Grammar: Parts of Speech Notes on Chapter 1, Holt Handbook Why
advertisement

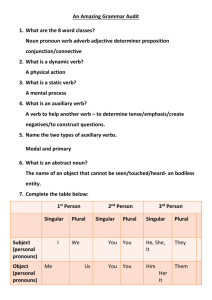
Grammar: Parts of Speech Notes on Chapter 1, Holt Handbook Why grammar, and how will this be covered during 9th grade? Grammar is a disciplined study and it is practically useful. For example, if you buy a new cell phone, you need to know how to use all the applications correctly and what steps to follow to operate the phone smoothly. Similarly, to write well, you need to understand the parts that make up sound writing. Also, to be an educated person, you must have passing vocabulary with grammar terms. During 9th grade we will focus on grammar with two goals in mind: 1. Reinforce and build your grammar vocabulary and discernment skills. 2. Utilize grammar knowledge to improve the clarity, accuracy and variety of word use applied to writing tasks. NOTES ON CH. 1: NOUNS A noun names a person, place, thing or idea [girl, Boston, ball, insight] Common Nouns name groups of persons, places, things or ideas. [woman] Proper Nouns name specific individuals, places, name-brand items or ideas. [Suzanne] Concrete Nouns name persons, places or things that can be directly perceived by the senses. [a sneeze, pool] Abstract Nouns name ideas, feelings, a quality or characteristic. [democracy, kindness] Collective Nouns name groups. [neighborhood, team] Compound Nouns use more than one word to identify the noun. [hallway, team spirit, New York City PRONOUNS A word that takes the place of one or more nouns or a pronoun. Personal Pronouns identify the one speaking (I, me), one spoken to (him, her), or one spoken about (he, her, them) Reflexive Pronouns reference the subject of the verb, and serve as complements or objects of the preposition. [Mary excused herself from the table.] Demonstrative Pronouns point to a noun or other pronoun. [Is this the one you want?] Relative Pronouns introduce an adjectival clause [that, which, who, whom, whose] [The girl who lives down the block goes to my school.] Indefinite Pronouns refer to a non-specific noun. [A few students had to rush to finish the test.] Pronoun or Adjective: Many words can be used as both pronouns and adjectives. o Of that pronoun points to something specific, it is called the Predicate Nominative. [This is the best English class ever.] o Pronouns can serve as adjectives by pointing to nouns. [This class is challenging.] ADJECTIVES A word that modifies (further clarifies or describes) a noun Adjectives may answer these questions about a noun: o What kind? Slovenly habits/joyful presence o Which one? Those papers/next door o How many? Eight times/first chance o How much? Nine pounds of chicken/8 oz of water Articles are adjectives that point to specific individuals, things, places or ideas (these are called Definite Articles…often “the” is used that way). Articles that point to general groups are called Indefinite Articles (usually “a” or “an”). Depending on the role the word uses in a sentences, there are words that can be used as both adjectives and pronouns. (see list on p. 12) Adjective or Noun? Most words used as nouns can also be used as adjectives. [high school student – tells you what type of student]. If the noun used as an adjective references a naming word, then this functions as a Proper Adjective [Notre Dame Academy graduate]. VERBS A word that expresses action or a state of being. Main verbs plus helping (or auxiliary verbs) form a verb phrase. [He should play soccer.] Common helping verbs are: o Forms of “to be” am, are, be, been, being, is, was, were o Forms of “to have” had, has, have o Forms of “to do” do, does, did A Model Auxiliary is a helping verb plus a main verb that tells of necessity or possibility. o Necessity: [I have to drive my daughter to school.] o Possibility: [I may arrive home a bit later than I expect.] Action Verbs tell of physical or mental activity [sleep, imagine] Linking Verbs connect subjects in an identifying or descriptive way. That group of words is called a Subject Complement. o The test looks hard. o Mrs. Smith was my best teacher ever. See list of Linking Verbs on p. 17. Transitive Verbs have an object (single or group) which receives the action of the verb. [I buzzed the front door intercom.] Intransitive Verbs have NO object. [Suzie cried. The car stopped.] ADVERBS A word that modifies a verb, adjective or other adverb. Adverbs tell when, where, how, how much, how often, how long, for example. Modifying verbs: She rambled endlessly. Modifying adjectives: She is a stunning beauty. Modifying other adverbs: He ran surprisingly quickly. Some words used as nouns can also be adverbs: [My parents are going to Colorado Wednesday.] [I’ll bring the paper to your house later.] PREPOSITIONS show relationship between a noun/pronoun to another word. That other word is called the Object of the Preposition. See preposition list handout (attached). The Object of the Preposition is a noun, pronoun (or word group) that acts as a noun. It answers a what/where/when kind of question. [I threw the ball over her head. I traveled around the world.] The Preposition + the Object of the Preposition = the Prepositional Phrase. A Preposition that includes two or more words is called a Compound Preposition. [By now you should have the textbook. Sally wants to come, along with Bill.] CONJUNCTIONS join words or word phrases Coordinating Conjunctions join words or word groups that are used in the same way. o And o But o For o Nor o Or o So o Yet Correlative Conjunctions form pairs of conjunctions: o Both/and o Either/or o Not only/but also o Neither/nor o Whether/or Subordinating Conjunctions begin a subordinate clause and connect it to an independent clause: See full list on p. 26 [Since you left, I’ve been lonely. Whenever you return, I’ll feel joyful.] Sometimes it’s hard distinguishing between a Prepositional Phrase and a Subordinating Conjunction. It depends on the function in the sentence. INTERJECTION expresses emotion ] MOST COMMON PREPOSITIONS •aboard •about •above •across •after •against •along •amid •among •anti •around •as •at •before •behind •below •beneath •beside •besides •between •beyond •but •by •concerning •considering •despite •down •during •except •excepting •excluding •following •for •from •in •inside •into •like •minus •near •of •off •on •onto •opposite •outside •over •past •per •plus •regarding •round •save •since •than •through •to •toward •towards •under •underneath •unlike •until •up •upon •versus •via •with •within •without