Year 9 Glaciation Work Booklet
advertisement

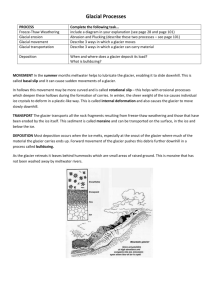
Learning Objectives: Year 9 Glaciation Work Booklet An Introduction to Glaciation Key words and definitions Understand what a glacier is and know the key terms associated with glaciers. Explain how glaciers erode and change landscapes. Sketch, describe, explain and annotate glacial features. Erosion is the wearing away and removal of material Weathering is the action of the weather wearing away material in situ (where it is). Accumulation zone: area in the upper glacial valley where new snow and ice forms. Ablation zone: the loss of ice from a glacier due to melting. Moraine: a mixture of rock and sediments left behind when a glacier melts. Bergschrund: A glacial crevasse (large crack) that forms when the glacier pulls away from the stagnant ice above. Tarn lake: when water collects in a depression in a glacial valley. Neve: new snow/ice that collects on a glacier. Snow and ice that survives one season becomes known as firn. Plucking is when melt water from a glacier enters cracks in the rock. It then freezes to the glacier and base rocks. When the ice moves downhill, rock is plucked (pulled out) from the back wall and carried a long by the glacier. Abrasion is a sandpapering action. It happens when rocks in the base and sides of the glacier rub against the valley floor and sides as it moves. This wears away the rock, often leaving them with scratches. Freeze-thaw is a process of weathering that happens when melt water or rain gets into cracks in the bedrock (usually the back wall). At night the water freezes and expands causing a crack to get larger. Fragments may then fall under gravity. Coree/Cirque: A round hollow in a hillside Arete: A sharp, narrow mountain ridge or spur. Pyramidal peak: geology a sharp peak formed where the ridges separating three or more cirques (corries) intersect; it’s horn shaped 1. Slide 1: What is a glacier and why should we study them? __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ Slide 7 - DIRT: Add to your answer above: __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ 2. Using Figure 1 on slide 8 and an atlas: List the names of 3 areas in the UK which were covered by snow in the last glaciations. 3. Slide 11: Annotate the diagram to illustrate what the key words mean. NB. A tarn lake isn’t shown 4. Slide 11: Complete the sentences below using the notes from the diagram above and the glossary on page 1. __________: a mixture of rock and sediments left behind when a glacier melts. __________: A glacial crevasse (large crack) that forms when the glacier pulls away from the stagnant ice above. __________: when water collects in a depression in a glacial valley. __________: new snow/ice that collects on a glacier. Snow and ice that survives one season becomes known as _________. 5. Slide 17 - Make an annotated sketch in the correct box for a tarn lake, a moraine and a bergschrund crevasse. Annotate how and why the feature have formed. NB: Tarn lakes generally form once the ice age has finished and the ice sheet has retreated. Glaciers – Why are they called natures Bulldozers? 6. Slide 23 - explain how ice shapes the land in no more than 20 words. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 7. Slide 35 – Complete the following table Process Diagram Description Freeze-Thaw Abrasion Plucking 8. Slide 38 - How does a glacier form? Rearrange the following letters into the correct order and write the order below: __________________________________________________________________________ 9. Slide 42 - Write the following statements in the correct order on the top row of table and draw an image to illustrate each one. Eventually this continuous process causes rocks to break up. As the water freezes it expands and causes the cracks to widen. This cycle continues, each time widening the cracks. During the day when the sun is out, cracks in rocks get filled with water as the glacial ice melts. The next time the temperature rises, the ice melts, the water thaws and contracts. At night the temperatures become colder and the water in the crack freezes. 10. Slide 43 - Abrasion is an important process of glacial erosion. Describe how it occurs. You can use a diagram in your answer if you wish. (3) ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ Dirt – Improve your answer: ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 11. Glacial mountain features – Slide 49 Label the following features onto the photograph: Aretes, Corrie, Tarn, Pyramidal Peak, Define what the following words mean: Arete = …………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. Corrie (Cirque) =……………………………………………………………………………………………… Pyramidal Peak = …………………………………………………………………………………………….. Tarn =………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 12. Slide 51 – Explain the formation of a corrie (4) _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ DIRT: _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ 13. Slide 64: Explain the formation of a medial moraine, with the use of a diagram _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ DIRT: _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________