Inside the atom
advertisement

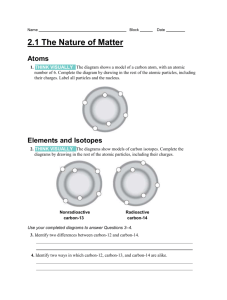
Inside the atom – how/why compounds are formed. Most elements do not exist in nature but must be processed to extract them from compound. Iron metal does not exist naturally but rather as iron oxide (iron ore) i.e. magnetite Fe3O4. The reason for this is that iron is an unstable atom and prefers to be combined with other atom(s) to become stable – it all comes down to how many electrons an atom has. Atoms contain electrons (- charges) , protons (+ charges) & neutrons (no charge). Giving & taking – IONIC BONDING 1. Let’s look at the chlorine atom – atomic number 17 on the Periodic Table. The atomic number tells us that it has: 17 electrons (-‘s) & 17 protons (+’s) = overall zero charge To become stable, a chlorine atom will tend to ‘grab’ an electron from another atom. So the chlorine atom now has; 18 electrons = -18 17 protons = +17 Overall -1 charge so can be written Cl – (chloride ion) 2. Let’s look at the sodium atom – atomic number 11 on the Periodic Table. The atomic number tells us that it has: 11 electrons (-‘s) & 11 protons (+’s) = overall zero charge To become stable, a sodium atom will tend to ‘lose’ an electron. So the sodium atom now has; 10 electrons = -10 11 protons = +11 Overall +1 charge so can be written Na+ (sodium ion) So a chlorine atom wants to grab an electron, and a sodium atom wants to lose an atom!!!! Na+ + Cl- ͢ NaCl (sodium chloride – table salt) The periodic table is arranged so we can predict with ease which atoms will lose electron(s) and which ones will grab electrons. We can thus work out chemical formulae of compounds) If we look at Group 1 elements, they will lose one electron. (i.e. Li, Na & K) If we look at Group 17 elements, they will grab one electron. (i.e. F, Cl, & Br) BBC Schools video http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/science/add_edexcel/ionic_compounds/ionicact.shtml IONIC BONDING GAME http://www.thephysicsfront.org/items/detail.cfm?ID=11318 +1 charge Li + Na + K+ +2 charge Mg 2+ Ca 2+ Ba 2+ Name of chemical compound Sodium chloride Calcium chloride Potassium chloride Magnesium sulfide Sodium carbonate Calcium sulfate Aluminium chloride Aluminium oxide Sodium hydroxide + 3 charge Al 3+ -1 charge Cl - (chloride ion) Br - (bromide ion) I - (iodide ion) (OH) – hydroxide ion -2 charge O 2- (oxide ion) (SO4) 2- (sulphate ion) (CO3) 2- (carbonate ion) S 2- (sulphide ion) Ions present Chemical Formula 1 X Na + & 1 X Cl - NaCl Ba(OH)2 Al 3+ & (OH) Li2O K+ & (CO3) 2-