Final Exam Study Guide 2
advertisement

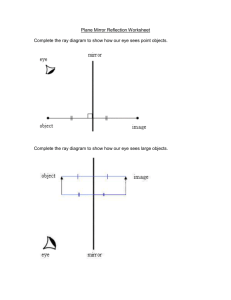
Grade 7/8 Science Final Study Guide Sample Questions Unit 1 1. What percent of the earth’s water is salt? Fresh? Frozen? 2. What is the hydrosphere? Atmosphere? Lithosphere? 5. What is the freezing point of salt water? Fresh water? 6. Identify 3 sources of fresh water (drainage basins, ground water, glaciers) 7. What is the water cycle? Label and recognize the 4 processes. 8. What happens in condensation, evaporation, precipitation and collection? 9. How does global warming affect glaciers and what impact does it have on the environment? 10. Identify organisms that live in both salt and fresh water environments 11. Explain what each of the following is and how it affects plant and animals: a)temperature b) dissolved oxygen c) phosphates d) increased acidity e) turbidity g) upwelling areas f) pollution 12. How did volcanoes and plate tectonics help create the ocean basins? 13. How did erosion and glaciation help create ocean basins? 14 Label diagram of the continental margins – include shelf, slope, abyssal plain and mid-ocean ridge 16 Recognize: headlands, bays, sea caves, sea arches and sea stacks 17. Describe ocean technologies such as satellites, SCUBA, sonar and submersibles, underwater photography/videography. What are some strengths and weaknesses of each? How have ocean technologies improved over time? 18. What are ocean currents? 19. What currents affect Newfoundland and how do they affect us? 22. Vertical convection currents result when cold, dense water sinks and pushes warmer water to the surface. 23. What are upwelling areas? Why are they important? 24. Define wavelength and recognize 26. What happens to the wavelength and wave height as waves approach the shoreline? 27. Define Tsunami. 28. What is the difference between weathering, erosion and deposition? 29. Wave interactions with shorelines depend on: shape of shoreline, slope of shoreline, type of rock material, wave energy. Explain each. 30. Define headland and bay and explain how waves affect them differently. 31. How does slope and rock type affect interaction between waves and shoreline? Small particles are more easily eroded but larger particles are more often left behind. Also, less resistant rock will erode faster 32. What are tides? What creates the high and low tides? (Gravitational pull of moon) 33. Where is the moon located in a spring tide? In a neap tide? Recognize the 2 tides from diagrams. 35. What are: beaches, shoals, sand bars, sea caves, sea arches, sea stacks? 36. Describe technology used to protect shores from waves and tides: wharves, breakwaters, jetties 39. How does the heat capacity of water affect climate? (Oceans have a high heat capacity and can store large amounts of heat for long times which can be transported through currents to other parts of the world, making them warmer) 40. How do convections affect weather? (Warm oceans heat the air above it resulting in thermals. As warm air rises, cool, denser air replaces it) 41. How do the oceans moderate climate? Affect coastal areas such that oceans stay warmer than land masses through the fall and winter due to high heat capacity of water. Oceans remain cooler through the spring and summer. Both regulate the temperature by preventing extreme cold in winter and extreme heat in summer) 42. Why is Newfoundland foggy? 43. Why does our temperature change (fluctuate) quickly? (Because of our location between warm tropical winds moving north and cold, arctic winds moving south. Local temp will depend on which prevails) 43. What are the characteristic of El Nino? La Nina? 44. What are some positive and negative effects of marine technologies? 45. How have technologies contributed to overfishing? 46. How has the offshore oil industry impacted marine environments? 47. What is aquaculture? How can it impact marine environments? 48. Discuss problems related to the ocean that cannot be fixed with science and technology. (remember: seal hunt, cod moratorium, oil and gas exploration – people need these for money, jobs and to survive but they hurt the environment. So, what’s the solution?) Unit 2 1. What is a matter? 2. What are the 5 key points of the particle theory of matter? 3. What are the 3 states of matter? Describe their shapes, volume, particle arrangement and particle movement. 4. Look at the particle arrangement in these pictures. Which is the solid, liquid and gas? How do you know? 5. What is a fluid? Identify each as a fluid or a non-fluid: A) Molasses B) Sand C) Nitrogen gas D) Water E) Oxygen gas F) Pepsi 6. What is viscosity? 7. What is viscous? 8. What is friction? 9. How does friction affect viscosity? 10. Describe the attraction of the particles in each of the following: A) Water B) Syrup C) Oxygen gas 11. Why is viscosity important in everyday life? 12. What type of oil (high or low viscosity) would you use in a car in winter and why? 13. What is flow rate? Describe the flow rate of: a) dishwashing liquid b) Pepsi c) molasses 14. How do viscosity and flow rate affect each other (what is their relationship)? 