6th Modern Living Unit Plan - The Tennessee STEM Innovation
advertisement
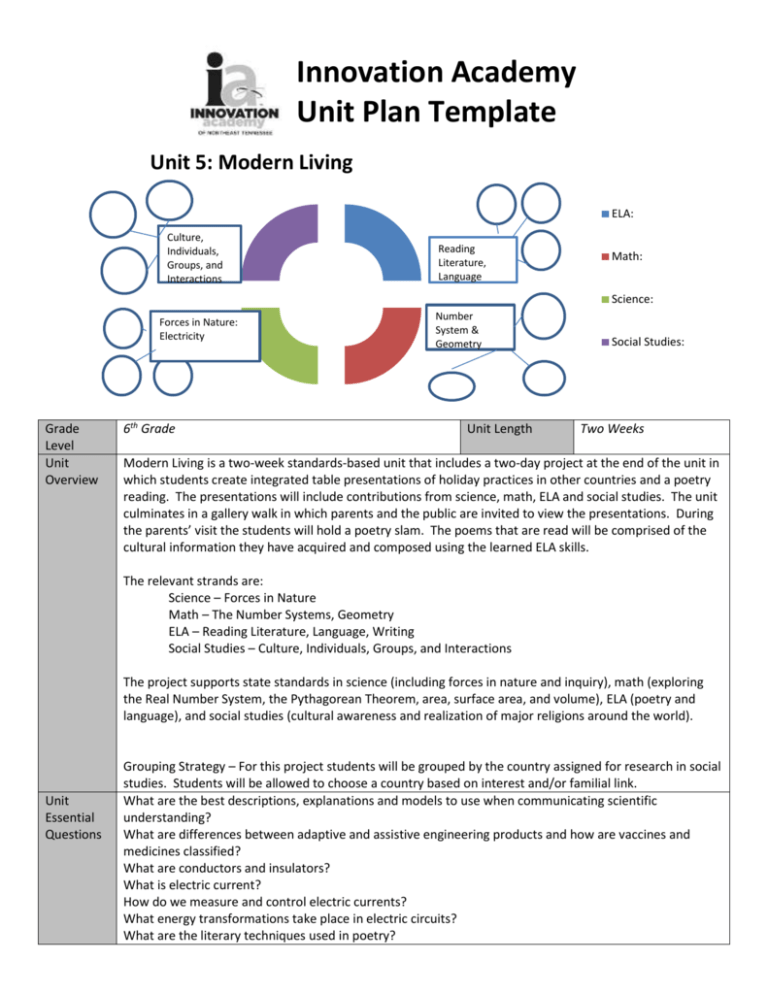
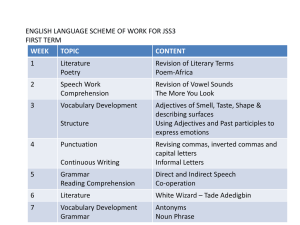
Innovation Academy Unit Plan Template Unit 5: Modern Living + ELA: Culture, bnadjbadsdsd Individuals, Groups, and Interactions Reading Literature, Language Math: Science: Forces in Nature: Electricity Grade Level Unit Overview 6th Grade Number System & Geometry Unit Length Social Studies: Two Weeks Modern Living is a two-week standards-based unit that includes a two-day project at the end of the unit in which students create integrated table presentations of holiday practices in other countries and a poetry reading. The presentations will include contributions from science, math, ELA and social studies. The unit culminates in a gallery walk in which parents and the public are invited to view the presentations. During the parents’ visit the students will hold a poetry slam. The poems that are read will be comprised of the cultural information they have acquired and composed using the learned ELA skills. The relevant strands are: Science – Forces in Nature Math – The Number Systems, Geometry ELA – Reading Literature, Language, Writing Social Studies – Culture, Individuals, Groups, and Interactions The project supports state standards in science (including forces in nature and inquiry), math (exploring the Real Number System, the Pythagorean Theorem, area, surface area, and volume), ELA (poetry and language), and social studies (cultural awareness and realization of major religions around the world). Unit Essential Questions Grouping Strategy – For this project students will be grouped by the country assigned for research in social studies. Students will be allowed to choose a country based on interest and/or familial link. What are the best descriptions, explanations and models to use when communicating scientific understanding? What are differences between adaptive and assistive engineering products and how are vaccines and medicines classified? What are conductors and insulators? What is electric current? How do we measure and control electric currents? What energy transformations take place in electric circuits? What are the literary techniques used in poetry? Culminating Event How can poetry be used to inform a reader of an unfamiliar culture? How can imagery improve the effectiveness of poetry? What are the best descriptions of each of the sets of numbers in the Real Number System? How do I estimate the location of a square root on a number line? How do I solve an equation involving a variable being squared? What is the Pythagorean Theorem? How do I prove that an angle is 90 degrees? How do I find the area of triangles, special quadrilaterals, and complex polygons? How do I find the volume of Right Rectangular Prisms with fractional lengths? How do I create a net of a geometric solid? How do I use a net to find the surface area of a geometric solid? What are the basic Christian beliefs? What are the basic Islamic beliefs? What are the basic beliefs of Judaism? What are the basic Buddhist beliefs? Who are the founders of these major religions? Students will be creating tri-fold poster displays for a gallery walk for their parents, peers, and teachers. Students will be grouped in heterogeneous groups of four students. Each group will be assigned a particular country in which they will research in terms that country’s major religious holiday, basic cultural traits, and dominant religion. When examining the major religious holiday students will look particularly close at Christmas (or the country’s equivalent holiday) traditions, holiday foods, and particularly unique holiday practices. Each item will have a visually appealing display and five solid bullet points of information for the audience to enjoy. In addition, students will display two and three dimensional holiday decorations and there will be a circuit of lights placed on the displays. STEM Project Rubric Common Assessment STEM Math IA Components Functions 25% STEM Math IB Components The Number System 25% Science Components: Forces in Nature Electricity 25% Social Studies Component Major Religions 25% ELA Component Project Title: Modern Living Student Name: _______________ Date: _______________________ Advanced Proficient Needs Improvement The display contains one proof of a right angle and one proof of an angle not being right. The reasoning is communicated clearly, both mathematically and verbally. 