PAF-30 - Springer Static Content Server
advertisement
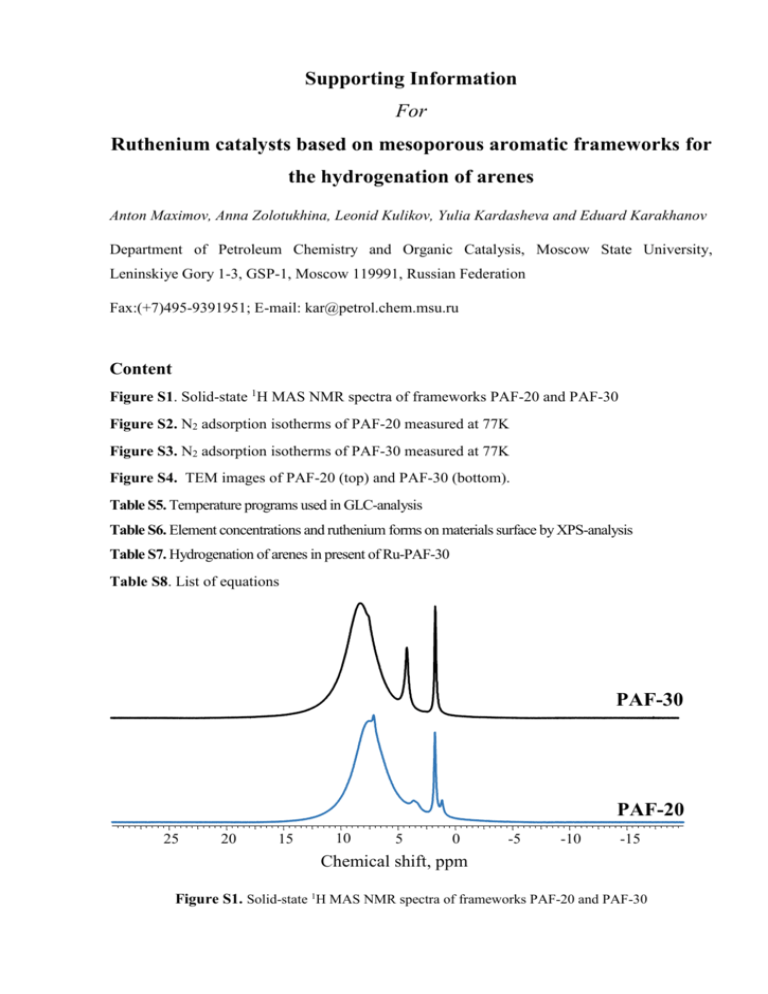
Supporting Information For Ruthenium catalysts based on mesoporous aromatic frameworks for the hydrogenation of arenes Anton Maximov, Anna Zolotukhina, Leonid Kulikov, Yulia Kardasheva and Eduard Karakhanov Department of Petroleum Chemistry and Organic Catalysis, Moscow State University, Leninskiye Gory 1-3, GSP-1, Moscow 119991, Russian Federation Fax:(+7)495-9391951; E-mail: kar@petrol.chem.msu.ru Content Figure S1. Solid-state 1H MAS NMR spectra of frameworks PAF-20 and PAF-30 Figure S2. N2 adsorption isotherms of PAF-20 measured at 77K Figure S3. N2 adsorption isotherms of PAF-30 measured at 77K Figure S4. TEM images of PAF-20 (top) and PAF-30 (bottom). Table S5. Temperature programs used in GLC-analysis Table S6. Element concentrations and ruthenium forms on materials surface by XPS-analysis Table S7. Hydrogenation of arenes in present of Ru-PAF-30 Table S8. List of equations PAF-30 . PAF-20 25 20 15 10 5 0 -5 -10 -15 Chemical shift, ppm Figure S1. Solid-state 1H MAS NMR spectra of frameworks PAF-20 and PAF-30 Figure S2. N2 adsorption isotherms of PAF-20 measured at 77K Figure S3. N2 adsorption isotherms of PAF-30 measured at 77K Figure S4. TEM images of PAF-20 (top) and PAF-30 (bottom). Table S5. Temperature programs used in GLC-analysis Parameters Program 1 Program 2 Program 3 250 250 250 250 250 250 250 150 250 Oven’s initial temperature, С 60 35 50 Oven’s final temperature, оС 220 35 220 Temperature rise, С/min 10 0 5 Initial time (time before rising oven’s temperature), min 5 20 10 Final time (time after reaching oven’s final temperature), min 10 1 5 Substances that analyzed Toluene, ethylbenzene, p-xylene, tetralin, styrene, phenylacetylene and products of their hydrogenation Benzene and products of its hydrogenation Phenol and products of its hydrogenation о Column limit, С о Detector temperature, С Injector temperature, оС о о Table S6. Element concentrations and ruthenium forms on materials surface by XPS-analysis Catalyst Ru-PAF-20 Ru-PAF-30 Element concentrations, atomic % C O Br Ru Pd 73,3 22,7 4,0 ― ― 82,6 15,9 1,5 ― ― Ruthenium forms, % Ru RuO2 RuO2*xH2O 79 21 ― 39 61 ― 0 Table S7. Hydrogenation of arenes in present of Ru-PAF-30 Substrate Substrate/Ru Conv., % Reaction rate, mole(Sub)* -1* h mole(Ru)-1 2000 97% 1940 2273 100% 2273 2013 63% 1274 96% 2038 36% 729 95% Products distribution 100% OH OH 2025 34% 100% 4% 5% 66% 29% 3% 1% 693 H H 85% 2352 27% 635 H 9% H 6% Reaction conditions: 80 оС, 3MPa. Н2, 1 h., 3 mg. Ru-PAF-30., V(H2O) = V(substrate). Table S8. List of equations Parameters Equation Initial reaction rate in recalculation on ruthenium content Ruthenium content Dispersion of ruthenium nanoparticles 𝑛(𝑅𝑢) = 𝐷= 𝑚(𝑐𝑎𝑡) ∗ 𝑊(𝑅𝑢) 𝑀(𝑅𝑢) 6𝑉A 6𝑉M(𝑅𝑢) ∗ 𝑘 = 𝑆A ∗ 𝑑pt 𝑁A ∗ 𝑆A ∗ 𝑑pt Constants and variables Conv – conversion; n(Sub) – arene quantity, mol n(Ru) – ruthenium quantity, mol D – NPs dispersion 𝛥t – reaction time; 5 minutes m(cat) – catalyst mass, g. W(Ru) – ruthenium content in catalyst M(Ru) – ruthenium molar mass; 101,07 g/mol dpt – mean diameter of the particle, Å VA – effective volume per metal atom in the bulk; 10,02 Å 3 for Ru SA – the effective average surface area per atom ; 6,13 Å 2 for Ru VM(Ru) – Ru molar volume; 8,14 cm3/mol k – packing density of hexagonal-close packed structure; 0,7405 NA – Avogadro number; 6,02*1023 mol-1