15. How does temperature affect the flow rate and viscosity of liquids? 16. How does temperature affect the flow rate and viscosity of gases? 17. How does concentration affect the flow rate of both liquids and gases? 18. Using the particle theory of matter explain what is happening to particles when we add more pancake powder to pancake batter. 19. How do attractive forces affect viscosity and flow rate of liquids and gases? 20. How does particle size affect the viscosity and flow rate of liquids and gases? 21. What is density? 22. Describe the relationship between density and the 3 states of matter: solid, liquid, gas 23. How do liquids of different densities react to one another? (remember our lab and the layering) 24. What is displacement? 25. Rearrange the D = m/V formula to solve for m and V. (density, mass, volume) 26. Calculate the density, volume and mass of solids and fluids 27. Recognize that the density of a solid is measured in g/cm3 and the density of a fluid is measures in g/ml 28. Based on the triangle, what is the formula for: Density = Mass = Volume = 29. What is the density of 45 g of water collected in a 100 mL glass? 30. What is the density of a 500 g brick that has a volume of 4.5 cm3? 31. What is the volume of 50 g of a substance that has a density of 3 g/mL? 32. What is the volume of a 75g substance that has a density of 15 g/cm3? 33. What is the mass of 90 mL of a substance that has a density of 2 g/mL? 34. What is the mass of a substance that has a density of 24 g/cm3 and a volume of 25 cm3? 35. Find the missing values: Substance Gold Orange juice Water Volume 4 cm3 55 mL Mass 8g 5 mL Density 19.3 g/cm3 1.025 g/mL 36. Explain force and unbalanced forces. Provide an example of unbalanced forces. 37. What is a newton and what is it measured in? 38. How are weight and mass different? Provide an example 39. Recognize that mass does not change no matter where you are in the universe but your weight will change when there is a change in gravity 40. Given the weight (N) on various planets in our solar system, determine which would have the least or most gravity. 41. What is buoyancy? 42. What is neutral buoyancy? 43. Why does an object float? Sink? 44. How does density affect buoyancy? 45. What is average density? 46. Why will certain objects float and other’s not float? (ex: wooden boat vs water logged stick, metal block vs metal boat) 47. What technologies have come from our knowledge of density? 48. What is pressure? What is the unit for pressure? 49. What is atmospheric pressure? 50. What is the relationship between force, area and pressure? 51. Rearrange the F = PxA formula to solve for P and A (force, pressure, area) 52. Recognize that N/m2 = Pa 53. Calculate force, area and pressure 54. A bathtub is filled with water that has a force of approximately 650 N. If the area is 25 m2 what is the pressure? 55. What is the area of a large container that can withstand 500 N of force and 23 Pa of pressure? 56. What force would have to be applied to a 12 m2 box that has a pressure of 4 Pa? 57. What is hydraulics? Provide examples of where it is used. 58. What is pneumatics? Provide examples of where it is used. 59. How are hydraulic and pneumatic systems different in terms of states, volume and pressure? 60. What is Pascal’s Law? Provide examples of Pascal’s Law. 61. What is the relationship between pressure, volume and temperature? Study Guide Unit 3 1. Explain Galileo, Pythagoras and Michelson’s theories of light 2. What is light? 3. What is the speed of light? 4. Compare the speed of light to the speed of sound. 5. How did our knowledge of light contribute to the development of microscopes and telescopes? 6. Describe the properties of visible light: a) rectilinear propagation e) travels through a vacuum b) reflection f) translucent, transparent, opaque c) refraction d) dispersion 7) What is the visible light spectrum? 8) What is dispersion? 9) What is the visible light spectrum? 10) What are the colors of white light, in order, starting with Red 11) What color of the visible light spectrum refracts the most? The least? 12) What is frequency? 13) What is wavelength? 14) Recognize that: high frequency waves have short wavelengths and low frequency waves have long wavelengths 15) Recognize: Red has longest wavelength and least refraction 16) Recognize: Violent has shortest wavelength and most refraction 17) What is the electromagnetic spectrum? 18) What are the 7 types of radiation on the electromagnetic spectrum? 18) Describe the electromagnetic spectrum in terms of frequency, wavelength and energy 20) Provide examples of how we use each of the 7 types of electromagnetic radiation in real life. 21) List positive and negative effects of using the various types of electromagnetic radiation 22) What is an incident light ray? 23) What is a reflected light ray? 24) What is the normal? 25) What is the angle of incidence? 26) What is the angle of reflection? 27) What is the difference between specular and diffuse reflection? Provide examples of each. 28) List 3 types of mirrors and provide examples of each. 29) What is the law of reflection? 