Potato Lab
advertisement

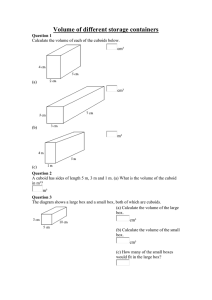
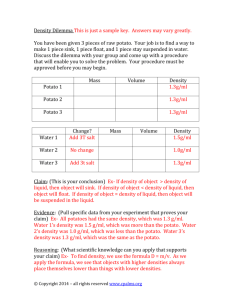
Name(s): Date: Potato Lab: Examining the effect of solutes on plant cells Objective: To observe the effect of various solutions on the mass and size of potato cells. Introduction: Plant and animal cells use diffusion to acquire or eliminate substances they need to maintain their metabolism. For example, oxygen diffuses into cells while carbon dioxide diffuses out. Diffusion of any substance occurs from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. No energy is required for diffusion to occur; thus, it is a form of passive transport. When water diffuses into and out of cells, the process is called osmosis. In this lab, you will track the movement of water into or out of potato cells. The movement of water, or osmosis, will be caused by a concentration gradient across the potato cell plasma membrane. Tonicity is the measure of pressure exerted against the semipermeable membrane. Solute concentration around the surrounding cell will directly influence the tonicity of the cell. If there is a higher solute concentration of solutes (ex. Salt or sugar), outside the cell this will cause water to move out of the cell, and in turn the cell would shrivel. The solution is said to be hypertonic. If there is a lower solute concentration of solute outside the cell than inside the cell, this will cause the water to enter the cell, and causes cells to burst (animal cells). This solution is said to be hypotonic. If the solution inside and outside the cell is the same, this will cause the same amount of water to enter and exit the cell. The cell size would remain the same. This solution is said to be isotonic. Volume of a cuboid: Within this lab you will create and work with samples of potato cells. These samples will be in the shape of 3D rectangles (cuboids). You must be able to calculate the volume of the cuboid (volume of cuboid = length x width x height). Hypothesis: (3 marks) What do you think will happen to the length, mass and volume of the potato tissue samples in the different concentrations of sugar?) If I place the potato into a hypertonic solution: If I place the potato into a hypotonic solution: If I place the potato into an isotonic solution: Variables: (3 marks) Control: ____________________________________ Manipulated: _______________________________ Responding: _______________________________ Materials: Potato Balances 4 cups/beakers Four concentrations of solutions of salt ( NaCl) dissolved in water: 100 mL of each per group. 0 % - pure distilled water 5%- 5 g NaCl/ 100 g solution 10%- 10g NaCl/ 100 g solution 15%- 15g NaCl/100 g solution Procedure: 1) Cut 5 cuboid pieces of potato (all must be the same size and shape). Record the dimensions (length, width, height) and record the cuboids’ volume. 2) Obtain or 100 ml of each of the four solutions in the cups/beakers provided. 3) Record the initial mass of each of the cuboids. 4) Place one cuboid into each cup. Keep one dry for a control. 5) Leave the potato cuboids in solution for 30 minutes. 6) Remove potatoes, pat dry with paper towel and record the final mass of each of the 5 potato cuboids. 7) Calculate the mass difference. Show one sample calculation. 8) Calculate the % change in mass of each. Show one sample calculation. 9) Calculate the average % change in mass. Show your calculation. 10) Complete the analysis Data: (33 marks) 1) Cuboid: length _________ width _________ height ________ volume________ 2) Complete the data table: Trial Salt water solution (%) Increase or Decrease? Initial Mass (g) Final Mass (g) Mass Difference (g) % Percent Change in Mass Average % Change in Mass 1 2 3 4 5 Control (dry) Sample Calculations: (6 marks) Include units in your calculations and your answers. 1) Mass difference: 2) % change in mass: 3) Average % change in mass: (do not include in average) Analysis: (8 marks) Answer on a separate piece of looseleaf. 1. What happens to a plant cell when it is put in distilled water? Would the same thing happen to an animal cell? 2. What happens to a plant cell when it is put in a 5% saline solution? Would the same thing happen to an animal cell? 3. What happens to a plant cell when it is put in a 10% saline solution? Would the same thing happen to an animal cell? 4. What happens to a plant cell when it is put in a 15% saline solution? Would the same thing happen to an animal cell? 5. What does the movement of water have to do with homeostasis in a cell? 6. What would happen to a plant cell that was placed in a solution that matched its internal salt concentration? How would you know? Did this happen in this experiment? 7. Did the results of your qualitative analysis support your hypothesis? Why or why not? 8. Which potatoes gained the most mass after 30 minutes? Which ones lost the most mass? Why? How does your quantitative data support your results?