Name Period _____ Date ______ EARTH SYSTEMS Chapter 25.1
advertisement

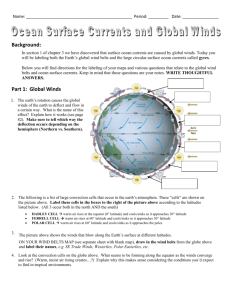
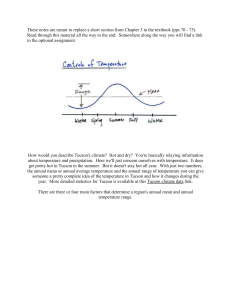
Name ________________________________________ Period _____ Date _________ EARTH SYSTEMS Chapter 25.1 Earth Systems Factors Affecting Climate Chart Directions: Sketch and label the Factors Affecting Climate Chart . Earth System Standard: SES5. Students will investigate the interaction of insolation and Earth systems to produce weather and climate. a. Explain how latitudinal variations in solar heating create atmospheric and ocean currents that redistribute heat globally. d. Describe how temperature and precipitation produce the pattern of climate regions (classes) on Earth. 1.) 2.) 3.) 4.) Placed chart in notebook behind the Chapter 25 Word Study. (Friday, April 22) Climate meanings and notes were accurate with no abbreviations. Factors chart was accurately copied with no abbreviations. Factors were accurate, shaded, complete, neatly drawn and written, and large enough to be easily read. ____ yes ____ no ____ yes ____ yes ____ no ____ no ____ yes ____ no MAJOR TWO FACTORS AFFECTING CLIMATE: Temperature and Pecipitation OTHER FACTORS AFFECTING CLIMATE LATITUDE 1.) Solar Energy: the higher the latitude, the smaller the angle at which the sun's rays hit Earth and the smaller the amount of solar energy the area receives because Earth's axis is tilted, the angle at whch the sun's rays hit an area changes as Earth orbits the sun 2.) Global Wind Patterns because Earth receives different amounts of solar energy at different latitudes, belts of cool, dense air form at latitudes near the poles, while belts of warm, less dense air form near the equator the doldrums are an equatorial belt of low pressure where the air rises and cools and water vapor condenses as seasons change, global wind belts shift in a north or south direction causing precipitation also to shift HEAT ABSORPTION AND RELEASE Latitude and cloud cover affect the amount of solar energy that an area receives land heats faster than water waves, currents and other movements continuously replace warm surface water with cooler water from the ocean depths 1.) Specific Heat and Evaporation 2.) Ocean Currents 3.) El Nino - Southern Oscillation or ENSO - warm water phase La Nina - cool water phase 4.) Seasonal Winds TOPOGRAPHY 1.) elevation 2.) rain shadows

















![mh SeasonsAroundWorldSE[1]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/007400642_1-ab04f9f91daf125b4d8509bef2c238b3-300x300.png)
![2juliaSeasonsAroundWorldSE[1]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/007358151_1-a51cd9e1c1c6d77cf26aadb05d25cd78-300x300.png)