30) What is a ray diagram? 31) What are SPOT image characteristics? 32) Draw ray diagrams of images in plane mirrors and state the SPOT characteristics 33) What is the difference between real and virtual images? 34) What is the focal point? 35) What is the principal axis? 36) Recognize that in concave mirrors: (i) incident rays parallel to the mirror’s principal axis are reflected through the focal point; and (ii) incident rays going through the focal point are reflected parallel to the mirror’s principal axis. 37) Construct ray diagrams in concave mirrors for objects between the mirror and focal point, between F and 2F and beyond 2F 38) Identify SPOT characteristic for concave mirrors 39) Construct ray diagrams for convex mirrors 40) Recognize the SPOT characteristics for images in convex mirrors 41) What is the bent stick effect? 42) Why are fish not where we see them when we look into water? 43) How does light refract? 44) Identify the incident ray, refracted ray, angle of incidence and angle of refraction 45) What happens to the speed of light as it passes from one medium to another that is denser? 46) What happens to the speed of light as it passes from one medium to another that is less dense? 47) Identify that a light ray traveling into a medium of greater density will bend towards the normal and a light ray traveling into a medium of lesser density will bend away from the normal 48) How does the difference in a medium’s density affect the relationship between angle of incidence and angle of refraction? (Will it bend toward or away from the normal?) 49) Recognize that the more dense the substance, the more the light refracts toward the normal. 50) Recognize that the less dense the substance, the less the light refracts toward the normal. 51) What is a lens? 52) What are the 2 type of lenses? 53) Provide an example of each type of lens. 54) How do concave and convex lenses refract light? 55) How do lenses correct near sightedness and far sightedness? Plane Mirrors Concave Mirrors – object between focal point and mirror Concave Mirrors - image between focal point and 2x the focal point Concave Mirror – object beyond 2x the focal point Convex Mirrors Study Guide Unit 4 1. What did early scientists believe about living thing? How did that change over time? 2. What is a cell? 3. What is the cell theory? 4. What 4 characteristics are common to all living things? Explain each. 5. How have optical technologies changed over time? How does that affect scientific theory? 6. Identify the major parts of the compound microscope: (i) eyepiece (ii) objective lenses (iii) stage (iv) coarse adjustment knob (v) fine adjustment knob (vi) light source/lamp (vii) iris diaphragm (viii) base (ix) barrel (or tube) (x) arm (xi) revolving nosepiece 7. Use a compound light microscope appropriately 8. Estimate the size of cells from the field of view 9. Prepare and observe a wet mount slide 10. Examine and explain the role of the following organelles: (i) cell wall (i) cell membrane (ii) chloroplast (iii) cytoplasm (iv) nucleus (v) vacuole (vii) mitochondria 11. Draw a plant and animal cell and label the organelles 12. What are the three differences between plant and animal cells? 13. How does the growth and reproduction of cells happen? 14. When does meiosis occur? When does mitosis occur? 15. What are the 2 characteristics of a system? 16. Draw an organizational chart showing the levels of cell organization 17. What are tissues made up of? Where are they found? What is an example of a tissue? 18. What are organs? What are they made up of? What are some examples of organs? 19. What are organ systems? What are they made up of? What are the 6 organ systems we are studying? 20. What are the 3 basic necessities of life that all cells and organisms need to live? 21. What is cellular respiration and why is it important? 22. Identify the parts and function for these 6 systems: circulatory, respiratory, digestive, excretory, nervous, muscular 23. What are some positive factors that affect how our body systems work? Explain why they are positive and what they do to your body. 24. Explain the roles that diet, nutrition, exercise and stress have on organ systems 25. What are some negative factors that affect how our body systems work? Explain why they are negative and what they do to your body. 26. What are 2 technologies that can help damaged organs or systems? 27. How do the circulatory and respiratory systems depend on each other? 28. How do the circulatory and digestive systems work together? 29. How do the nervous system and muscular system depend on each other? 31. Name careers that are associated with the health of body systems. 32. What are some personal decisions humans can make about their own health? Explain choices. 33. Discuss lifestyle choices such as diet choices, smoking, drinking alcohol, or sedentary lifestyle and their effects on body systems 34. How is your heart rate affected by increased physical activity? 35. How is your breathing rate affected by increased physical activity?