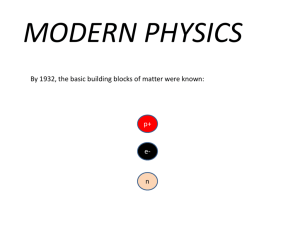
Chapter: Scientific Inquiry Science Branches of science Scientific
advertisement

Chapter: Scientific Inquiry Science Branches of science Scientific inquiry definition and steps critical thinking bias theory vs law measurement tools and SI units density types of graphs independent vs dependent variable control vs constant accuracy and precision models Chapter 1: Motion motion reference point & position describing position in 2D Displacement vs. distance Distance/time graph Speed Formula and units Constant vs Instantaneous average speed scalar quantity Velocity Velocity/time graphs vector quantity Acceleration Formula & units Relationships Chapter 2: Laws of Motion Force contact vs noncontact formula and units Relationship with mass and acceleration Newton Newton’s three Laws of Motion 2nd Law formula relationship between acceleration, balance of forces, & mass Forces balanced vs unbalanced net force force pairs Inertia Gravity value on earth? Law of Universal Gravitation Gravitational forces depends on mass and distance Weight depends on distance from center of Earth formula and units Centripetal forces Friction types reducing friction Air resistance Freefall Terminal velocity Momentum formula & units Law of Conservation of Momentum Collisions elastic inelastic total momentum (before & after) is equal Projectile motion Chapter 3: Work and Simple Machines work and power formulas & units factors affecting work input vs output forces input vs output work Simple machines how machine make work easier 6 types of machines levers first class, second class, & third class examples parts of simple machines fulcrum,..... compound machines examples mechanical advantage ideal vs actual formula and units? efficiency formula & units? Chapter 4: Forces and Fluids Fluids gases & liquids pressure formula & units direction of pressure in fluids relationship between pressure & area atmospheric pressure underwater pressure density factors affecting density buoyant force in air in water affect of pressure of weight of density Archimede’s principle Pascal”s principle hydraulic lifts Bernoulli’s Principle drag force Chapter 5: Energy & Energy Resources Kinetic energy SI Units Formula and relationship Potential energy types of PE SI Units Formula for gravitational PE Transfer of energy = work types of energy energy transformations Law of Conservation of Energy sources of energy renewable vs nonrenewable advantages & disadvantages of resources conservation of energy Chapter 6: Thermal Energy Thermal energy temperature & measurement heat Three types of energy transfer conduction medium used examples conductors insulators thermal contraction vs expansion examples convection convection currents mediums used examples radiation examples solar collectors heat movers refrigerator heat engines internal combustion engine know 4 stroke cycle – p. 218 intake compression ignition expansion heat pumps modern air conditioners Chapter 7: Foundations of Chemistry Classification of Matter p.236 Physical and chemical properties States of matter Volume, shape,… sublimation, condensation, …(ch.8) size dependent properties size independent properties Tyndall effect Melting pt., boiling pt., Physical and chemical changes signs of chemical changes Law of Conservation of Mass how is rate of chemical reactions affected Chapter 9: Understanding the Atom Atom and parts Quarks Atomic Models & scientists Atomic number Average atomic mass Isotopes vs ions Radioactivity and types of decay Chapter 10: Periodic Table Dmitri Mendeleev & development of periodic table Periods and families/groups Metals, nonmetals,… Alkali, alkali earth, …. Periodic table trends general properties of groups Chapter 11: Elements & Chemical Bonds electrons and energy levels valence electrons stable atom chemical bond – involvement of electrons oxidation number superscript types ionic covalent = molecules polar nonpolar metallic electron dot diagrams chemical symbols & formulas subscripts naming ionic and covalent rules polyatomic ions naming rule hydrates Chapter 12: Chemical Reactions & Equations balanced equations reactants, products, coefficients,.. endergonic and exergonic reactions exothermic/endothermic activation energy & graphs types of reactions synthesis decomposition single replacement double replacement combustion rate of reaction affected by? catalyst vs inhibitor Chapter 13: Mixtures, Solubility, & Acid/Base Solutions mixture vs solution(homogenous mixture) alloys compounds vs mixtures solute & solvent water as solvent polar molecule like dissolves like concentration solubility Saturated/unsaturated/supersaturated Solubility curves Factors that speed up solubility acids hydronium ion names and uses of common acids bases hydroxide ion names and uses of common bases pH scale & measurement ( items below from powerpoint) neutralization reactions products soaps composition how they clean detergents composition changes to formula and why esters and polyesters importance Chapter 15: Waves types of mechanical waves transverse compressional Wave parts crest; trough; compression; rarefaction; nodal line wave properties amplitude frequency wavelength wave speed & formula relationship with energy of wave reflection refraction diffraction interference and different types interaction of waves with matter absorption reflection transmission Chapter 16: Sound sound = longitudinal & mechanical vibration speed of sound factors that affect speed detecting sound ear energy of sound waves amplitude & intensity decibel scale frequency & wavelength Doppler Effect Resonance Echo Chapter 17: Electromagnetic Spectrum Speed of EM waves How are waves generated Types of waves EM is composed of Wave properties EM spectrum range and uses Chapter 18 – Section 2, 3 & 4: Mirrors and Lenses Types of mirrors and examples Plane Concave Convex Types of lenses and examples Convex Concave Divergent or convergent rays Refracted or reflected rays rainbows Eye telescopes, microscopes, cameras Lasers and uses Optical fibers