Combined ESM file for Pearse and Hipp
advertisement
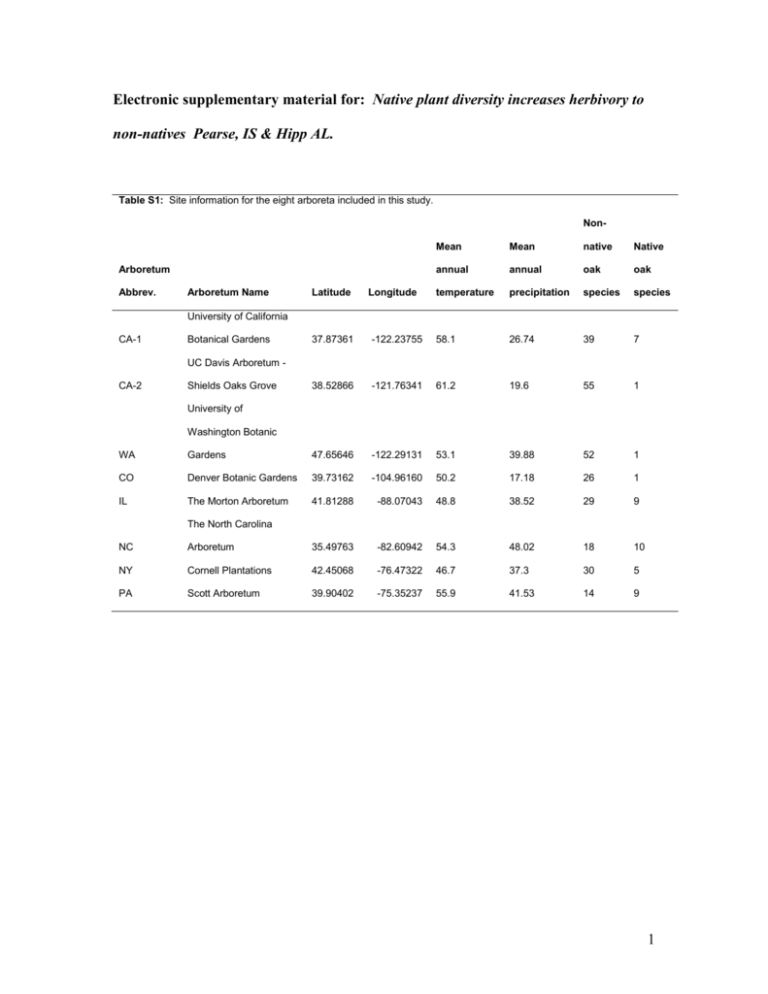
Electronic supplementary material for: Native plant diversity increases herbivory to non-natives Pearse, IS & Hipp AL. Table S1: Site information for the eight arboreta included in this study. Non- Arboretum Abbrev. Arboretum Name Latitude Longitude Mean Mean native Native annual annual oak oak temperature precipitation species species University of California CA-1 Botanical Gardens 37.87361 -122.23755 58.1 26.74 39 7 38.52866 -121.76341 61.2 19.6 55 1 UC Davis Arboretum CA-2 Shields Oaks Grove University of Washington Botanic WA Gardens 47.65646 -122.29131 53.1 39.88 52 1 CO Denver Botanic Gardens 39.73162 -104.96160 50.2 17.18 26 1 IL The Morton Arboretum 41.81288 -88.07043 48.8 38.52 29 9 The North Carolina NC Arboretum 35.49763 -82.60942 54.3 48.02 18 10 NY Cornell Plantations 42.45068 -76.47322 46.7 37.3 30 5 PA Scott Arboretum 39.90402 -75.35237 55.9 41.53 14 9 1 1 Table S2: Description of oak taxa and phylogenetic treatment. Species treatment clade rationale or citation added at base of tree, with 1my yr separation between Notholithocarpus Quercus and densiflorus Notholithocarpus Notholithocarpus (1) Q acutissima in core phylogeny Cerris (3) polytomy with Q. acuta Cyclobalanopsis Cyclobanalopsis Cyclobalanopsis monophyletic (6,13) Eurasian white oaks infraspecies and synonyms Q. acutidentata sister to Q. aliena s.s. placed sister Q. agrifolia in core phylogeny Lobatae (3) American white Q. alba Q. aliena in core phylogeny sister to Q. acutidentata oaks (3) Eurasian white oaks infraspecies and synonyms s.s. placed sister American white Q. arizonica sister to Q. englemanii oaks (12) Q. ballota in core phylogeny Cerris (3) Monophyly of Latin Q. benthami Latin American polytomy Lobatae American red oaks (3) American white Q. berberidifolia in core phylogeny oaks (3) 2 eastern white oaks with polytomy with bur and American white resemblance to bur oak; Q. bicolor bicolor oaks microsatellite data (11) Q. brandegei in core phylogeny Geminata group (3) Q. buckleyi in core phylogeny Lobatae (3) Ilex group of Cerris Q. calliprinos in core phylogeny section (3) Eurasian white oaks Q. canariensis in core phylogeny s.s. (3) Monophyly of Latin Q. canbyi Latin American polytomy Lobatae American red oaks (3,12) Q. candicans in core phylogeny Lobatae (3) Q. castaneifolia in core phylogeny Cerris (3) Q. cedrosensis polytomy with Protobalanus Protobalanus (5,6) Q. cerris in core phylogeny Cerris (3) Treated as an infraspecies of Q. acutissima; Q. chenii sister to Q. acutissima Cerris infraspecies placed sister Q. chrysolepis in core phylogeny Protobalanus (3) Q. coccifera in core phylogeny Ilex group of cerris (3) Lobatae morphology; (4) sister to Q. ellipsoidalis; with Q. coccinea Q. velutina Monophyly of Latin Q. costaricensis Latin American polytomy Lobatae American red oaks (3) 3 Q. crassifolia in core phylogeny Lobatae (3) Q. crassipes in core phylogeny Lobatae (3) Q. petraea polytomy, at Q. dalechampii divergence between Q. Eurasian white oaks robur and Q. canariensis s.s. (9) Monophyly of Eurasian Q. dentata Asian white oak polytomy Eurasian white oaks white oaks (3); s.s. biogeography American white Q. diversifolia in core phylogeny oaks (3) American white Q. douglasii in core phylogeny oaks (3) polytomy with Q. johntuckeri, Q. turbinella, Q. Q. dumosa Q. durandii dumosa, Q. durata, Q American white