LADD Logic Model - National Child Welfare Workforce Institute
advertisement
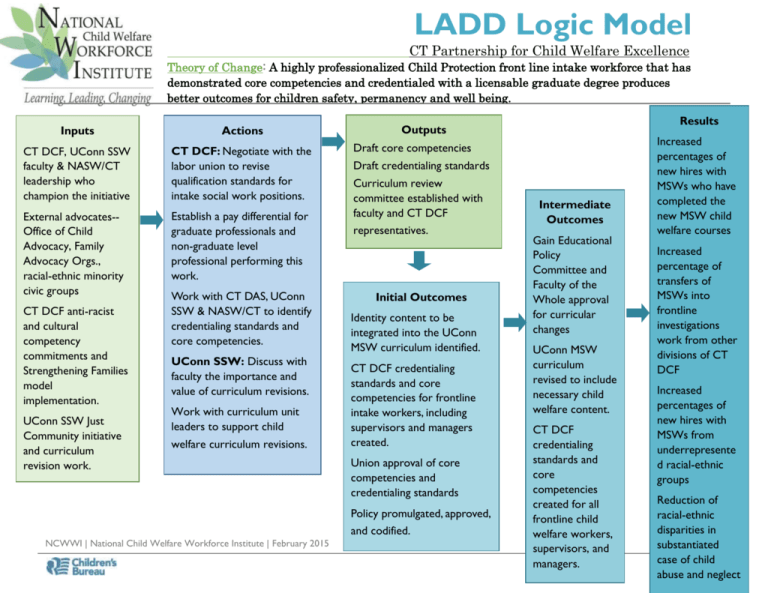
LADD Logic Model CT Partnership for Child Welfare Excellence Theory of Change: A highly professionalized Child Protection front line intake workforce that has demonstrated core competencies and credentialed with a licensable graduate degree produces better outcomes for children safety, permanency and well being. Inputs Actions CT DCF, UConn SSW faculty & NASW/CT leadership who champion the initiative CT DCF: Negotiate with the labor union to revise qualification standards for intake social work positions. External advocates-Office of Child Advocacy, Family Advocacy Orgs., racial-ethnic minority civic groups Establish a pay differential for graduate professionals and non-graduate level professional performing this work. CT DCF anti-racist and cultural competency commitments and Strengthening Families model implementation. UConn SSW Just Community initiative and curriculum revision work. Work with CT DAS, UConn SSW & NASW/CT to identify credentialing standards and core competencies. UConn SSW: Discuss with faculty the importance and value of curriculum revisions. Work with curriculum unit leaders to support child welfare curriculum revisions. Draft core competencies Draft credentialing standards Curriculum review committee established with faculty and CT DCF representatives. Initial Outcomes Identity content to be integrated into the UConn MSW curriculum identified. CT DCF credentialing standards and core competencies for frontline intake workers, including supervisors and managers created. Union approval of core competencies and credentialing standards Policy promulgated, approved, and codified. NCWWI | National Child Welfare Workforce Institute | February 2015 Results Outputs Intermediate Outcomes Gain Educational Policy Committee and Faculty of the Whole approval for curricular changes UConn MSW curriculum revised to include necessary child welfare content. CT DCF credentialing standards and core competencies created for all frontline child welfare workers, supervisors, and managers. Increased percentages of new hires with MSWs who have completed the new MSW child welfare courses Increased percentage of transfers of MSWs into frontline investigations work from other divisions of CT DCF Increased percentages of new hires with MSWs from underrepresente d racial-ethnic groups Reduction of racial-ethnic disparities in substantiated 1 case of child abuse and neglect