Weathering Project - Duplin County Schools
advertisement

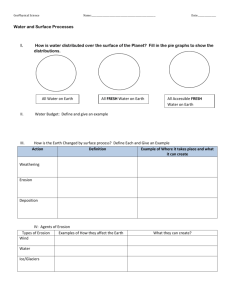
-Recall that soil is the result of weathering of rocks and includes weathered particles: sand, silt and clay. -What is the difference in sand, silt and clay? -Define Chemical Weathering and Physical Weathering -Explain differences in chemical and physical weathering and how weathering rates are affected by a variety of factors including climate, topography and rock composition. -List and explain the types of physical weathering : Joints, Ice Wedging, Oganic activity, abrasion -List and explain the types of chemical weathering: Decomposition, Dissolution, Speroidal Weathering, Hydrolysis, Acid Precipitation, Plant Acids, Oxidation - Define Erosion - Outline erosional processes by water, wind, ice, and gravity - Compare erosion by water, wind, ice, and gravity and the effect on various landforms. -Soil is an important part of weathering, what is soil? What are the parts of the soil horizon? Describe three common types of soil are pedalfer, pedocal, and laterite. -What is a geohazard? -Identify areas of risk for various geohazards (landslides, avalanches, earthquakes, and volcanoes) This should include what the following hazards are, what causes them, and what are areas prone to these risks (Landslide, Earthquake, Tsunami , Sinkhole , Groundwater, Pollution, Flooding) -Conclude the best location for various types of development to reduce impacts by geohazards and protect property. - Explain precautions that can be made to protect life from various geohazards and include meteorological hazards. Some examples include landslides, earthquakes, tsunamis, sinkholes, groundwater pollution, and flooding.