pacifica oaks Morphology, (10) American white infraspecies and synonyms oaks placed sister sister to Q. sinuata polytomy with john-tuckeri, Q. durata turbinella, dumosa, durata, American white pacifica oaks Morphology (10) sister to coccinea; with Q. Q. ellipsoidalis velutina Lobatae (4) Q. engelmanii in core phylogeny American white (3) 4 oaks Monophyly of Eurasian Q. fabri East Asian white oak Eurasian white oaks white oaks (3); polytomy s.s. biogeography Eurasian white oaks Q. faginea in core phylogeny s.s. (3) Lobatae (12) divergence between Q. Eurasian white oaks (9) roburoids geneticaly Q. frainetto robur and Q. canariensis s.s. identical Q. fusiformis in core phylogeny Geminata group (3) base of eastern North Q. falcata American Lobatae Q. petraea group, at American white Q. gambelii in core phylogeny oaks (3) American white Q. garryana in core phylogeny Q. garryana var. breweri oaks (3) American white sister to garryana oaks Varieties placed sister Monophyly of Latin Q. gentryi Latin American polytomy Lobatae American red oaks (3) Lobatae Morphology base of eastern North Q. georgiana American Lobatae polytomy with Q. gilva Cyclobalanopsis Cyclobanalopsis Cyclobalanopsis monophyletic (6,13) 5 Eurasian white oaks Synonyms and infraspecies Q. glandulifera sister to serrata s.s. placed sister Q. glauca in core phylogeny Cyclobalanopsis (3) Monophyly of Latin Q. graciliformis Latin American polytomy Lobatae American red oaks (3) Q. gravesii in core phylogeny Lobatae (3) American white Q. gregii in core phylogeny oaks (3) American white Q. grisea in core phylogeny oaks (3) divergence between Q. Eurasian white oaks (9) roburoids geneticaly robur and Q. canariensis s.s. identical divergence between Q. Eurasian white oaks (9) roburoids geneticaly robur and Q. canariensis s.s. identical polytomy with gambelii, American white Biogeography; garryana oaks morphological similarity petraea polytomy, at Q. haas petraea polytomy, at Q. hartwissia[na] Q. havardii petraea polytomy, at Q. iberica divergence between Q. Eurasian white oaks robur and Q. canariensis s.s. (9) roburoids clustered Ilex group of cerris Q. ilex in core phylogeny section (3) Q. ilicifolia base of eastern North Lobatae Morphology, 6 Q. imbricaria American lobatae biogeography (8) base of eastern North Morphology, American lobatae Lobatae biogeography (8) Eurasian white oaks Q. infectoria in core phylogeny s.s. (3) Q. ithaburensis in core phylogeny Cerris section (3) polytomy with Q. johntuckeri, Q. turbinella, Q. Q. johntuckeri dumosa, Q. durata, Q. American white pacifica oaks polytomy with Q. agrifolia, Q. kellogii Q. wislizenii, Q. kellogii Morphology, Lobatae base of eastern North Q. laurifolia American Lobatae Morphology (10) biogeography (8) Morphology, Lobatae biogeography (8) Eurasian white oaks Q. lioatungensis sister to mongolica s.s. synonyms placed sister American white Q. lobata Q. lyrata in core phylogeny oaks (3) polytomy with bur and American white eastern white oaks with bicolor oaks resemblance to bur oak American white Q. macrocarpa in core phylogeny oaks (3) American white Q. margarettiae in core phylogeny oaks (3) 7 base of eastern North Q. marilandica American lobatae Q. mexicana in core phylogeny Lobatae (3) American white Q. michauxii sister to alba oaks (12) American white Q. mohriana in core phylogeny oaks (3) American white Q. mongolica Q. montana in core phylogeny oaks polytomy with michauxii