1. The display contains two traditional holiday decorations, one twodimensional and one threedimensional. 2. The area of a complex polygon in the twodimensional decoration is calculated and explained clearly. 3. A net of the threedimensional decoration is created and the surface area of the threedimensional decoration is calculated and explained clearly. Two completed circuits work and: 1. Are labeled as parallel and series. 2. At least three energy transformations are described for each circuit 3. The current is labeled for each loop 4. The voltage drop across each component is labeled. 5. All work is completed on time. The display contains one proof of a right angle and one proof of an angle not being right. The reasoning is communicated clearly either mathematically or verbally. 1. The display contains two traditional holiday decorations, one twodimensional and one threedimensional. 2. The area of a complex polygon in the twodimensional decoration is calculated. 3. A net of the threedimensional decoration is created and the surface area of the threedimensional decoration is calculated. The display contains either one proof of a right angle or one proof of angle not being right. The reasoning is communicated clearly either mathematically or verbally. 1. The display contains two traditional holiday decorations, one twodimensional and one threedimensional. 2. The area of a complex polygon in the twodimensional decoration is calculated. OR A net of the three-dimensional decoration is created and the surface area of the threedimensional decoration is calculated. Two completed circuits work and: 1. Are labeled as parallel and series. 2. At least two energy transformations are described for each circuit 3. The current is labeled for each loop 4. The voltage drop across ten components is labeled. 5. All work is completed on time. Visually appealing display with 5 images and 20 well-written bullet points of information with 2 or fewer grammatical mistakes. Visually appealing display with 4 images and 17 well-written bullet points of information with 3 or fewer grammatical mistakes. Two completed circuits work and: 1. Are labeled as parallel and series. 2. At least two energy transformations are described for each circuit 3. The current is labeled for the main loops 4. The voltage drop across seven components is labeled. 5. All work is completed on time. Visually appealing display with 3 images and 14 well-written bullet points of information with 5 or fewer grammatical mistakes. 1. 1. 1. Poem 2. 25% 3. 4. 5. At least four types of figurative language are used 0 grammatical or spelling errors Two examples of symbolism Poem vividly depicts the culture it is being used to describe without factual errors Poem includes 10 facts about the assigned culture 2. 3. 4. 5. At least three types of figurative language are used 1-3 grammatical or spelling errors One example of symbolism Poem depicts the culture it is being used to describe without factual errors Poem includes 8-9 facts about the assigned culture 2. 3. 4. 5. At least two types of figurative language are used >4 grammatical or spelling errors One example of symbolism Poem depicts the culture it is being used to describe without factual errors Poem includes <8 facts about the assigned culture Unit Objectives I can describe electric current. I can describe and explain energy transformations in electric circuits. I can use poetry and figurative language to communicate facts about a culture. I can determine the meaning of words and phrases as they are used in poetry, including figurative and connotative meanings and analyze the impact of a specific word choice on meaning and tone. I can identify the world’s major religions, what they believe, and their founders. Strands (main ideas taught in unit) ELA Reading Literature, Writing, Language Math The Number System, Geometry Science Forces in Nature: Electricity Social Studies Culture, Individuals, Groups, and Interactions Vocabulary ELA Math Science Poetry- a literary work in metrical form; verse Connotative language- a secondary meaning of a word- positive or negative Denotative language- dictionary meaning of the word Imagery- using language to form mental images Symbolic language- language that figuratively represents something else STEM Math IA Rational Number— a number that can be written in the form 𝑎 , 𝑤ℎ𝑒𝑟𝑒 𝑎 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑏 𝑎𝑟𝑒 𝑖𝑛𝑡𝑒𝑔𝑒𝑟𝑠 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑏 ≠ 0, or fraction form. 