Raja_HTN_12.08.09
advertisement
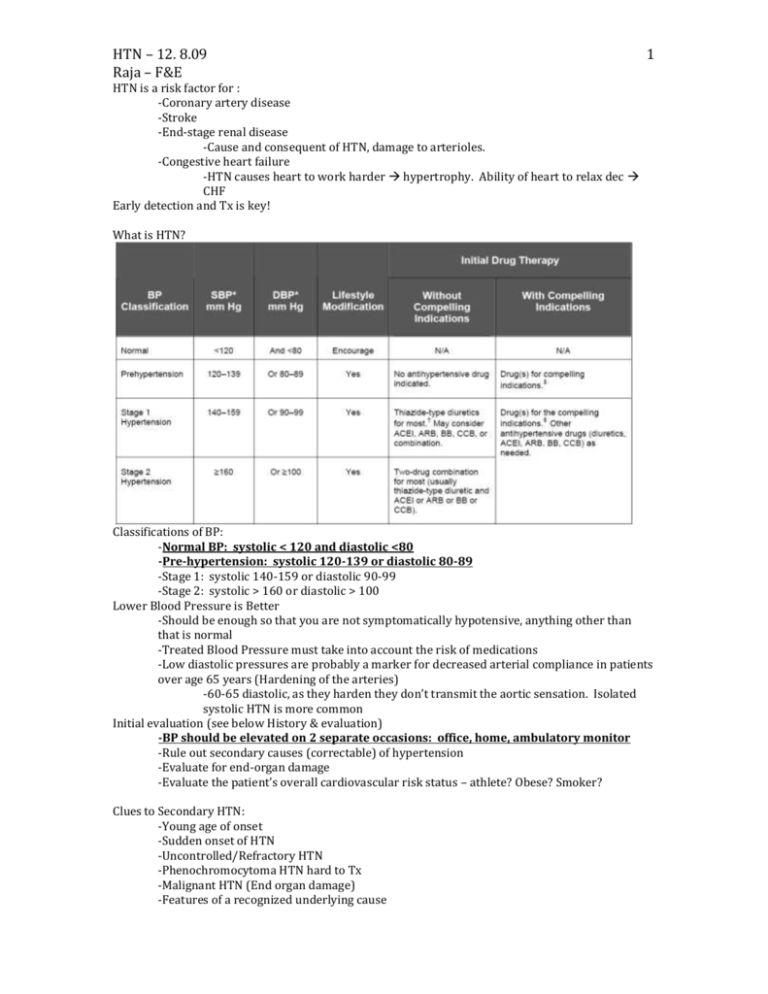
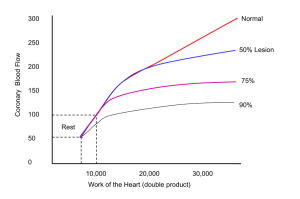
HTN – 12. 8.09 Raja – F&E 1 HTN is a risk factor for : -Coronary artery disease -Stroke -End-stage renal disease -Cause and consequent of HTN, damage to arterioles. -Congestive heart failure -HTN causes heart to work harder hypertrophy. Ability of heart to relax dec CHF Early detection and Tx is key! What is HTN? Classifications of BP: -Normal BP: systolic < 120 and diastolic <80 -Pre-hypertension: systolic 120-139 or diastolic 80-89 -Stage 1: systolic 140-159 or diastolic 90-99 -Stage 2: systolic > 160 or diastolic > 100 Lower Blood Pressure is Better -Should be enough so that you are not symptomatically hypotensive, anything other than that is normal -Treated Blood Pressure must take into account the risk of medications -Low diastolic pressures are probably a marker for decreased arterial compliance in patients over age 65 years (Hardening of the arteries) -60-65 diastolic, as they harden they don’t transmit the aortic sensation. Isolated systolic HTN is more common Initial evaluation (see below History & evaluation) -BP should be elevated on 2 separate occasions: office, home, ambulatory monitor -Rule out secondary causes (correctable) of hypertension -Evaluate for end-organ damage -Evaluate the patient’s overall cardiovascular risk status – athlete? Obese? Smoker? Clues to Secondary HTN: -Young age of onset -Sudden onset of HTN -Uncontrolled/Refractory HTN -Phenochromocytoma HTN hard to Tx -Malignant HTN (End organ damage) -Features of a recognized underlying cause 2 HTN – 12. 8.09 Raja – F&E Secondary HTN Renovascular hypertension (secondary hyperaldosteronism) Mech - S/S ischemic loss of renal func, unexplained sudden onset pulmonary edema, flank pain Primary hyperaldosteronism Excess Aldo Na Retention vol expansion HTN Hypertension, hypokalemia Muscle weakness Primary hyperparathyroidism Cushing’s disease excessive Ca in bld vasoconstriction high bp HTN from mineralocorticoid effect of the excess glucocorticoids pheochromocytoma epi secreting, episodic tachycardia, high BP, tumor Cause Atherosclerotic Disease stenosis Fibromuscular dysplasia BOARDS “string of beads leading to kidney in renal artery” -Adrenal adenoma, -bilat adrenal hyperplasia Dx angiogram Notes Most common secondary HTN -Serum renin and aldosterone -Serum calcium Thinning of the skin Episodic headache, tremor, sweating & inc HR, -50% have paroxysmal HTN, the rest apparently have “essential” HTN Excess glucorticoid – exogenous or endogenous Dexamethasone suppression test -24 hour urine collection for metanephrines Other causes of secondary HTN: -Primary renal disease -Hypothyroidism – unknown mechanism -Oral contraceptives -Sleep apnea – snoring, thought that while you are asleep there is a shut down of the stress horm (corticosteroids etc) as you wake up they inc. If you wake up the signals get mixed up. -Coarctation of the aorta – constriction above the renal artery peds dec bld flow to the kidneys. HTN – 12. 8.09 Raja – F&E 3 Know the RAAS system well! History & Evaluation: -Features of Essential Hypertension without End organ damage? NONE! Need to check BP -Cardiovascular Risk Factors: Smoking, Diabetes mellitus, Dyslipidemia, Physical inactivity, Chronic kidney disease -Symptoms of target organ damage -Headache – inc intracranial pressure form inc HTN -Transient weakness or blindness -Loss of visual acuity -Chest pain -Dyspnea -Claudication – muscle pain in calves after walking a certain distance. -Aggravating factors: -Drugs: estrogens, adrenal steroids, sympathomimetics, and NSAIDS (Na rention) -Diet: salt, alcohol, caffeine, and weight -Family history – some correlation -Race -Sleep apnea Physical Exam: -Is there evidence for end-organ damage? -Retinopathy (Flame Hemorrhage, hard exudates, cotton wool spot, papilloedema) -Heart rhythm, extra sounds –S4 (if you have a thick ventricle) -Bruits (renal artery variety may suggest a secondary cause) -Pulses -Edema – Na retention -Rales – lung crackles Labs: -Electrolytes (Na+, K+, Cl-, CO2-) -Creatinine – marker for kidney func -Urinalysis – protein or cells in the urine kidney disease -Lipid profile -EKG – L vent hypertrophy (L axis deviation) tall QRS complexes, deep T waves -Echocardiogram Treatment: Lifestyle Modifications: (test Q) -Weight loss for the overweight -Increased aerobic physical activity -Moderate sodium restriction -Moderate alcohol consumption HTN – 12. 