Planning guidance - Mathematics Mastery
advertisement

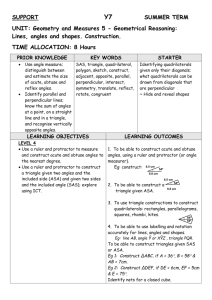
Unit 5: Constructing triangles and quadrilaterals Planning guidance Unit objectives Within this unit, students will learn to: Measure and draw angles Identify and name angles Define triangles and quadrilaterals Draw a triangle given two sides and one angle Draw a triangle given one side and two angles Draw a triangle given three sides Draw a square given one side Draw a rectangle given its length and width Draw a rhombus given one side and one angle Draw a parallelogram given two adjacent sides and an angle Draw a trapezium given two adjacent sides and two angles Identify types of angles produced by parallel lines Find unknown angles Having covered types of angle, triangle and quadrilateral in Year 7, these topics will be consolidated and built on within the tasks involving construction of triangles and quadrilaterals. Teachers may choose to spend additional time with students ensuring competency at measure (angles and length), practising the constructions and using angle properties to find missing angles in various shapes. This unit should take three weeks. There are three key sections to this unit. Within each section there are a number of department tasks to be completed collaboratively. These tasks should form the starting point of planning lessons and are designed to encourage debate and discussion amongst teachers. As this topic involved use of precision equipment, it would be worthwhile discussing how tasks can be used in lessons and how competency in using equipment can be developed. Suggested Structure The actual number of lessons spent on each section will depend on the individual class and the number of lessons available to teachers. We suggest the following based on a total of 9, 12 or 15 lessons over the three weeks: Section Constructing Triangles Constructing Quadrilaterals Properties of angles in parallel lines 9 lessons 3 2 4 12 lessons 4 3 5 Copyright © Mathematics Mastery 2014 15 lessons 4 4 7 Constructing triangles Objectives Measure and draw angles Identify and name angles Define triangles Recognise the properties of triangles Recognise impossible triangles Draw a triangle given two sides and one angle Draw a triangle given one side and two angles Draw a triangle given three sides In this unit students work to develop their knowledge of angle facts as well as refining their construction skills and their skills in using mathematical equipment accurately. Since this is a three week unit, enough time should be given to ensuring students feel confident in using protractors and pairs of compasses. When working on the construction of triangles, students have the chance to revisit types of triangles and triangle properties and should be encouraged to explore the minimum information needed to construct a triangle. In addition, there is an emphasis on use of technical notation for equal length lines and parallel lines. To really extend students and to encourage them to think carefully about the properties of triangles rather by considering impossible triangles and thinking about what conditions are needed for a triangle to be ‘possible’. For further guidance, including the Department Tasks for this section, click Constructing triangles under Planning resources on the main page for this unit. Constructing quadrilaterals Objectives: Use coordinates Measure and draw angles Identify and name angles Define quadrilaterals Recognise the properties of quadrilaterals Draw a square given one side Draw a rectangle given its length and width Draw a rhombus given one side and one angle Draw a parallelogram given two adjacent sides and an angle Draw a trapezium given two adjacent sides and two angles For this section, students extend their skills to looking at quadrilaterals. Again, names and properties of the shapes should be considered and students should be confident in identifying quadrilaterals and Copyright © Mathematics Mastery 2014 deciding what makes ‘a square a square’ etc. In the same way as working with triangles, students then spend time constructing shapes accurately, each time considering whether shapes are possible to construct and what the minimum require information is. Considering different orientations is extremely important. Excellent group or pair tasks can be implemented through asking students to challenge each other with construction questions and also by asking those more confident in their skills (especially in using pairs of compasses and protractors) to support their peers. For further guidance, including the Department Tasks for this section, click Constructing quadrilaterals under Planning resources on the main page for this unit. Angles in parallel lines Objectives: Measure and draw angles Identify and name angles Identify types of angles produced by parallel lines Find the values of unknown angles Having worked with triangles and quadrilaterals and discussed some angle properties, students will spend the last week of this unit looking at angles in parallel lines. There is ample opportunity to explore and investigate angle properties and consolidate measuring angles skills. Throughout the unit we encourage using the correct technical terminology for angle relationships and correct notation in diagrams. There is emphasis here on developing reasoning skills (which would work well as talk tasks and group work), but some teachers may wish to encourage students to develop their written skills in this unit. For further guidance, including the Department Tasks for this section, click angles in parallel lines under Planning resources on the main page for this unit. Copyright © Mathematics Mastery 2014