Burn Injuries and Management Notes
advertisement

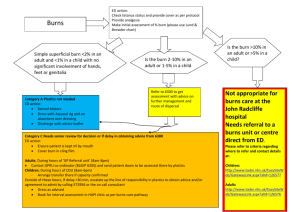
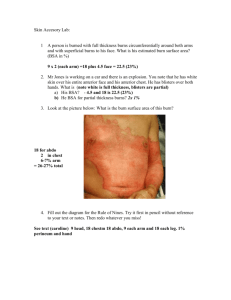
HS 20 Mini Unit A: Integumentary System Unit 2: Body Systems Burn Injuries and Management BURNS Wounds caused by exposure to: 1. excessive heat 2. _________________________ 3. fire/steam 4. radiation 5. electricity Results in 10-20 thousand deaths annually Survival best at ages 15-45 o Children, elderly, and diabetics are most in danger Survival best burns cover less than ____________ of TBA (total body area) TYPES OF BURNS ____________________________ - exposure to flame or a hot object Chemical - exposure to acid, alkali or organic substances _____________________________________ - result from the conversion of electrical energy into heat. Extent of injury depends on the type of current, the pathway of flow, local tissue resistance, and duration of contact Radiation - result from radiant energy being transferred to the body resulting in production of cellular toxins BURN WOUND ASSESSMENT Classified according to ______________________ of injury and extent of ___________________________ involved HS 20 Mini Unit A: Integumentary System Unit 2: Body Systems Burn wounds differentiated depending on the level of _____________________ and ___________________________________________ involved 1. superficial (first-degree) 2. deep (second-degree) 3. full thickness (third and fourth degree) SUPERFICIAL BURNS (FIRST DEGREE) ___________________________________ tissue only affected Erythema (redness of skin), blanching on pressure, mild swelling No blister initially Not serious unless large areas involved i.e. ______________________________ DEEP (SECOND DEGREE) Involves the epidermis and deep layer of the __________________________ Fluid-filled vesicles – red, shiny, wet, severe pain Hospitalization required if over ________________ of body surface involved i.e. ____________________________ FULL THICKNESS (THIRD/FOURTH DEGREE) Destruction of _______________ skin layers Requires __________________________ hospitalization Dry, waxy white, leathery, or hard skin, no pain Exposure to flames, electricity or chemicals can cause 3rd degree burns HS 20 Mini Unit A: Integumentary System Unit 2: Body Systems Calculation of Burned Body Surface Area TOTAL BODY SURFACE AREA (TBSA) Superficial burns are not involved in the calculation Lund and Browder Chart is the most accurate because it adjusts for age Rule of _______________ divides the body – adequate for initial assessment for adult burns RULES OF NINES Head & Neck = _______% Each upper extremity (Arms) = ______% Each lower extremity (Legs) = _______% Anterior trunk= __________% Posterior trunk = _________% Genitalia (perineum) = __________% VASCULAR CHANGES RESULTING FROM BURN INJURIES Circulatory________________________ occurs at the burn site immediately after a burn injury Blood flow ______________________ or _________________ due to occluded blood vessels Damaged macrophages within the tissues release chemicals that cause constriction of vessel o Macrophage: A type of white blood that ingests (takes in) foreign material. Macrophages are key players in the immune response to foreign invaders such as infectious microorganisms. Blood vessel thrombosis (clotting) may occur causing necrosis FLUID SHIFT HS 20 Mini Unit A: Integumentary System Unit 2: Body Systems Occurs after initial vasoconstriction, then dilation Blood vessels dilate and leak ____________________ into the interstitial space Known as third spacing or ______________________________________________ Causes ______________________ blood volume and blood pressure Occurs within the first ________ hours after the burn and can continue to up to 36 hours FLUID IMBALANCES Occur as a result of fluid shift and ____________________________________ ___________________________ - decrease of volume of circulating blood Metabolic acidosis - pH imbalance in the body Hyperkalemia - increased potassium levels Hyponatremia - low sodium levels Hemoconcentration (elevated blood osmolarity, hematocrit/hemoglobin) due to dehydration FLUID REMOBILIZATION Occurs after 24 hours Capillary leak _____________ See diuretic stage where edema fluid shifts from the interstitial spaces into the vascular space Blood volume ____________________ leading to increased renal blood flow and diuresis Body weight returns to normal CURLING’S ULCER Acute ulcerative gastro duodenal disease Occur within 24 hours after burn Due to reduced __________________________ and mucosal damage PHASES OF BURN INJURIES ________________________ (24-48 hrs) HS 20 Mini Unit A: Integumentary System ____________________________ ____________________________ Unit 2: Body Systems EMERGENT PHASE *Immediate problem is fluid loss, edema, reduced blood flow (fluid and electrolyte shifts) Goals: 1. secure _____________________ 2. support circulation by fluid replacement 3. keep the client comfortable with analgesics (pain relievers) 4. prevent ______________________ through wound care 5. maintain __________________________________ 6. provide emotional support CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS IN THE EMERGENT PHASE Clients with major burn injuries and with inhalation injury are at risk for ____________________________ problems ____________________________ injuries are present in 20% to 50% of the clients admitted to burn centers Assess the respiratory system by inspecting the mouth, nose, and pharynx Burns of the lips, face, ears, neck, eyelids, eyebrows, and eyelashes are strong indicators that an inhalation injury may be present Change in respiratory ______________________ may indicate a pulmonary injury. The client may: become progressively hoarse, develop a brassy cough, drool or have difficulty swallowing, produce expiratory sounds that include audible wheezes, and crowing Cardiovascular problems will begin immediately which can include ____________________________________ (Shock is a common cause of death in the emergent phase in clients with serious injuries) Changes in renal function are related to decreased renal blood flow HS 20 Mini Unit A: Integumentary System Unit 2: Body Systems Urine output is decreased during the first 24 hours of the emergent phase SKIN ASSESSMENT Assess the skin to determine the ________________ and ___________________ of burn injury The size of the injury is first estimated in comparison to the total ___________________________________ area (TBSA). For example, a burn that involves 40% of the TBSA is a 40% burn Use the rule of nines for clients whose weights are in normal proportion to their heights IV FLUID THERAPY Clients with burns involving 15% to 20% of the TBSA require _______________________ Purpose is to _____________________ by maintaining adequate circulating blood fluid volume Severe burn requires large fluid loads in a short time to maintain blood flow to vital organs Fluid replacement formulas are calculated from the time of injury and not from the time of arrival at the hospital ACUTE PHASE OF BURN INJURY o Lasts until wound ______________________e is complete o Care is directed toward continued assessment and maintenance of the cardiovascular and respiratory system o _________________________________ is a concern which can result in respiratory failure requiring mechanical ventilation o Weight daily without dressings or splints and compare to pre-burn weight o Monitor for signs of infection HS 20 Mini Unit A: Integumentary System Unit 2: Body Systems DRESSING THE BURN WOUND After burn wounds are cleaned and _____________________________, topical antibiotics are reapplied to prevent infection Standard wound dressings are multiple layers of gauze applied over the topical agents on the burn wound REHABILITATIVE PHASE OF BURN INJURY Started at the time of _____________________________ Technically begins with wound closure and ends when the client returns to the highest possible level of functioning Provide psychosocial support Assess home environment, financial resources, medical equipment, prosthetic rehab Health __________________________ should include symptoms of infection, drugs regimens, follow up appointments, comfort measures to reduce pruritus (severe itching of the skin) DIET Initially nothing by mouth Begin oral fluids after bowel sounds return Do not give ice chips or free water lead to electrolyte imbalance High protein, high calorie DEBRIDEMENT Done with forceps and curved scissor or through hydrotherapy (application of water for treatment) Only loose eschar removed ______________________________________ are left alone to serve as a protector HS 20 Mini Unit A: Integumentary System Unit 2: Body Systems SKIN GRAFTS Done during the ___________________________ phase Used for full-thickness and deep partial-thickness wounds POST CARE OF SKIN GRAFTS Maintain dressing Use aseptic technique Graft should look __________________ if it has taken after 5 days Skeletal traction may be used to prevent contractures Elastic bandages may be applied for 6 mo to 1 year to prevent _____________________________________ scarring (raised scarring)