’s Personal Trainer Manual, 4th Edition 1) The most commonly reported knee injury involves damage to the __________. a. b. c. d. Anterior cruciate ligament Medial collateral ligament Patella Menisci Explanation d. Menisci The most commonly reported knee injury is damage to the menisci. The menisci have an important role within the knee due to their multiple functions—shock absorption, stability, joint congruency, lubrication, and proprioception. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 536 2) What type of injury can be classified as longitudinal, oblique, transverse, or compression? a. b. c. d. Stress fractures Sprains Bursitis Shin splints Explanation a. Stress fractures Longitudinal, oblique, transverse, and compression are the four types of stress fractures, which often occur in distance runners, track athletes, and court sport athletes (e.g., volleyball, basketball). ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 536 3) What is the first phase of healing after an injury occurs? a. b. c. d. Remodeling phase Inflammation phase Proliferation phase Fibroblastic phase Explanation b. Inflammation phase The first phase of healing is the inflammatory phase, which can typically last for up to six days, depending on the severity of the injury. The focus of this phase is to immobilize the injured area and begin the healing process. Increased blood flow occurs to bring in oxygen and nutrients to rebuild the damaged tissue. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 537 4) Which of the following is an ABSOLUTE contraindication to stretching? a. b. c. d. Joint hypermobility Pain in the affected area Presence of osteoporosis Joint swelling Explanation a. Joint hypermobility The absolute contraindications to stretching are as follows: A fracture site that is healing Acute soft-tissue injury Post-surgical conditions Joint hypermobility An area of infection The other three choices are all relative contraindications. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 538 5) Lateral epicondylitis is commonly known as __________. a. b. c. d. Golfer’s elbow Jumper’s knee Tennis elbow Runner’s knee Explanation c. Tennis elbow Lateral epicondylitis, which is commonly called “tennis elbow,” is defined as an overuse or repetitivetrauma injury of the wrist extensor muscle tendons near their origin on the lateral epicondyle of the humerus. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 541 6) A client complains of pain in the wrist during sleep and numbness and loss of grip strength during exercise. What injury is the MOST likely cause of these symptoms? a. b. c. d. Greater trochanteric bursitis Iliotibial band syndrome Medial epicondylitis Carpal tunnel syndrome Explanation d. Carpal tunnel syndrome The symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome include: Night or early-morning pain or burning Loss of grip strength and dropping of objects Numbness or tingling in the palm, thumb, index, and middle fingers ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 542 7) A client comes to you with recommendations from her doctor regarding exercise with greater trochanteric bursitis. One of the focuses or her training should be strengthening which of the following muscle groups? a. b. c. d. Hamstrings Gluteals Quadriceps Iliotibial band complex Explanation b. Gluteals When working with a client with greater trochanteric bursitis, strengthening the gluteals and deeper hip rotator muscles is important to maintain adequate strength. Stretching of the iliotibial band complex, hamstrings, and quadriceps should be the focus to ensure proper lower-extremity mobility. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 544 8) Which of the following injuries is primarily caused by training errors among athletes? a. b. c. d. Patellofemoral pain syndrome Infrapatellar tendinitis Achilles tendinitis Iliotibial band syndrome Explanation d. Iliotibial band syndrome ITBS is common among active individuals 15 to 50 years of age and is primarily caused by training errors in runners, cyclists, volleyball players, and weight lifters. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 545 9) A client reports feeling terrible pain in the heel during his first few steps each morning, which then dissipates as he walks around the house. What is the MOST likely cause of this pain? a. b. c. d. Plantar fasciitis Achilles tendinitis Ankle sprain Infrapatellar tendinitis Explanation a. Plantar fasciitis Typically, individuals with plantar fasciitis report pain on the plantar, medial heel at its calcaneal attachment that worsens after rest but improves after 10 to 15 minutes of activity. In particular, clients will commonly report excessive pain during the first few steps in the morning. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 553 10) When programming exercise for a client who is recovering from a lateral ankle sprain, it is important to begin with side-to-side motions before progressing to straight-plane and then multidirectional motions. a. True b. False Explanation a. False It is recommended that personal trainers progress individuals with this injury first with straight-plane motions such as forward running, then side-to-side motions such as sidestepping, and then multidirectional motions such as carioca. ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4th ed., p. 551