Science Final Exam Review (Answer Key) UNIT 1.1
advertisement

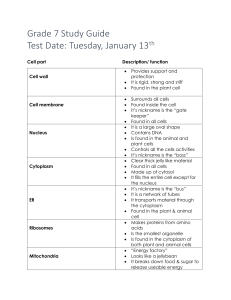
Science Final Exam Review (Answer Key) UNIT 1.1 Organic Compounds 1. What elements do all organic compounds contain? – Carbon and Hydrogen Cell Theory 2. What is common in all living things? – All living things are made up of cells 3. List the three parts of the Cell Theory. 1. Cells are the basic unit of life 2. All living things are made up of cells. 3. Cells are the basic unit of life. Levels of Organization 4. What are the levels of organization starting with the smallest unit of life? Cell – Tissue – Organ – Organ System – Organism UNIT 1.2 Cell Organelles and Cell vs. Organism 5. List 5 organelles that plant and animal cells have in common. Nucleus Mitochondria Cytoplasm Cell Membrane Lysosome 6. List the 2 organelles that are found only in a plant cell. – Cell Wall and Chloroplast 7. List all 7 organelles and give their function. 1. Nucleus—Control center of the cell. 2. Mitchondria—Powerhouse of the cell. 3. Lysosomes—Trash men of the cell. Break down broken and worn out cell parts. 4. Cytoplasm—Gel like substance that packages the organelles of a cell. 5. Cell Membrane—Controls what enters and exits the cell. The gate keeper. 6. Vacuole—Storage center for the cell. Stores food, water, and waste. 7. Endoplasmic Reticulum—Highway of the cell. Transports materials throughout the cell. 8. (Obtain energy/ absorb wastes/ use oxygen/ continue growing): Which one of these is something all cells must do to survive? Obtain Energy 9. Study the structure of cell organelles. Label the two diagrams on the next page. Cell Wall Cytoplasm Cell Membrane Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Central Vacuole Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Nucleus Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Chloroplast Cytoplasm Mitochondria Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Cell Membrane Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Nucleus Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Vacuole Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Mitochondria Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Photosynthesis Cytoplasm 10. Write the chemical formula for photosynthesis. Also using words, identify what each part of the Cytoplasm formula stands for. Ex. H2O= water Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Cytoplasm 11. What is the energy transformation (___________ ___________)that occurs during photosynthesis? Radiant Energy---Chemical Energy UNIT 2.1 Body Systems12. List the 11 body systems and their function. As a reminder, the Skeletal System and Integumentary System both have 3 functions. List all three functions for these two systems. Integumentary system-- Skin, hair, nails, sweat and other exocrine glands. Skeletal system --Bones supporting the body and its organs. Nervous system --Collects and processes information from the senses via nerves and the brain and tells the muscles to contract to cause physical actions. Cardiovascular system -- Circulates blood around the body via the heart, arteries and veins, delivering oxygen and nutrients to organs and cells and carrying their waste products away. Endocrine system --Provides chemical communications within the body using hormones. Muscular system --Enables the body to move using muscles. Respiratory system -- The lungs and the trachea that bring air into the body. Excretory system -- Eliminates waste from the body. Reproductive system-- The sex organs required for the production of offspring. Digestive system --Mechanical and chemical processes that provide nutrients via the mouth, esophagus, stomach and intestines. Immune system --Defends the body against disease-causing agents. UNIT 2.2 Physical and Chemical Changes in Digestion 13. List 3 examples/verbs that show physical changes that occur during digestion. Squeeze, Mix, Tear, Pull Apart, etc. 14. List 3 examples/verbs that show chemical changes that occur during digestion. Acid, Thermal, Heat Released, New Substance, Bile, Insulin, etc. 15. Carbohydrates break down into smaller molecules called __glucose_______ which is a type of sugar. Energy Transformation in Digestion 16. What energy transformation (___________ ___________) occurs during digestion? Chemical --- Thermal UNIT 3.1 Sexual vs. Asexual Reproduction 17. (Sexual reproduction/ Asexual Reproduction) Which type describes each list of characteristics? Sexual Reproduction Asexual Reproduction 1 parent 2 parents Exactly the same DNA Genetic diversity Identical physical appearance Variation in physical appearance Heredity 18. Define heredity. The passing on of genetic traits from one generation to the next (Parents to offspring) 19. Are scars inherited? Why or why not? – No because scars are not determined by DNA. Location of Genetic Information 20. Create a flow map that shows the progression of DNA to Cell. DNA-genes-chromosome-nucleus-cell (Smallest to Largest) 21. What structure within the nucleus contains the genetic material? Chromosomes UNIT 3.2 Internal/External Adaptations 22. Give 3 examples of an internal adaptation. Xylem in plants Hollow bones in birds A cows 4 chambered stomach 23. Give 4 examples of an external adaptation (2 Behavioral and 2 Structural) Structural: Behavioral: Camouflaged Fur/Skin Migration Feathers Hibernation Selective Breeding and Natural Selection 24. Define selective breeding. Also called artificial selection, humans select the desired traits that they want to see in plants/animals. List 3 examples. Dog Breeding Cow Breeding Cross Breeding Farm Crops 25. Explain Natural Selection. The stronger trait that allows a species to survive will be passed along to the next generation. This is due to the fact that the organisms with the stronger trait will survive and