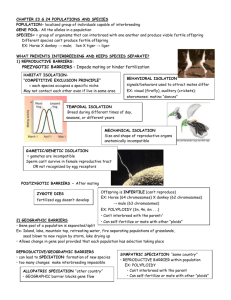
Pukeko AS 3.5 Processes of evolution corrected 20may
advertisement
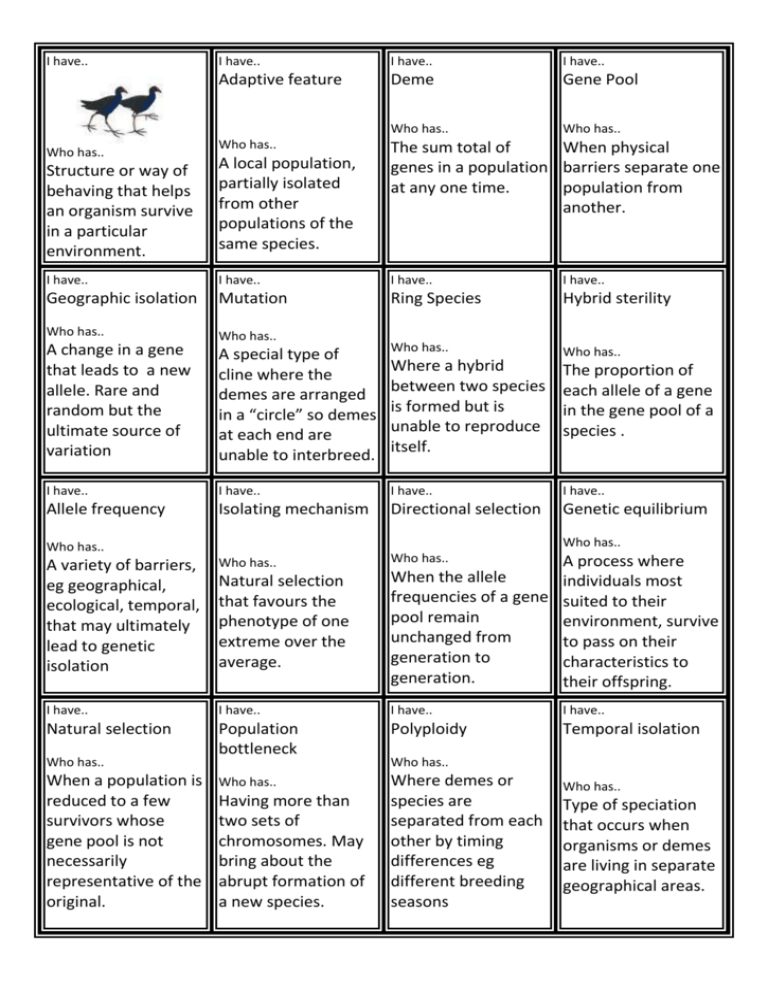
I have.. Who has.. Structure or way of behaving that helps an organism survive in a particular environment. I have.. I have.. I have.. Adaptive feature Deme Gene Pool Who has.. Who has.. Who has.. A local population, partially isolated from other populations of the same species. The sum total of When physical genes in a population barriers separate one at any one time. population from another. I have.. I have.. I have.. I have.. Geographic isolation Mutation Ring Species Hybrid sterility Who has.. Who has.. A special type of cline where the demes are arranged in a “circle” so demes at each end are unable to interbreed. Who has.. Who has.. I have.. I have.. I have.. I have.. Allele frequency Isolating mechanism Directional selection Genetic equilibrium A change in a gene that leads to a new allele. Rare and random but the ultimate source of variation Where a hybrid between two species is formed but is unable to reproduce itself. The proportion of each allele of a gene in the gene pool of a species . Who has.. Who has.. Who has.. A variety of barriers, eg geographical, ecological, temporal, that may ultimately lead to genetic isolation Who has.. Natural selection that favours the phenotype of one extreme over the average. A process where When the allele individuals most frequencies of a gene suited to their pool remain environment, survive unchanged from to pass on their generation to characteristics to generation. their offspring. I have.. I have.. I have.. I have.. Natural selection Population bottleneck Polyploidy Temporal isolation Who has.. Where demes or species are separated from each other by timing differences eg different breeding seasons Who has.. When a population is reduced to a few survivors whose gene pool is not necessarily representative of the original. Having more than two sets of chromosomes. May bring about the abrupt formation of a new species. Who has.. Who has.. Type of speciation that occurs when organisms or demes are living in separate geographical areas. I have.. I have.. I have.. I have.. Allopatric speciation Disruptive selection Genetic drift Instant speciation Who has.. Who has.. Who has.. Natural selection that favours both extremes at the expense of the average. Random changes in gene pools that can be highly significant in altering allele frequency in small gene pools. When an organism is isolated from its original species in one generation by polyploidy. How species avoid direct competition with other species eg by exploiting slightly different food sources. I have.. I have.. I have.. I have.. Niche differentiation Post-zygotic Autopolyploidy Fitness Who has.. Who has.. Who has.. Refers to isolating factors that act after fertilisation Where an individual has more than two chromosome sets that have arisen from non-disjunction within the same species. Who has.. I have.. Who has.. A measure of how well suited an organism is to survive and reproduce in its habitat. Occurs when a small number of individuals colonise a new area and whose alleles may not be representative of he parent gene pool I have.. I have.. I have.. Founder Effect Microevolution Phenotype Pre-zygotic Who has.. Who has.. Who has.. Who has.. The generation to generation changes in the frequency of alleles in the gene pool of a population. Physical expression of genotype which is acted on by natural selection Refers to isolating factors that act before fertilisation. When a species or group can no longer breed successfully with any other organism but the members of its own species or group I have.. I have.. I have.. I have.. Reproductive isolation Stabilising selection Gene flow Macroevolution Who has.. Who has.. The movement of Who has.. Natural selection genes from one part that favours the of a population to average phenotype another or from one at the expense of the population to extremes. another, via gametes. Large scale changes in groups of species or genera over time, as viewed in the fossil record Who has.. The proportion of each genotype in the gene pool. I have.. I have.. I have.. I have.. Genotype frequency Allopolyploidy Cline Who has.. Sexual recombination Who has.. Who has.. The shuffling of genes by independent assortment of chromosomes and random joining of gametes . Pattern of variation within a species. A continuous increase or decrease in some characteristic between adjacent populations eg from north to south. A group of actually or potentially interbreeding natural populations that is reproductively isolated from other such groups. I have.. I have.. I have.. I have.. Species Amphiploidy Artificial Selection Non-random mating Who has.. Who has.. Who has.. Who has: Where an individual has more than two chromosome sets that has arisen from combining two different genomes (species) and generally forms infertile hybrids. The doubling of sterile hybrid chromosome sets in plants to create a fertile plant. I have... Sympatric speciation Who has ... Selection by humans, Occurs when of desirable traits in individuals select a certain phenotype to plants or animals. mate with I have.... Who has ... Who has.. Where species evolve in the same area without geographical isolation I have.... I have.... Who has ... Who has ...