American white and prinoides oaks (3) morphology American white Q. muehlenbergii in core phylogeny oaks polytomy with Q. myrsinifolia cyclobalanopsis Cyclobanalopsis Cyclobalanopsis base of eastern North Q. nigra American lobatae (3) monophyletic (6,13) Morphology, Lobatae biogeography (8) Morphology, Q. nuttallii sister to texana Lobatae biogeography (8) American white Q. oblongifolia in core phylogeny oaks (3) American white Q. obtusata in core phylogeny oaks (3) 8 base of predominantly Q. eastern North American American white Morphology, oglethorpensis white oak clade oaks biogeography (10) Q. oleoides in core phylogeny Geminata group (3) western North American American white Morphology, white oak clade oaks biogeography (10) base of predominantly Q. oocarpa polytomy with john-tuckeri, turbinella, dumosa, durata, American white Q. pacifica pacifica oaks Morphology, (10) Q. palmeri in core phylogeny Protobalanus (3) branch inside of agrifolia et Q. palustris al. Lobatae (12) Q. parvula in core phylogeny Lobatae (3) divergence between Q. Eurasian white oaks (9) roburoids genetically robur and Q. canariensis s.s. identical petraea polytomy, at Q. petraea base of eastern North Q. phellos American lobatae Morphology, Lobatae biogeography (8) Ilex group of cerris Q. phillyreoides in core phylogeny section (3) divergence between Q. Eurasian white oaks (9) roburoids geneticaly robur and Q. canariensis s.s. identical petraea polytomy, at Q. polycarpa 9 Q. polymorpha polytomy with vaseyana, American white pungens, mohriana oaks (12) divergence between Q. Eurasian white oaks (9) roburoids genetically robur and Q. canariensis s.s. identical petraea polytomy, at Q. pontica American white Q. prinoides Q. prinus in core phylogeny oaks (3) American white Infraspecies and synonyms oaks placed sister divergence between Q. Eurasian white oaks (9) roburoids genetically robur and Q. canariensis s.s. identical sister to Q. montana petraea polytomy, at Q. pubescens American white Q. pungens in core phylogeny oaks (3) Eurasian white oaks Q. robur in core phylogeny s.s. (3) Morphology, Q. rubra near shumardii Lobatae biogeography (8) American white Q. rugosa in core phylogeny oaks (3) Monophyly of Latin Q. rysophylla Latin American polytomy Lobatae American red oaks (3) Monophyly of Latin Q. saltillensis Latin American polytomy Lobatae American red oaks (3) 10 Monophyly of Latin Q. sartorii Latin American polytomy Lobatae American red oaks (3) Monophyly of Latin Q. scytophylla Latin American polytomy Lobatae American red oaks (3) Eurasian white oaks Q. serrata in core phylogeny s.s. (3) Morphology, Q. shumardii near rubra Lobatae biogeography (8) American white Q. sinuata in core phylogeny oaks (3) polytomy with bur and American white Morphology, Q. stellata bicolor oaks biogeography (12) Q. suber in core phylogeny Cerris (3) Infraspecies and synonyms Q. texana with buckleyi, gravesii Lobatae placed sister Q. tomentella in core phylogeny Protobalanus (3) Monophyly of Latin Q. tristis Latin American polytomy Lobatae American red oaks (3) Q. trojana in core phylogeny Cerris (3) American white Q. turbinella in core phylogeny oaks (3) in polytomy with Q. Q. vaccinifolia chrysolepis and Q. palmeri Protobalanus (5,6) Q. variabilis in core phylogeny Cerris (3) 11 American white Q. vaseyana in core phylogeny oaks (3) with Q. ellipsoidalis and Q. Q. velutina coccinea Lobatae (4) Q. virginiana in core phylogeny Geminata group (3) polytomy with Q. agrifolia, Q. wislizeni Q. wislizenii, Q. kellogii Californian Lobatae (2), Lobatae microsatellite data 2 3 Table S2 references: 4 1. 