8.09 Raja – F&E 4 -Minimize caffeine consumption PharmTx: (see HTN table above) -First choice is ALWAYS a thiazide diuretic!!! -In stage 2, you need to add a second, ACEi or ARB, then a B-blker -In Stage 2, thiazide + ACEi -other meds: -Alpha 2 central blockers -Clonidine – dec in sympt activity -Direct vasodilators -Nitro, hydralazine -Sympathetic blockers -Beta & Alpha blockers -Direct renin inhibitors -Thiazide diuretics: -Mechanism of action is unclear but probably is a combination of mild plasma volume decrease plus decreased intracellular calcium concentration leading to vasodilation -Cheap, Effective, Very low incidence of side effects at low doses -provide cardioprotection in: Left vent hypertrophy, Type 2 diabetes mellitus, previous MI, stroke, current cigarette smoking, hyperlipidemia, atherosclerotic CV disease Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors: agents of choice in hypertension and …. -Congestive heart failure -ST elevation myocardial infarction -Non-ST elevation anterior myocardial infarction -Diabetes mellitus -Proteinuric chronic renal failure -Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers used together are indicated in: Congestive heart failure & Proteinuric chronic renal failure -ACEi work by: Decreasing angiotensin II Increasing kinin levels (block kininase activity) secretion of NO from endothelial surface. They also cause the cough side effect. -Decrease aldosterone -Increase insulin sensitivity -Ang II recp antagonist: -Impair binding of angiotensin II to AT1 receptors -No cough (no increased kinin levels) -No reduction in AT2 receptor activity (key in keeping other systems going, less arterial hypertrophy, improved left ventricular activity after ischemia) -Production of angiotensin II in the heart may be through another enzyme (chymase), therefore AII receptor antagonists may be more effective than ACE inhibitors locally -No change in insulin sensitivity (kinin mediated) -Indications for and efficacy of ARB’s are not different from ACE inhibitors -Direct Renin Inhibitors: Aliskiren, recently approved by FDA -Beta blockers (without intrinsic sympathomimetic activity) are indicated in: -Post myocardial infarction!! Sued if you don’t give them to pt! -Stable patients with congestive heart failure -Rate control in atrial fibrillation -Control of angina pectoris -Calcium channel blockers - Dihydropyridines, Verapamil, Diltiazem -no absolute indication for Tx in HTN but helpful in: Rate control in atrial fibrillation, Control of angina pectoris, May be preferred in obstructive airway disease -dihydropyridines side effects: Headache, Dizziness, Flushing, Edema (due to a redistribution of fluid from vascular to interstitial space Pregnancy: -Difficult to Tx –essential HTN or preeclampsia -Maintstay: Alpha Methyl Dopa -Ok: Labetalol -CCB -Diuretics +/- HTN – 12. 8.09 Raja – F&E -No ACE-I or ARB!! Neural tube defects! Stop immediately and switch to dif drugs. Practice Questions: 1. Normal BP: systolic < ? and diastolic < ? 2. Pre-hypertension: systolic 120-? or diastolic 80-? 3. Which of the following may cause neural tube defects if used during pregnancy? (2) A. ACEi B. ARB C. Alpha methyl dopa D. labetaol 4. Which of the following is first line drug treatment in HTN? A. Calcium channel blockers B. Thiazide diuretic C. Beta Blocker D. Alpha blocker 5. Which drug must you give post-MI or you may get sued? A. Calcium channel blockers B. Thiazide diuretic C. Beta Blocker D. Alpha blocker 6. When evaluating blood pressure it should be elevated on _____ occasions, both in the office and outside the office. A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 Answers: 1. Normal BP: systolic < 120 and diastolic <80 2. Pre-hypertension: systolic 120-139 or diastolic 80-89 3. A & B 4. B 5. C 6. B 5