chapter 6 math review packet answer key
advertisement

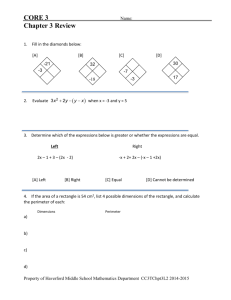
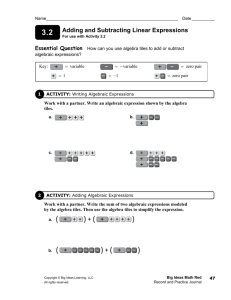
Core Connections 1 (6th Grade Mathematics) Chapter 6: Dividing and Building Expressions Learning Targets We are learning to determine portions resulting from dividing a quantity among a specified number of groups. Example Problems: 6-5, 6-10, 6-34, 6-52, 6-59 and 6-99 6-5. If you had 2 pieces of licorice to share equally among 3 people, how much licorice would each person get? Show your thinking clearly. 6-5. See below: Each person should get a quantity equivalent to of a piece. 6-52. At the school’s fall bake sale, all of the pies were cut into 6 pieces, so each person who bought a piece bought of a pie. Each slice of pie sold for $1.00. How much money did the school make if all eleven pies were sold? (In other words, find 11 divided by 6-52. See below: $66 .) We are learning to use diagrams to divide by portions. 6-21, 6-34, 6-38, 6-99and CL 6-124 6-34. Draw a diagram that shows how to divide 9 pieces of licorice into packages that hold 5 pieces each. Then find 9 ÷ 5. 6-34. See below: See sample diagram below. 1 So, when you divide 9 into groups of 5, you have one whole group and 4/5 of a second group CL 6-124. Draw diagrams to calculate each of the following quotients. a. You can make 7 groups of 2/3 b. You can make 4 groups of 2 1/2 Learning Targets Example Problems: We are learning to simplify algebraic expressions, including writing and simplifying expressions to describe the area and perimeter of shapes formed by algebra tiles. 6-106, 6-107, 6-115, CL 6-121 (a) & (b) and CL 126. 6-107. Sketch the collection of algebra tiles that is described by the following expression. Rewrite the area of the collection by combining like terms. 7x + 2x2 + 3x2 + 3 + x CL 6-126. Copy the following expressions on your paper and simplify them by combining like terms. Using algebra tiles may be helpful. a. 4x + 2 + 2x + x2 + x b. 10x + 4 −3 + 8x + 2 c. 4 + x2 + 3x + 2x2 + 4 d. x + 4 + (x − 1) + 3 + 2x a. x2 + 7x + 2 b. 18x + 3 c. 3x2 + 3x + 8 d. 4x + 6 We are learning to calculate the perimeter of shapes composed of rectangles and of algebra tiles. 6-91, 6-96, 6-106, and CL 6-121 © 6-96. Copy the diagrams of algebra tiles below on your paper. Then find the perimeter of each shape. A. B. 6-96. See below: a. 4x + 4 units b. 4x + 4 units CL 6-121. On your paper, sketch the algebra-tile shape at right. Then answer parts (a) through (c) below. a. Find the perimeter of the figure. b. Find the area of the figure. c. If the algebra tiles were rearranged how would the area change? CL 6-121. a. P = 4x + 6 units b. A = x2 + 2x + 2 square units c. The area would not change. Learning Targets Example Problems: We are learning to evaluate simple algebraic expressions. 6-75, 6-110, 6-115, and CL 6-122 6-75. Evaluate the expressions below using r = 3 and h = 5. a. a. 6h − 4 b. 8r + h c. r2 6-75. See below: a. 26 b. 29 c. 9 6-110. Evaluate the expressions below for the given values of the variables a. 6j − 3 for j = 4 b. b2 + 5 c. 8 + 4k for k = 3.5 6-110. See below: a. 21 b. 14 c. 22 for b = 3 We are learning to locate points on a number line and on a coordinate graph. 6-13, 6-25, 6-37, 6-40, 6-51, 6-56, 6-73, 6-88, and 6-119. 6-13. Copy the number line and label the following numbers at their approximate place on the number line a. b. 0.75 c. d. 6-13. See below: See diagram below. Write the points on the graph below as ordered pairs. 6-25. See below: A (2, 3), B (3.5, 8), C (4, 1.5), D (5.5, 4.5), E(8, 8)