𝑏 Irrational Number— a number that cannot be written in the form 𝑎 , 𝑤ℎ𝑒𝑟𝑒 𝑎 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑏 𝑎𝑟𝑒 𝑖𝑛𝑡𝑒𝑔𝑒𝑟𝑠 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑏 ≠ 0, or fraction form. 𝑏 Square Root—a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the number. Hypotenuse— the longest side of a right triangle, opposite the right angle. Legs of a Right Triangle— The sides adjacent to the right angle STEM Math IB Area- the number of square units it takes to cover a two-dimensional object. Surface Area- the total area of the surface of a three-dimensional object Volume-the number of cubic units it takes to fill a three-dimensional object. Net- Net is a two-dimensional pattern of a three-dimensional figure that can be folded to form the figure. In other words, net is a flattened three-dimensional figure, which can be turned into the solid by folding it. Rectangular Prism-a three-dimensional figure that is composed of 6 rectangular faces. Opposite faces in a rectangular prism are congruent and parallel. Atom – unit of matter consisting of electrons, protons and neutrons Charges – negative or positive particles that exert forces on each other Electric current – movement of charges in time Voltage – potential energy per charge Resistance – quality of a material that resists the flow of electric charges (compare Conductors Social Studies and Insulators in terms of resistance) Monotheism—Belief in one god. Polytheism—Belief in more than one god. Religion—Belief in and worship of god or gods. Quran—Sacred text of Islam. Torah—Sacred text of Judaism. Key Questions ELA Math Science What are the literary techniques used in poetry? How do I prove an angle is a right angle? What are insulators and conductors How are denotation and connotation different? How do I find the area of a complex polygon? What is voltage? How can imagery improve the effectiveness of poetry? How do I create a net of a threedimensional figure? What is electric current? Social Studies CTE & Technology How are Christianity and Islam similar and different? What are the basic beliefs of Judaism? How are Hinduism and Buddhism similar and different? Why did Buddhism begin? Hook for Unit Literature / Informativ e Text Componen t “Intercultural Training” see resource folder Writing Closure Students will compose a piece of poetry that depicts the uniqueness of an assigned culture. Each poem will contain at least four types of figurative language, two examples of symbolism, and ten vivid cultural facts. Poems will be written in correct format using stanzas and lines. Poems will also be written using rhythm techniques in order for them to be easily read. At the end of the unit, parents will be invited to hear the students recite their poetry and view the cultural displays. In Multi-Media, students will create a visual to display along with the poem to enhance its meaning and symbolism. Card Stock Tri-fold Displays Materials Needed for Culminating Students will be exposed to several pieces of poetry that depicts different cultures and techniques. Throughout the study, students will analyze the poems for symbolic meanings, imagery, rhythm, and figurative language. “Twas the Night Before Christmas” by Clement Clarke Moore “A Christmas Carol” by G.K. Chesterton “The Three Kings” by Henry Wadsworth Longfellow “Christmas Bells” by Henry Wadsworth Longfellow Event Color Printer Construction Paper Tacky Glue Ticky Tack Strands of Christmas Lights (25-50 bulbs to a strand) Strands of LED Christmas Lights (25-50 bulbs to a strand) 9-volt batteries Aluminum Foil Floral Tap 18 Gauge Flexible Wire 18 Gauge Copper or Alloy Wire Single-Throw Light Switch Power Strip Standards: Common Core Standards, Tennessee State Standards ELA RL.6.1 Cite textual evidence to support analysis of what the text says explicitly as well as inferences Common drawn from the text. Core RL.6.2 Determine a theme or central idea of a text and how it is conveyed through particular details; Standards. provide a summary of the text distinct from personal opinions or judgments. RL.6.4 Determine the meaning of words and phrases as they are used in a text, including figurative and