5 6 inferred from nuclear CRABS CLAW sequences. Taxon 57(2):434-451. 2. 7 8 3. Pearse IS & Hipp AL (2009) Phylogenetic and trait similarity to a native species predict herbivory on non-native oaks. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the 10 United States of America 106(43):18097-18102. 4. 12 13 Dodd RS & Afzal-Rafii Z (2004) Selection and dispersal in a multispecies oak hybrid zone. Evolution 58(2):261-269. 9 11 Oh SH & Manos PS (2008) Molecular phylogenetics and cupule evolution in Fagaceae as Hipp AL & Weber JA (2008) Taxonomy of Hill's oak (Quercus ellipsoidalis : Fagaceae): Evidence from AFLP data. Syst. Bot. 33(1):148-158. 5. Manos PS, Doyle JJ, & Nixon KC (1999) Phylogeny, biogeography, and processes of 14 molecular differentiation in Quercus subgenus Quercus (Fagaceae). Molecular 15 Phylogenetics and Evolution 12(3):333-349. 16 6. 17 18 Manos PS, Zhou ZK, & Cannon CH (2001) Systematics of Fagaceae: Phylogenetic tests of reproductive trait evolution. Int. J. Plant Sci. 162(6):1361-1379. 7. Nixon KC & Muller CH (1994) New names in California oaks. Novon 4:391-393. 12 19 8. 20 21 America North of Mexico vol. 3), pp 447-468. 9. 22 23 10. 11. 30 Craft KJ & Ashley MV (2006) Population differentiation among three species of white oak in northeastern Illinois. Can. J. For. Res 36(1):206-215. 12. 28 29 Nixon KC (2002) The oak (Quercus) biodiversity of California and adjacent regions. in USDA Forest Service General Technical Report PSW (Vallejo, CA). 26 27 Denk T & Grimm GW (2010) The oaks of western Eurasia: Traditional classifications and evidence from two nuclear markers. Taxon 59(2):351-366. 24 25 Jensen RJ (1997) Quercus section Lobatae. In: Flora of North America. Flora of North Hipp AL, et al. (2014) A framework phylogeny of the American oak clade based on sequenced RAD data. PlosOne in press. 13. Deng M (2013) Taxonomy and systematics of Quercus subgenus Cyclobalanopsis. International Oaks 24:48-60 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 13 Table S3: The influence of phylogenetic distance (branch length) between nonnative oaks and native oaks on herbivore damage to non-native oaks (square root transformed) at eight arboreta across the United States. β r2 P CA1 -0.192 0.093 0.059 CA2 -0.160 0.201 0.001 WA -0.028 0.018 0.348 CO -0.066 0.062 0.218 IL -0.112 0.177 0.023 NC 0.071 0.112 0.174 NY -0.191 0.185 0.018 PA -0.162 0.438 0.010 Arboretum 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 14 Table S4: The effect of alternate phylogenetic resolutions on the phylogenetic distance - herbivory relationship. Mixed models include 'arboretum' as a random intercept. Phylogeny Description F P (fixed) Tree 1 Supertree 29.84 <0.001 Tree 2 Old world white oaks sister 28.44 <0.001 Tree 3 Polytomies at sections 23.29 <0.001 Tree 4 Even branching 20.4 <0.001 Tree 5 Pearse & Hipp 2009 phylogeny 23.36 <0.001 Table S5: Alternative correlates of herbivore pressure to non-natives (mean herbivore damage) at eight arboreta across the United States. Factor r P|t| Latitude -0.27 0.53 Mean Temperature -0.53 0.17 Mean Precipitation 0.61 0.11 Water Balance (10-yr mean) 0.51 0.19 Number of non-native oaks -0.56 0.15 Number of native non-oaks 0.28 0.51 Oak phylo. diversity (native + non-native) -0.61 0.11 15







