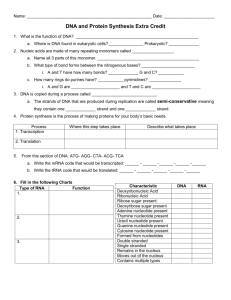
Name: DNA and Protein Synthesis Study Guide Part 1: DNA 1
advertisement
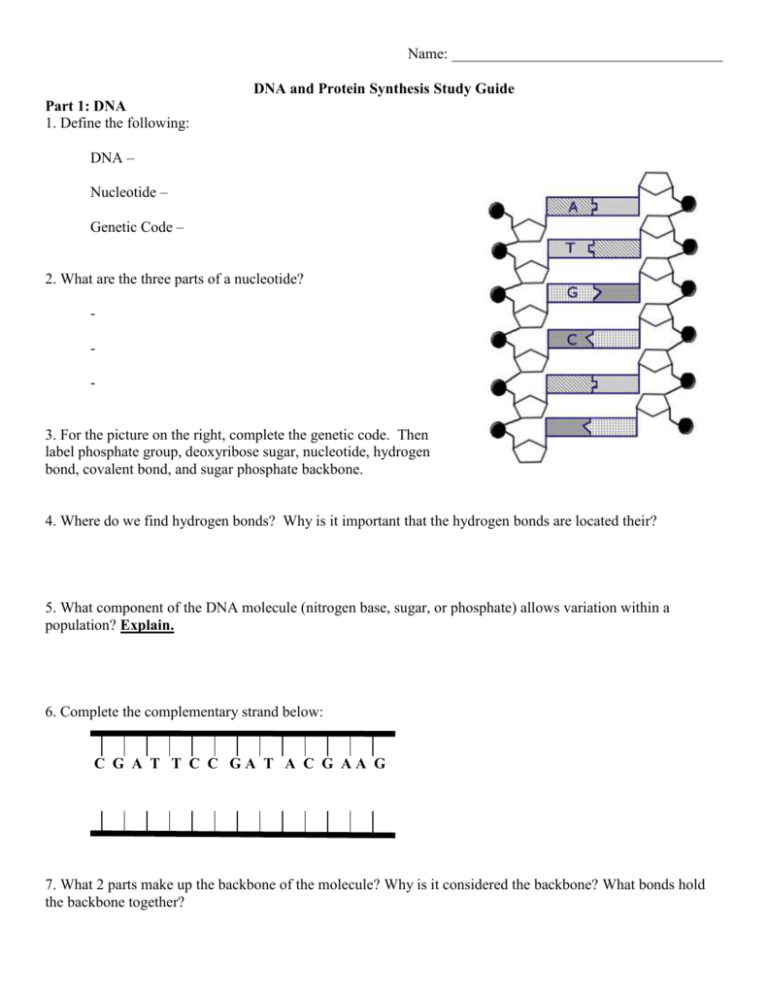
Name: ____________________________________ DNA and Protein Synthesis Study Guide Part 1: DNA 1. Define the following: DNA – Nucleotide – Genetic Code – 2. What are the three parts of a nucleotide? - 3. For the picture on the right, complete the genetic code. Then label phosphate group, deoxyribose sugar, nucleotide, hydrogen bond, covalent bond, and sugar phosphate backbone. 4. Where do we find hydrogen bonds? Why is it important that the hydrogen bonds are located their? 5. What component of the DNA molecule (nitrogen base, sugar, or phosphate) allows variation within a population? Explain. 6. Complete the complementary strand below: C G A T T C C GA T A C G AA G 7. What 2 parts make up the backbone of the molecule? Why is it considered the backbone? What bonds hold the backbone together? 8. If a sample of DNA is taken and contains 17% cytosine: a. How much guanine is there? b. Explain your answer for “a”. c. How much adenine is there? d. Explain your answer for “c”. 9. Which series is arranged in order from LARGEST to SMALLEST in size? A. chromosome… nucleus… cell… DNA… nucleotide B. cell… nucleus… chromosome… DNA… nucleotide C. nucleotide… chromosome… cell… DNA… nucleus D. cell… nucleotide… nucleus… DNA… chromosome Part 2: Protein Synthesis 1. Put the following steps of transcription in the correct order from 1 (first) to 4 (last): ________ ________ ________ ________ DNA is unzipped by the Helicase mRNA strand is made mRNA leaves the nucleus RNA Polymerase connects to the DNA strand 2. Where does transcription occur in the cell? ____________________ 3. If the DNA strand reads AGGCATTACT, what would the mRNA strand read? ________________________ 4. What process is being show in the image below? ________________________________________________ 5. On the image to the right, label the following: 1. DNA Template Strand 2. Non-Template Strand 3. RNA Polymerase 4. mRNA Strand 6. What is the difference between the DNA template strand and DNA non-template strand? 7. What is the product (made) in transcription? ______________________ 8. What is the purpose of transcription? 9. Where does translation occur in the cell? (There are two places) _________________________________ 10. Place the following statements in order from 1 (first) to 4 (last). ________ The ribosome moves to the next codon ________ The tRNA binds to the start codon ________ The ribosome attaches to the start codon ________ The tRNA binds a specific amino acid 11. If one codon read UAC, what would the anti-codon read? ____________ 12. What process is being shown in the image below? ______________________________________________ 13. On the image to the right, match the item to the letter on the diagram: _______ Amino Acid Chain _______ Ribosome _______ Anti-codon _______ Start codon _______ A single amino acid _______ mRNA strand _______ Stop codon _______ tRNA molecule 14. What is the product (made) in translation? ___________________________________ 15. Based on your answer to #14, what is the importance of this? What does it do? 16. Fill in the chart below comparing transcription and translation TRANSCRIPTION TRANSLATION 1. Location(s) in the Cell 2. Is DNA directly involved (yes or no) 3. Type(s) of RNA used 4. What are the bases that pair together? 5. What is the final product (made)? 17. Given the information below, figure out the missing information for each molecule. (work up/down, not left/right) MOLECULE #1 DNA STRAND MOLECULE #2 GATTAC mRNA STRAND ANTICODONS AMINO ACID SEQUENCE (USE CHART ON NEXT PAGE) 18. What is the start codon? 19. What is the amino acid for the start codon? 20. What are the three stop codons? CGAUUG 21. Explain the 3 types of point/substitution mutations: a. b. c. 22. Explain the 2 types of framshift mutations: a. b. 23. Place an “X” in the boxes that make each statement true. Some descriptions may have more than 1 “X”. DNA Used in transcription Used in translation Contains anticodons Contains codons Helicase breaks the hydrogen bonds here Carries amino acids to the ribosomes Make up the ribosome Can be found only in the nucleus Can be found at the ribosome at some time or another 24. Define Gene Expression. mRNA tRNA rRNA 25. Using the picture above, explain which genes would be turned on and off in each cell and why. 26. Explain how you would be able to determine if a given cell was a muscle cell based on what proteins were present.