reproduce, while those organisms that do not show the stronger trait are not likely to survive and reproduce. UNIT 4.1: Dichotomous keys 26. You will need to be able to read a dichotomous key. Using this example, What type of tree has leaf needles in bundles of 5? White Pine If a tree had compound leaves, you would go to step 15. Tropisms and Turgor Pressure 27. What is…? Phototropism: plants’ response to _________. Light Geotropism: plants’ response to _________. Gravity Hydrotropism: plants’ response to _________. Water Thigmotropism: plants’ response to ________. Touch 28. What does it mean if a plant has low turgor pressure? The plant does not have enough water which makes the cell droopy. What will the plant look like? The plant will be wilted and not able to stand rigid and upright. Stimulus/Response 29. Give an example of an external stimulus that causes an internal response. External Stimulus- The temperature is hot outside. Internal Response-You begin to sweat so that your body stays cool. 30. Getting food poisoning is a ___________ stimulus that would cause vomiting. Internal Stimulus UNIT 4.2: Flow of Energy 31. (flower, snake, sun, hummingbird): Put these organisms in the correct order in a food chain. Sun—Flower--Hummingbird Cycling of Matter 32. What do decomposers do to the stored energy in dead organisms? They return the energy back to the soil to be used by producers. UNIT 5.1: Microhabitats and Biomes 33. Which biome would a cactus be best suited to survive in? Desert biome Biodiversity 34. The more biodiversity an area has, the (more or less) sustainable it is. The more biodiversity, the more sustainability an area has 35. Deforestation, pollution, and over hunting all cause biodiversity to (increase/ decrease). DECREASE UNIT 5.2: Catastrophic Events 36. Hardened lava from volcanoes creates igneous rock which builds up the land. Would this increase or decrease the surface area of the land? INCREASE the surface area Succession 37. What is the definition of a pioneer species? The first organisms to appear in an area. 38. What is primary succession? The colonization of new sites by communities of organisms. It often occurs after a devastating event has wiped out the organisms that lived in an area, or with the creation of a new habitat. It is the slowest type of succession because not even topsoil is present in the community. What is the pioneer species in primary? Lichen and algae What event causes primary succession to begin? Some type of catastrophic event that completely wipes out an area, usually a volcano. 39. What is secondary succession? This is the faster type of succession because topsoil is already present within the community. refers to the concept of an ecosystem reviving itself after all or a portion has been destroyed. What is the pioneer species in secondary? Weeds and small grasses What types of events can cause secondary succession to begin? Wildfires, Flooding or Humans leaving a particular area such as a farm or garden unattended. UNIT 6.1: Weathering, Erosion, Deposition in Texas Eco-regions 40.Define weathering, erosion and deposition. Weathering is the breakdown of rock at the Earth’s surface. Erosion is when rock and soil are moved from one place to another by natural forces. Deposition is when the sediment being carried is dropped (or deposited) in a new area. 41.Explain how waves affect the quantity of sand on a beach. Waves can increase the quantity of sand on a beach if it breaks down large rocks or sides of cliffs down. Waves can also pick up sand and drag it out to sea and decrease the quantity of sand. 42.What effect will rain and wind have on mountaintops over time? The will break them down and cause them to become shorter over time. Groundwater/Watershed 43.What is the difference between groundwater and surface water? Groundwater is found underneath Earth’s surface. Surface water is visible and can be seen on top of the Earth’s surface. 44.How does a well affect the quantity (amount) of groundwater? Pumping wells drain the water found below Earth’s surface. Rain must refill the well so that they do run dry. How does it affect the quantity of surface water? If the water table is lowered, then the surface water is lowered as well. 45.True/False: Pollution in surface water can leach into the groundwater. Explain. True, polluted ponds, lakes and streams can end up slowly leaching into groundwater and contaminating the water source. 46.If spilled gasoline from a tanker truck contaminated the water supply, would it increase or decrease plant growth? DECREASE, harmful chemicals, such as gasoline, will be detrimental to the growth of plants. UNIT 6.2: Work 47. What is formula for work? W=Fxd Work (Joules) = Force (Newtons) x distance (meters) Make up a problem and solve for work. Coach Russell wanted to see if he could throw Eli to the Moon. He picked Eli up who weighed 40 Newtons and threw him a distance of 450,000 meters. How much work was done during this crazy trip to space? 48. If you exert a force but the object does not move, are you doing work? Why or why not? No work is being done. The object must move in the direction of the force in order for work to be done. Space 49. What is the inhabitable zone? An area can support life and allow life to exist. 50. For life to exist on a planet there must be liquid ________ in addition to Nitrogen and ________ as atmospheric gases. Water; Oxygen 51. Lack of gravity has a (positive OR negative) effect on the muscles of astronauts. Explain. NEGATIVE, a prolonged exposure to lack of gravity causes astronauts to lose bone density and muscle (muscular atrophy). ESSAY: The multiple choice portion is worth 80% of your final exam grade and the essay is worth 20% of the final exam grade. There will be one essay on the exam and it can be over any of the above topics.