connotative meanings; analyze the impact of a specific word choice on meaning and tone. RL.6.5 Analyze how a particular sentence, chapter, scene, or stanza fits into the overall structure of a text and contributes to the development of the theme, setting, or plot. RL.6.9 Compare and contrast texts in different forms or genres (e.g., stories and poems; historical novels and fantasy stories) in terms of their approaches to similar themes and topics. L.6.5 Demonstrate understanding of figurative language, word relationships, and nuances in word meanings. L.6.5.a Vocabulary Acquisition and Use Interpret figures of speech (e.g., personification) in context. L.6.5.b Use the relationship between particular words (e.g., cause/effect, part/whole, item/category) to better understand each of the words. L.6.5.c Distinguish among the connotations (associations) of words with similar denotations (definitions) (e.g., stingy, scrimping, economical, unwasteful, thrifty). Math Common Core Standards. STEM Math IA 8.NS.2. Use rational approximations of irrational numbers to compare the size of irrational numbers, locate them approximately on a number line diagram, and estimate the value of expressions. 8.EE.A.1 Know and apply the properties of integer exponents to generate equivalent numerical expressions. 8.G.6. Explain a proof of the Pythagorean Theorem and its converse. 8.G.7. Apply the Pythagorean Theorem to determine unknown side lengths in right triangles in real-world and mathematical problems in two- and three-dimensions. STEM Math IB 6.G.1. Find the area of right triangles, other triangles, special quadrilaterals, and polygons by composing into rectangles or decomposing into triangles and other shapes; apply these techniques in the context of solving real-world and mathematical problems. 6G. 2. Find the volume of a right rectangular prism with fractional edge lengths by packing it with unit cubes of the appropriate unit fraction edge lengths, and show that the volume is the same as would be found by multiplying the edge lengths of the prism. Apply the formulas V = l w h and V = b h to find volumes of right rectangular prisms with fractional edge lengths in the context of solving real-world and mathematical problems. 6.G. 4. Represent three-dimensional figures using nets made up of rectangles and triangles, and use the nets to find the surface area of these figures. Apply these techniques in the context of solving real-world and mathematical problems. Science Tennessee State Standards. SPI 0607.12.1 Identify how simple circuits are associated with the transfer of electrical energy when heat, light, sound, and chemical changes are produced. SPI 0607.12.2 Identify materials that can conduct electricity. SPI 0607.Inq.1 Design a simple experimental procedure with an identified control and appropriate variables. SPI 0607.Inq.2 Select tools and procedures needed to conduct a moderately complex experiment. SPI 0607.Inq.3 Interpret and translate data in a table, graph, or diagram. SPI 0607.Inq.4 Draw a conclusion that establishes a cause and effect relationship supported by evidence. SPI 0607.Inq.5 Identify a faulty interpretation of data that is due to bias or experimental error. Social Studies Tennessee State Standards. 1.01 Understand the nature and complexity of culture. 1.02 Recognize the role of major religions. 6.02 Understand how groups can impact change at world levels. SPI’s6.1.spi.3. recognize the world's major religions and their founders (i.e., Judaism, Christianity, Islam, Buddhism, Hinduism, Moses, Jesus, and Mohammed). 6.1.spi.8. recognize how migration and cultural diffusion influenced the character of world societies (i.e., spread of religions, empire building, exploration, languages). 6.3.spi.6. interpret a graph that illustrates a major trend in world history (i.e. population growth, economic development, governance land areas, growth of religions). 6.6.spi.1 identify examples of groups impacting world history (i.e., Muslims, Christians, Mongolians, Vikings, slave traders, explorers, merchants/traders, inventors.) Project Day 1 – Research day focusing on cultural tradition around the world. Project Day 2 – Assemble tri-fold poster presentations and set up table areas with artifacts. Prepare posters for wiring. Project Day 3 – Wire posters, test lighting and troubleshoot. Label back of posters with electrical circuit information. Notes